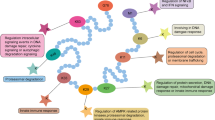
Abstract
Post translational modifications (PTMs) are involved in variety of cellular activities and phosphorylation is one of the most extensively studied PTM, which regulates a number of cellular functions like cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis and cell signaling in healthy condition. However, alterations in phosphorylation pathways result in serious outcomes in the form of diseases, especially cancer. Many signalling pathways including Tyrosine kinase, MAP kinase, Cadherin–catenin complex, Cyclin-dependent kinase etc. are major players of the cell cycle and deregulation in their phosphorylation-dephosphorylation cascade has been shown to be manifested in the form of various types of cancers. Tyrosine kinase family encompasses the greatest number of oncoproteins. MAPK cascade has an importance role in cancer growth and progression. Bcl-2 family proteins serve either proapoptotic or antiapoptotic function. Cadherin–catenin complex regulates cell adhesion properties and cyclins are the key regulators of cell cycle. Altered phosphorylations in any of the above pathways are strongly associated with cancer, at the same time they serve as the potential tergets for drug development against cancer. Drugs targeting tyrosine kinase are potent anticancer drugs. Inhibitors of MEK, PI3K and ERK signalling pathways are undergoing clinical trials. Thus, drugs targeting phosphorylation pathways represent a promising area for cancer therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PTM:
-
Post-translational modification
- FAK:
-
Focal adhesion kinase
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- Bcl-2:
-
B-cell lymphoma 2
- PKD1:
-
Protein kinase D1
- pRb:
-
Retinoblastoma protein
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-κB
References
Mann M, Jensen ON (2003) Proteomic analysis of post-translational modifications. Nat Biotechnol 21:255–261
Walsh, CT (2006) Posttranslational modification of proteins: expanding nature’s inventory. Roberts and Company Publishers, Englewood
Levene PA, Alsberg CL (1906) The cleavage products of vitellin. J Biol Chem 2:127–133
Burnett G, Kennedy EP (1954) The enzymatic phosphorylation of proteins. J Biol Chem 211:969–980
Fischer EH, Krebs EG (1955) Conversion of phosphorylase b to phosphorylase a in muscle extracts. J Biol Chem 216:121–132
Cohen P (2000) The regulation of protein function by multisite phosphorylation: a 25 year update. Trends Biochem Sci 25:596–601
Cohen P (2002) The origins of protein phosphorylation. Nat Cell Biol 4:E127–E130
Humphrey SJ, James DE, Mann M (2015) Protein phosphorylation: a major switch mechanism for metabolic regulation. Trends Endocrinol Metab 26:676–687
Hunter T (1995) Protein kinases and phosphatases: the yin and yang of protein phosphorylation and signaling. Cell 80:225–236
Ubersax JA, Ferrell JE (2007) Mechanisms of specificity in protein phosphorylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:530–541
Chen SL, Huddleston MJ, Shou W, Deshaies RJ, Annan RS, Carr SA (2002) Mass spectrometry-based methods for phosphorylation site mapping of hyperphosphorylated proteins applied to net1, a regulator of exit from mitosis in yeast. Mol Cell Proteom 1:186–196
Dajani R, Fraser E, Roe SM, Young N, Good V, Dale TC, Pearl LH (2001) Crystal structure of glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta: structural basis for phosphate-primed substrate specificity and autoinhibition. Cell 105:721–732
Ahmad I, Hoessli DC, Walker-Nasir E, Choudhary MI, Rafik SM, Shakoori AR, Nasir-ud-Din (2006) Phosphorylation and glycosylation interplay: protein modifications at hydroxy amino acids and prediction of signaling functions of the human beta3 integrin family. J Cell Biochem 99:706–718
Orford K, Crockett C, Jensen JP, Weissman AM, Byers SW (1997) Serine phosphorylation regulated ubiquitination and degradation of b-Catenin. J Biol Chem 272:24735–24738
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The Hallmarks of Cancer. Cell 100:57–70
Appella E, Anderson CW (2001) Post-translational modifications and activation of p53 by genotoxic stresses The. FEBS J 268:2764–2772
Roberts PJ, Der CJ (2007) Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene 26:3291–3310
Jaggi M, Rao PS, Smith DJ, Hemstreet GP, Balaji KC (2003) Protein kinase Cμ is down-regulated in androgenindependent prostate cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 307:254–260
Radivojac P, Baenziger PH, Kann MG, Mort ME, Hahn MW, Mooney SD (2008) Gain and loss of phosphorylation sites in human cancer. Bioinformatics 24:241–247
Lim YP (2005) Mining the tumor phosphoproteome for cancer markers. Clin Cancer Res 11:3163–3169
Gorini G, Harris RA, Mayfield RD (2014) Proteomic Approaches and Identification of Novel Therapeutic Targets for Alcoholism. Neuropsychopharmacol 39:104–130
Fischer OM, Streit S, Hart S, Ullrich A (2003) Beyond herceptin and gleevec. Curr Opin Chem Biol 7:490–495
Hunter T (2000) Signaling-2000 and Beyond. Cell 100:113–127
Spector N, Xia W, Hariry IE, Yarden Y, Bacus S (2007) HER2 therapy. Breast Cancer Res 9:205. doi:10.1186/bcr1652
Nahta R, Yuan LX, Du Y, Esteva FJ (2007) Lapatinib induces apoptosis in trastuzumab-resistant breast cancer cells: effects on insulin-like growth factor I signaling. Mol Cancer Ther 6:667–674
Hunter T, Cooper JA (1985) Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem 54:897–930
Martin GS (2003) Cell signaling and cancer. Cancer Cell 4:167–174
Avizienyte E, Wyke AW, Jones RJ, McLean GW, Westhoff MA, Brunton VG, Frame MC (2002) Src-induced de-regulation of E-cadherin in colon cancer cells requires integrin signalling. Nat Cell Biol 4:632–638
Neshat MS, Mellinghoff IK, Tran C, Stiles B, Thomas G, Petersen R, Frost P, Gibbons JJ, Wu H, Sawyers CL (2001) Enhanced sensitivity of PTEN-deficient tumors to inhibition of FRAP/mTOR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:10314–10319
Giancotti FG, Ruoslahti E (1999) Integrin signaling. Science 285:1028–1032
Shields JM, Pruitt K, McFall A, Shaub A, Der CJ (2000) Understanding Ras: ‘it ain’t over ‘til it’s over’. Trends Cell Biol 10:147–154
Benson JD, Chen YN, Cornell-Kennon SA Dorsch M, KimS, Leszczyniecka M, Sellers WR, Lengauer C (2006) Validating cancer drug targets. Nature 441:451–456
O’Neill LA (2006) Targeting signal transduction as a strategy to treat inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:549–563
Green DR, Reed JC (1998) Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 281:1309–1312
Appella E, Anderson CW (2000) Signaling to p53: breaking the posttranslational modification code. Pathol Biol 48:227–245
Blaydes JP, Luciani MG, Pospisilova S, Ball HM, Vojtesek B, Hupp TR (2000) Stoichiometric phosphorylation of human p53 at Ser315 stimulates p53-dependent transcription. J Biol Chem 276:4699–4708
Sakaguchi K, Saito SI, Higashimoto Y, Roy S, Anderson CW, Appella E (2000) Damage-mediated phosphorylation of human p53 threonine 18 through a cascade mediated by a casein 1-like kinase. Effect on Mdm2 binding. J Biol Chem 275:9278–9283
Higashimoto Y, Saito S, Tong XH, Hong A, Sakaguchi K, Appella E, Anderson CW (2000) Human p53 is phosphorylated on serines 6 and 9 in response to DNA damage-inducing agents. J Biol Chem 275:23199–23203
Bushmann T, Potapova O, Ivanov VN Fuchs SY, Henderson S, Fried VA, Minamoto T, Alarcon-Vargas D, Pincus MR, Gaarde WA, Holbrook NJ, Shiloh Y, Ronai Z (2001) Jun NH2-terminal kinase phosphorylation of p53 on Thr-81 is important for p53 stabilization and transcriptional activities in response to stress. Mol Cell Biol 21:2743–2754
Haldar S, Chintapalli J, Croce CM (1996) Taxol Induces bcl-2 Phosphorylation and Death of Prostate Cancer Cells. Cancer Res 56:1253–1255
Lilien J, Balsamo J, Arregui C, Xu G (2002) Turn-off, dropout: functional state switching of cadherins. Dev Dyn 224:18–29
Yap AS (1998) The morphogenetic role of cadherin cell adhesion molecules in human cancer: a thematic review. Cancer Invest 16:252–261
Jaggi M, Rao PS, Smith DJ, Wheelock MJ, Johnson KR, Hemstreet GP, Balaji KC (2005) E-Cadherin phosphorylation by protein kinase D1/protein kinase C(mu) is associated with altered cellular aggregation and motility in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 65:483–492
Lickert H, Bauer A, Kemler R, Stappert J (2000) Casein kinase II phosphorylation of E-cadherin increases E-cadherin/h-catenin interaction and strengthens cell-cell adhesion. J Biol Chem 275:5090–5095
Powell CT, Fair WR, Heston WD (1994) Differential expression of protein kinase C isozyme messenger RNAs in dunning R-3327 rat prostatic tumors. Cell Growth Differ 5:143–149
Tang FY, Nguyen N, Meydani M (2003) Green tea catechins inhibit VEGF-induced angiogenesis in vitro through suppression of VE-cadherin phosphorylation and inactivation of Akt molecule. Intl. J Cancer 106:871–878
Benzeno S, Lu F, Guo M, Barbash O, Zhang F, Herman JG, Klein PS, Rustgi A, Diehl JA (2006) Identification of mutations that disrupt phosphorylation-dependent nuclear export of cyclin D1. Oncogene 25:6291–6303
Datto MB, Hu PP, Kowalik TF, Yingling J, Wang XF (1997) The viral oncoprotein E1A blocks transforming growth factor β-mediated induction of p21/WAF1/Cip1 and p15/INK4B. Mol Cell Biol 17:2030–2037
Zuo L, Weger J, Yang Q, Goldstein AM, Tucker MA, Walker GJ, Hayward N, Dracopoli NC (1996) Germline mutations in the p16INK4A binding domain of CDK4 in familial melanoma. Nat Genet 12:97–99
Devin A, Cook A, Lin Y, Rodriguez Y, Kelliher M, Liu Z (2000) The distinct roles of TRAF2 and RIP in IKK activation by TNF-R1: TRAF2 recruits IKK to TNF-R1 while RIP mediates IKK activation. Immunity 12:419–429
Yamaoka S, Courtois G, Bessia C, Whiteside ST, Weil R, Agou F, Kirk HE, Kay RJ, Israel A (1998) Complementation cloning of NEMO, a component of the I kB kinase complex essential for NF-kB activation. Cell 93:1231–1240
Xiao G, Cvijic ME, Fong A, Harhaj EW, Uhlik MT, Waterfield M, Sun SC (2001) Retroviral oncoprotein Tax induces processing of NF-kB2/p100 in T cells: evidence for the involvement of IKKα. EMBO J 20:6805–6815
Eliopoulos AG, Caamano JH, Flavell J, ,Reynolds GM, Murray PG, Poyet JL, Young LS (2003) Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent infection membrane protein 1 regulates the processing of p100 NF-kB2 to p52 via an IKKgamma/NEMO-independent signalling pathway. Oncogene 22:7557–7569
Kato T Jr, Delhase M, Hoffmann A, Karin M (2003) CK2 is a C-terminal IkB kinase responsible for NF-kB activation during the UV response. Mol Cell 12:829–839
Tergaonkar V, Bottero V, Ikawa M, Li Q, Verma IM (2003) IkB kinase-independent IkBa degradation pathway: functional NF-kB activity and implications for cancer therapy. Mol Cell Biol 23:8070–8083
Viatour P, Merville MP, Bours V, Chariot A (2005) Phosphorylation of NF-kB and IkB proteins: implications in cancer and inflammation. Trends Biochem Sci 30:43–52
Karin M, Ben-neriah Y (2000) Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-kB activity. Annu Rev Immunol 18:621–663
Wu C, Ghosh S (2003) Differential phosphorylation of the signalresponsive domain of IkBα and IkBβ by IkB kinases. J Biol Chem 278:31980–31987
Greten FR, Eckmann L, Greten TF, Park JM, Li ZW, Egan LJ, Kagnoff MF, Karin M (2004) IKKb links inflammation and tumorigenesis in a mouse model of colitis-associated cancer. Cell 118:285–296
Pikarsky E, Porat RM, Stein I, Abramovitch R, Amit S, Kasem S, Gutkovich-Pyest E, Urieli-Shoval S, Galun E, Ben-Neriah Y (2004) NF-kB functions as a tumor promoter in inflammation-associated cancer. Nature 431:461–466
Nakanishi C, Toi M (2005) Nuclear factor factor-kappaB inhibitors as sensitizers to anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer 5:297–309
Baud V, Karin M (2009) Is NF-κB a good target for cancer therapy? Hopes and pitfalls. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8:33–40
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, V., Ram, M., Kumar, R. et al. Phosphorylation: Implications in Cancer. Protein J 36, 1–6 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-017-9696-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-017-9696-z