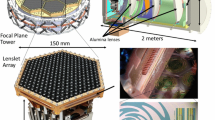
Abstract
The BICEP/Keck experiment (BK) is a series of small-aperture refracting telescopes observing degree-scale cosmic microwave background (CMB) polarization from the South Pole in search of a primordial B-mode signature. This B-mode signal arises from primordial gravitational waves interacting with the CMB and has amplitude parametrized by the tensor-to-scalar ratio r. Since 2016, BICEP3 and the Keck Array have been observing with 4800 total antenna-coupled transition-edge sensor detectors, with frequency bands spanning 95, 150, 220, and 270 GHz. Here we present the optical performance of these receivers from 2016 to 2019, including far-field beams measured in situ with an improved chopped thermal source and instrument spectral response measured with a field-deployable Fourier transform spectrometer. As a pair differencing experiment, an important systematic that must be controlled is the differential beam response between the co-located, orthogonally polarized detectors. We generate per-detector far-field beam maps and the corresponding differential beam mismatch that is used to estimate the temperature-to-polarization leakage in our CMB maps and to give feedback on detector and optics fabrication. The differential beam parameters presented here were estimated using improved low-level beam map analysis techniques, including efficient removal of non-Gaussian noise as well as improved spatial masking. These techniques help minimize systematic uncertainty in the beam analysis, with the goal of constraining the bias on r induced by temperature-to-polarization leakage to be subdominant to the statistical uncertainty. This is essential as we progress to higher detector counts in the next generation of CMB experiments.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keck Array/BICEP2 Collaborations X., Phys. Rev. Lett., 121, 221301 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.221301
The BICEP2, Keck Array, and SPIDER Collaborations, ApJ 812, 176 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1088/0004-637X/812/2/176
J.H. Kang, P.A.R. Ade, Z. Ahmed, R.W. Aikin, K.D. Alexander, D. Barkats, S.J. Benton, C.A. Bischoff, J.J. Bock, et al., in Proceedings of the SPIE, Volume 10708, id. 107082N (2018). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2313854
The BICEP2 Collaboration III, ApJ 814, 110 (2015) https://doi.org/10.1088/0004-637X/814/2/110
The Keck Array and BICEP2 Collaborations XI, ApJ 884, 114 (2019) https://doi.org/10.3847/1538-4357/ab391d
K.S. Karkare, P.A.R. Ade, Z. Ahmed, R.W. Aikin, K.D. Alexander, M. Amiri, D. Barkats, S.J. Benton, C.A. Bischoff, J.J. Bock, et al., in Society of photo-optical instrumentation engineers (SPIE) conference series, vol. 9153, p. 3 (2014)
A. Cukierman, et al., J. Low Temp. Phys. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-019-02296-2
Paine, S. (2019). The am atmospheric model (Version 11.0). Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3406483
K.S. Karkare, P.A.R. Ade, Z. Ahmed, K.D. Alexander, M. Amiri, D. Barkats, S.J. Benton, C.A. Bischoff, J.J. Bock, et al., in Proceedings of the SPIE, Volume 9914, id. 991430 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2231747
A. Soliman, et al, in Proc. SPIE 10708, id. 107082G, (2018). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2312942
Acknowledgements
The BICEP/Keck projects have been made possible through a series of Grants from the National Science Foundation including 0742818, 0742592, 1044978, 1110087, 1145172, 1145143, 1145248, 1639040, 1638957, 1638978, 1638970, and 1726917, by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, by the Keck Foundation, and by the Grant 55802 from John Templeton Foundation. The development of antenna-coupled detector technology was supported by the JPL Research and Technology Development Fund and NASA Grants 06-ARPA206-0040, 10-SAT10-0017, 12-SAT12-0031, 14-SAT14-0009 and 16-SAT16-0002. The development and testing of focal planes were supported by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation at Caltech. Readout electronics were supported by a Canada Foundation for Innovation grant to UBC. The computations in this paper were run on the Odyssey cluster supported by the FAS Science Division Research Computing Group at Harvard University. The analysis effort at Stanford and SLAC is partially supported by the U.S. DoE Office of Science. We thank the staff of the U.S. Antarctic Program and in particular the South Pole Station without whose help this research would not have been possible. We thank all those who have contributed past efforts to the BICEP/Keck series of experiments, including the Bicep1 team. Tireless administrative support was provided by Kathy Deniston, Sheri Stoll, Irene Coyle, Donna Hernandez, Dana Volponi, and Julie Shih.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
St Germaine, T., Ade, P.A.R., Ahmed, Z. et al. Optical Characterization of the Keck Array and BICEP3 CMB Polarimeters from 2016 to 2019. J Low Temp Phys 199, 824–832 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-020-02392-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-020-02392-8