Abstract
Purpose
Primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis is a severe and uncommon disease affecting pediatric patients. Genetic abnormalities have been related to altered apoptosis and exaggerated inflammatory reactions. Chemoimmunotherapy and stem cell transplantation are treatment options, but transplant is the only curative treatment. Here we aim to describe the treatment with hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with a novel strategy and the outcomes.
Methods
An observational, descriptive, case series study was performed in pediatric patients of two high complexity medical centers in Colombia. Data was collected retrospectively between 2015 and 2020.
Results
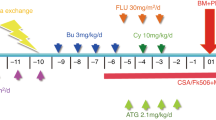
We describe five pediatric cases with a diagnosis of primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. All were treated with replete-cell haploidentical hematopoietic stem transplantation, reduced-intensity conditioning, and post-transplant cyclophosphamide, in two high-complexity centers in Colombia. All patients are alive, and one is receiving management for chronic graft-versus-host disease.
Conclusion
To the best of our knowledge, there are few reports in the literature with this strategy, promising a possible alternative when there are no other donor options.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Fundación Valle de Lili (FVL) in Cali and Hospital Pablo Tobón Uribe (HPTU) in Medellín
Abbreviations
- HLH:
-
hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
- FHLH:
-
familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
- HSCT:
-
hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- MSD:
-
matched sibling
- MUD:
-
matched unrelated donor
- PTCy:
-
post-transplantation cyclophosphamide
- FVL:
-
Fundación Valle de Lili
- HPTU:
-
Hospital Pablo Tobón Uribe
- EBV:
-
Ebstein-Barr virus
- CMV:
-
cytomegalovirus
- GvHD:
-
graft-vs-host disease
- aGVHD:
-
acute graft-vs-host disease
- cGVHD:
-
chronic graft-vs-host disease
- GI:
-
gastrointestinal
- VOD:
-
veno-occlusive disease
- TA-TMA:
-
transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy
- TRM:
-
transplant-related mortality
References
Marsh RA, Haddad E. How I treat primary haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Br J Haematol. 2018;182(2):185–99.
Marsh RA, Vaughn G, Kim M-O, Li D, Jodele S, Joshi S, et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning significantly improves survival of patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood. 2010;116(26):5824–31 Available from: https://ashpublications.org/blood/article/116/26/5824/28172/Reducedintensity-conditioning-significantly.
Ouachée-Chardin M, Elie C, De Saint BG, Le Deist F, Mahlaoui N, Picard C, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a single-center report of 48 patients. Pediatrics. 2006;117(4):e743–50.
Jia C, Wang B, Zhu G, Zhang R, Wang K, Yan Y, et al. Haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation using reduced-intensity conditioning for pediatric patients with familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Investig. 2018;2(4):216–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/ped4.12096.
Uppuluri R, Sivasankaran M, Patel S, Swaminathan VV, Ramanan KM, Ravichandran N, et al. Haploidentical stem cell transplantation with post-transplant cyclophosphamide for primary immune deficiency disorders in children: challenges and outcome from a tertiary care center in South India. J Clin Immunol. 201918;39(2):182–7 Available from: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=prem&NEWS=N&AN=30778805.
Kohli S, Rastogi N, Nivargi S, Thakkar D, Katewa S, Yadav SP. Successful haploidentical stem cell transplant with posttransplant cyclophosphamide for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2019;41(3):E158–60.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation and data collection were performed by DC, NB, and EB. Critical revision and analysis were performed by MO, NB, AAF, AFE, and DMV. The first draft of the manuscript was performed by DC and EB. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript and read and approved the final manuscript version to be published. Also, agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work and to ensure that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval
The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Medina-Valencia, D., Cleves, D., Beltran, E. et al. Haploidentical Stem Cell Transplant with Post-Transplant Cyclophosphamide in Pediatric Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. J Clin Immunol 41, 1172–1177 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-021-01009-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-021-01009-3