Abstract
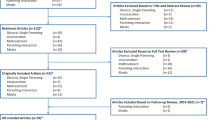
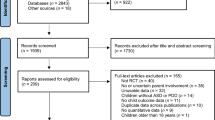
The purpose of the study was to identify profiles of social functioning for preschoolers with externalizing behavior problems (EBP) and examine how profiles are predictive of response to a behavioral treatment program. 139 preschoolers with EBP participated in an 8-week Summer Treatment Program for Pre-Kindergartners (STP-PreK). Latent profiles of social functioning were created from parent and teacher rated atypicality and social skills scales, along with child performance on an emotion knowledge and hostile attribution task. Baseline and treatment outcomes included behavioral, academic, and executive functioning measures. Latent profile analyses resulted in two profiles (e.g., average and low) marked by differences in social skills, emotion knowledge and rates of atypical behaviors. Children in the low social functioning group had higher teacher rated hyperactivity and attention problems at baseline (d = .44 & 1.07), as well as lower IQ (d = .39). Children in the low social functioning group also had poorer treatment response as they had lower executive functioning scores (β = −.17, p < .05) at the completion of treatment. IQ moderated the association between social functioning profiles and behavioral treatment outcomes, such that lower social functioning was only associated with higher rates of attention problems for children with average IQ. Findings highlight the differential impact of social functioning in predicting treatment outcomes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abikoff, H., Hechtman, L., Klein, R. G., Gallagher, R., Fleiss, K., Etcovitch, J., et al. (2004). Social functioning in children with ADHD treated with long-term methylphenidate and multimodal psychosocial treatment. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 43(7), 820–829.
Aiken, L. S., West, S. G., & Reno, R. R. (1991). Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions. Newcastle upon Tyne: Sage.
Arnold, L. E., Elliott, M., Sachs, L., Bird, H., Kraemer, H. C., Wells, K. C., et al. (2003). Effects of ethnicity on treatment attendance, stimulant response/dose, and 14-month outcome in ADHD. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 71(4), 713.
Atkins, M. S., & Stoff, D. M. (1993). Instrumental and hostile aggression in childhood disruptive behavior disorders. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 21(2), 165–178.
Bagner, D. M., & Eyberg, S. M. (2007). Parent–child interaction therapy for disruptive behavior in children with mental retardation: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 36(3), 418–429.
Bagwell, C. L., Schmidt, M. E., Newcomb, A. F., & Bukowski, W. M. (2001). Friendship and peer rejection as predictors of adult adjustment. New Directions for Child and Adolescent Development, 2001(91), 25–50.
Baker, B. L., Blacher, J., Crnic, K. A., & Edelbrock, C. (2002). Behavior problems and parenting stress in families of three-year-old children with and without developmental delays. Journal Information, 107(6), 371–378.
Baker, B. L., McIntyre, L. L., Blacher, J., Crnic, K., Edelbrock, C., & Low, C. (2003). Pre-school children with and without developmental delay: behaviour problems and parenting stress over time. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 47(4-5), 217–230.
Beauchaine, T. P., Webster-Stratton, C., & Reid, M. J. (2005). Mediators, moderators, and predictors of 1-year outcomes among children treated for early-onset conduct problems: A latent growth curve analysis. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 73(3), 371.
Bloomquist, M. L., August, G. J., Cohen, C., Doyle, A., & Everhart, K. (1997). Social problem solving in hyperactive-aggressive children: How and what they think in conditions of automatic and controlled processing. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 26(2), 172–180.
Cadesky, E. B., Mota, V. L., & Schachar, R. J. (2000). Beyond words: How do children with ADHD and/or conduct problems process nonverbal information about affect? Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 39(9), 1160–1167.
Campbell, S. B. (1994). Hard-to-manage preschool boys: Externalizing behavior, social competence, and family context at two-year followup. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 22(2), 147–166.
Campbell, S. B., Shaw, D. S., & Gilliom, M. (2000). Early externalizing behavior problems: Toddlers and preschoolers at risk for later maladjustment. Development and Psychopathology, 12(03), 467–488.
Carlson, S. M., & Moses, L. J. (2001). Individual differences in inhibitory control and children's theory of mind. Child Development, 1032–1053.
Clark, T., Feehan, C., Tinline, C., & Vostanis, P. (1999). Autistic symptoms in children with attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 8(1), 50–55.
Clark, C., Prior, M., & Kinsella, G. (2002). The relationship between executive function abilities, adaptive behaviour, and academic achievement in children with externalising behaviour problems. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 43(6), 785–796.
Corbett, B., & Glidden, H. (2000). Processing affective stimuli in children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Child Neuropsychology, 6(2), 144–155.
Crick, N. R., & Dodge, K. A. (1994). A review and reformulation of social information-processing mechanisms in children's social adjustment. Psychological Bulletin, 115(1), 74.
Da Fonseca, D., Seguier, V., Santos, A., Poinso, F., & Deruelle, C. (2009). Emotion understanding in children with ADHD. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 40(1), 111–121.
De Castro, B. O., Veerman, J. W., Koops, W., Bosch, J. D., & Monshouwer, H. J. (2002). Hostile attribution of intent and aggressive behavior: a meta-analysis. Child Development, 73(3), 916–934.
Dekker, M. C., Koot, H. M., Ende, J. v. d., & Verhulst, F. C. (2002). Emotional and behavioral problems in children and adolescents with and without intellectual disability. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 43(8), 1087–1098.
Denham, S. A. (1986). Social cognition, prosocial behavior, and emotion in preschoolers: Contextual validation. Child Development, 194–201.
Denham, S. A., Caverly, S., Schmidt, M., Blair, K., DeMulder, E., Caal, S., et al. (2002). Preschool understanding of emotions: contributions to classroom anger and aggression. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 43(7), 901–916.
Denham, S. A. (2006). Social-emotional competence as support for school readiness: What is it and how do we assess it? Early Education and Development, 17(1), 57–89.
Denham, S. A., Bouril, B., & Belouad, F. (1994). Preschoolers' affect and cognition about challenging peer situations. Child Study Journal, 24, 1–1.
Dennis, M., Francis, D. J., Cirino, P. T., Schachar, R., Barnes, M. A., & Fletcher, J. M. (2009). Why IQ is not a covariate in cognitive studies of neurodevelopmental disorders. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 15(03), 331–343.
DeRosier, M. E., & Mercer, S. H. (2009). Perceived behavioral atypicality as a predictor of social rejection and peer victimization: Implications for emotional adjustment and academic achievement. Psychology in the Schools, 46(4), 375–387.
Diamantopoulou, S., Rydell, A.-M., Thorell, L. B., & Bohlin, G. (2007). Impact of executive functioning and symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder on children's peer relations and school performance. Developmental Neuropsychology, 32(1), 521–542.
Dirks, M. A., Treat, T. A., & Weersing, V. R. (2007). Integrating theore- tical, measurement, and intervention models of youth social competence. Clinical Psychology Review, 27, 327–347.
Dodge, K. A. (1980). Social cognition and children's aggressive behavior. Child Development, 162–170.
Downer, J. T., Booren, L. M., Lima, O. K., Luckner, A. E., & Pianta, R. C. (2010). The Individualized Classroom Assessment Scoring System (inCLASS): preliminary reliability and validity of a system for observing preschoolers’ competence in classroom interactions. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 25(1), 1–16.
DuPaul, G. J., McGoey, K. E., Eckert, T. L., & VanBrakle, J. (2001). Preschool children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Impairments in behavioral, social, and school functioning. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 40(5), 508–515.
Eisenberg, N., Fabes, R., & Spinrad, T. (2006). Prosocial behaviour. Handbook of Child Psychology, 3, 646–718.
Emerson, E., Einfeld, S., & Stancliffe, R. J. (2010). The mental health of young children with intellectual disabilities or borderline intellectual functioning. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 45(5), 579–587.
Evans, S. W., Owens, J. S., & Bunford, N. (2014). Evidence-based psychosocial treatments for children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 43(4), 527–551.
Flanagan, D. P., Alfonso, V. C., Primavera, L. H., Povall, L., & Higgins, D. (1996). Convergent validity of the BASC and SSRS: Implications for social skills assessment. Psychology in the Schools, 33(1), 13–23.
Graziano, P. A., Geffken, G. R., & McNamara, J. P. (2011). Atypical behaviors and comorbid externalizing symptoms equally predict children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder’s social functioning. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 42(4), 377–389.
Graziano, P. A., Slavec, J., Hart, K., Garcia, A., & Pelham, W. E. (2014). Improving school readiness in preschoolers with behavior problems: Results from a summer treatment program. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 36(4), 555–569.
Graziano, P. A., Slavec, J., Ros, R., Garb, L., Hart, K., & Garcia, A. (2015). Self-regulation assessment among preschoolers with externalizing behavior problems. Psychological Assessment, 27(4), 1337.
Graziano, P. A., & Hart, K. (2016). Beyond behavior modification: benefits of social–emotional/selfregulation training for preschoolers with behavior problems. Journal of school psychology, 58, 91–111.
Graziano, P. A., Ros, R., Hart, K. C., & Slavec, J. (2017). Summer treatment program for preschoolers with externalizing behavior problems: a preliminary examination of parenting outcomes. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 1–13.
Gifford-Smith, M. E., & Brownell, C. A. (2003). Childhood peer relationships: Social acceptance, friendships, and peer networks. Journal of School Psychology, 41(4), 235–284.
Greene, R. W., Biederman, J., Faraone, S. V., Sienna, M., & Garcia-Jetton, J. (1997). Adolescent outcome of boys with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and social disability: Results from a 4-year longitudinal follow-up study. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 65(5), 758.
Gresham, F. M. (1986). Conceptual and definitional issues in the assessment of children's social skills: implications for classifications and training. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 15(1), 3–15.
Gresham, F. M., & Elliott, S. N. (1987). The relationship between adaptive behavior and social skills issues in definition and assessment. The Journal of Special Education, 21, 167–181.
Jensen, P., Arnold, L. E., Richters, J. E., Severe, J. B., Vereen, D., Vitiello, B., ... & Wells, K. C. (1999). Moderators and mediators of treatment response for children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: The multimodal treatment study of children with attentiondeficit/hyperactivity disorder. Archives of General Psychiatry, 56(12), 1088–1096.
Harrison, J. R., Vannest, K. J., & Reynolds, C. R. (2011). Behaviors that discriminate ADHD in children and adolescents: Primary symptoms, symptoms of comorbid conditions, or indicators of functional impairment? Journal of Attention Disorders, 2, 147–160.
Hayes, A. F., & Matthes, J. (2009). Computational procedures for probing interactions in OLS and logistic regression: SPSS and SAS implementations. Behavior Research Methods, 41(3), 924–936.
Hinshaw, S. P. (1992). Academic underachievement, attention deficits, and aggression: Comorbidity and implications for intervention. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 60(6), 893.
Hinshaw, S. P. (2007). Moderators and mediators of treatment outcome for youth with ADHD: Understanding for whom and how interventions work. Ambulatory Pediatrics, 7(1), 91–100.
Hoza, B., Waschbusch, D. A., Pelham, W. E., Molina, B. S., & Milich, R. (2000). Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disordered and control Boys' responses to social success and failure. Child Development, 71(2), 432–446.
Hubbard, J. A., & Newcomb, A. F. (1991). Initial dyadic peer interaction of attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder and normal boys. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 19(2), 179–195.
Keenan, K., & Wakschlag, L. S. (2000). More than the terrible twos: The nature and severity of behavior problems in clinic-referred preschool children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 28(1), 33–46.
King, S., Waschbusch, D. A., Pelham, W. E., Frankland, B. W., Corkum, P. V., & Jacques, S. (2009). Subtypes of aggression in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: Medication effects and comparison with typical children. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 38(5), 619–629.
La Greca, A. M., Silverman, W. K., & Lochman, J. E. (2009). Moving beyond efficacy and effectiveness in child and adolescent intervention research. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 77(3), 373.
Manning, S., & Miller, D. (2001). Identifying ADHD subtypes using the parent and teacher rating scales of the behavior assessment scale for children. Journal of Attention Disorders, 5(1), 41–51.
Mashburn, A. J., Hamre, B. K., Downer, J. T., & Pianta, R. C. (2006). Teacher and classroom characteristics associated with teachers’ ratings of prekindergartners’ relationships and behaviors. Journal of Psychoeducational Assessment, 24(4), 367–380.
Mather, N., & Woodcock, R. W. (2001). Examiners manual: Woodcock–Johnson III tests of achievement. Itasca: IL7 Riverside Publishing.
McClelland, M. M., Cameron, C. E., Connor, C. M., Farris, C. L., Jewkes, A. M., & Morrison, F. J. (2007). Links between behavioral regulation and preschoolers' literacy, vocabulary, and math skills. Developmental Psychology, 43(4), 947.
McIntyre, L. L. (2008). Parent training for young children with developmental disabilities: Randomized controlled trial. Journal Information, 113(5).
Mikami, A. Y., Huang-Pollock, C. L., Pfiffner, L. J., McBurnett, K., & Hangai, D. (2007). Social skills differences among attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder types in a chat room assessment task. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 35(4), 509–521.
Mikami, A. Y., Lee, S. S., Hinshaw, S. P., & Mullin, B. C. (2008). Relationships between social information processing and aggression among adolescent girls with and without ADHD. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 37(7), 761–771.
Milich, R., & Dodge, K. A. (1984). Social information processing in child psychiatric populations. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 12(3), 471–489.
Mitsis, E. M., McKAY, K. E., Schulz, K. P., Newcorn, J. H., & Halperin, J. M. (2000). Parent–teacher concordance for DSM-IV attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in a clinic-referred sample. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 39(3), 308–313.
Murphy, J., Shevlin, M., & Adamson, G. (2007). A latent class analysis of positive psychosis symptoms based on the British Psychiatric Morbidity Survey. Personality and Individual Differences, 42(8), 1491–1502.
Mostow, A. J., Izard, C. E., Fine, S., & Trentacosta, C. J. (2002). Modeling emotional, cognitive, and behavioral predictors of peer acceptance. Child Development, 1775–1787.
Muthén, B., & Muthén, L. (2012). Mplus Version 7: User’s guide. Los Angeles: Muthén & Muthén.
Narad, M. E., Garner, A. A., Peugh, J. L., Tamm, L., Antonini, T. N., Kingery, K. M., et al. (2015). Parent–teacher agreement on ADHD symptoms across development. Psychological Assessment, 27(1), 239.
Nigg, J. T., & Barkley, R. A. (2014). Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. In E. Mash & R. Barkley (Eds.), Child Psychopathology (Vol. 3rd ed., pp. 75–144). New York: Guilford Press.
Nigg, J. T., Quamma, J. P., Greenberg, M. T., & Kusche, C. A. (1999). A two-year longitudinal study of neuropsychological and cognitive performance in relation to behavioral problems and competencies in elementary school children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 27(1), 51–63.
Nigg, J. T., Stavro, G., Ettenhofer, M., Hambrick, D. Z., Miller, T., & Henderson, J. M. (2005). Executive functions and ADHD in adults: Evidence for selective effects on ADHD symptom domains. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 114(4), 706.
Nixon, E. (2001). The social competence of children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A review of the literature. Child Psychology and Psychiatry Review, 6(04), 172–180.
Norvilitis, J., Casey, R., Brooklier, K., & Bonello, P. (2000). Emotion appraisal in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and their parents. Journal of Attention Disorders, 4(1), 15–26.
Owens, E. B., Hinshaw, S. P., Kraemer, H. C., Arnold, L. E., Abikoff, H. B., Cantwell, D. P., et al. (2003). Which treatment for whom for ADHD? Moderators of treatment response in the MTA. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 71(3), 540.
Owens, J. S., Goldfine, M. E., Evangelista, N. M., Hoza, B., & Kaiser, N. M. (2007). A critical review of self-perceptions and the positive illusory bias in children with ADHD. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 10(4), 335–351.
Ozonoff, S., Goodlin-Jones, B., & Solomon, M. (2007). Autism Spectrum disorders Assessment of Childhood Disorders (pp. 487–525). New York: Guilford.
Parker, J. G., & Asher, S. R. (1987). Peer relations and later personal adjustment: Are low-accepted children at risk? Psychological Bulletin, 102(3), 357.
Pearson, D. A., Lachar, D., Loveland, K. A., Santos, C. W., Faria, L. P., Azzam, P. N., et al. (2000). Patterns of behavioral adjustment and maladjustment in mental retardation: Comparison of children with and without ADHD. American Journal on Mental Retardation, 105(4), 236–251.
Pelc, K., Kornreich, C., Foisy, M.-L., & Dan, B. (2006). Recognition of emotional facial expressions in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Pediatric Neurology, 35(2), 93–97.
Pelham Jr., W. E., & Fabiano, G. A. (2008). Evidence-based psychosocial treatments for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 37(1), 184–214.
Polanczyk, G. V., Willcutt, E. G., Salum, G. A., Kieling, C., & Rohde, L. A. (2014). ADHD prevalence estimates across three decades: An updated systematic review and meta-regression analysis. International Journal of Epidemiology, 43(2), 434–442.
Ponitz, C. E. C., McClelland, M. M., Jewkes, A. M., Connor, C. M., Farris, C. L., & Morrison, F. J. (2008). Touch your toes! Developing a direct measure of behavioral regulation in early childhood. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 23(2), 141–158.
Ponitz, C. C., McClelland, M. M., Matthews, J., & Morrison, F. J. (2009). A structured observation of behavioral self-regulation and its contribution to kindergarten outcomes. Developmental Psychology, 45(3), 605.
Power, T. J., Andrews, T. J., Eiraldi, R. B., Doherty, B. J., Ikeda, M. J., DuPaul, G. J., & Landau, S. (1998). Evaluating attention deficit hyperactivity disorder using multiple informants: The incremental utility of combining teacher with parent reports. Psychological Assessment, 10(3), 250.
Raver, C. C., Gershoff, E. T., & Aber, J. L. (2007). Testing equivalence of mediating models of income, parenting, and school readiness for white, black, and Hispanic children in a national sample. Child Development, 78(1), 96–115.
Reynolds, C. R., & Kamphaus, R. W. (2004). BASC-2: Behavior assessment system for children.
Riggs, N. R., Jahromi, L. B., Razza, R. P., Dillworth-Bart, J. E., & Mueller, U. (2006). Executive function and the promotion of social–emotional competence. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 27(4), 300–309.
Rimm-Kaufman, S. E., & Pianta, R. C. (2000). An ecological perspective on the transition to kindergarten: a theoretical framework to guide empirical research. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 21(5), 491–511.
Roberts, C., Mazzucchelli, T., Studman, L., & Sanders, M. R. (2006). Behavioral family intervention for children with developmental disabilities and behavioral problems. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 35(2), 180–193.
Ros, R., & Graziano, P. A. (2017). Social functioning in children with or at risk for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A meta-analytic review. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 1–23.
Runions, K. C., & Keating, D. P. (2007). Young children's social information processing: family antecedents and behavioral correlates. Developmental Psychology, 43(4), 838.
Saarni, C. (1999). The development of emotional competence: Guilford Press.
Sattler, J., & Dumont, R. (2004). Assessment of children: WISC-IV and WPPSI-III supplement. San Diego: Jerome M. Sattler, Publisher: Inc.
Sclove, S. L. (1987). Application of model-selection criteria to some problems in multivariate analysis. Psychometrika, 52(3), 333–343.
Shaffer, D., Fisher, P., Lucas, C. P., Dulcan, M. K., & Schwab-Stone, M. E. (2000). NIMH diagnostic interview schedule for children version IV (NIMH DISC-IV): Description, differences from previous versions, and reliability of some common diagnoses. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 39(1), 28–38.
Singh, S. D., Ellis, C. R., Winton, A. S., Singh, N. N., Leung, J. P., & Oswald, D. P. (1998). Recognition of facial expressions of emotion by children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Behavior Modification, 22(2), 128–142.
Sjöwall, D., Roth, L., Lindqvist, S., & Thorell, L. B. (2013). Multiple deficits in ADHD: Executive dysfunction, delay aversion, reaction time variability, and emotional deficits. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 54(6), 619–627.
Spence, S. H. (2003). Social skills training with children and young people: Theory, evidence and practice. Child and Adolescent Mental Health, 8(2), 84–96.
Walker, S. (2005). Gender differences in the relationship between young children's peer-related social competence and individual differences in theory of mind. The Journal of Genetic Psychology, 166(3), 297–312.
Wanless, S. B., McClelland, M. M., Acock, A. C., Ponitz, C. C., Son, S. H., Lan, X., et al. (2011). Measuring behavioral regulation in four societies. Psychological Assessment, 23(2), 364.
Webster-Stratton, C., & Hammond, M. (1997). Treating children with early-onset conduct problems: A comparison of child and parent training interventions. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 65(1), 93–109.
Webster-Stratton, C., & Hammond, M. (1998). Conduct problems and level of social competence in head start children: Prevalence, pervasiveness, and associated risk factors. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 1(2), 101–124.
Wechsler, D. (2002). WPPSI-III administration and scoring manual. San Antonio: Psychological Corp.
Wechsler, D. (2012). Wechsler, D. (2012). Wechsler preschool and primary scale of intelligence (4th ed.). San Antonio: NCS Pearson.
Woodcock, R. W., McGrew, K. S., & Mather, N. (2001). Woodcock-Johnson® III NU tests of achievement.
Yuill, N., & Lyon, J. (2007). Selective difficulty in recognising facial expressions of emotion in boys with ADHD. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 16(6), 398–404.
Zalewski, M., Lengua, L. J., Wilson, A. C., Trancik, A., & Bazinet, A. (2011). Emotion regulation profiles, temperament, and adjustment problems in preadolescents. Child Development, 82(3), 951–966.
Acknowledgements
The research reported here was supported by the Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education, through Grant R324A120136 as well as a local grant from The Children’s Trust (1329-7290) to the second author. The opinions expressed are those of the authors and do not represent views of the Institute or the U.S. Department of Education or The Children’s Trust.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
Rosmary Ros, Paulo A. Graziano and Katie C. Hart declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ros, R., Graziano, P.A. & Hart, K.C. Treatment Response among Preschoolers with EBP: The Role of Social Functioning. J Psychopathol Behav Assess 40, 514–527 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-018-9646-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-018-9646-x