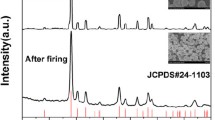
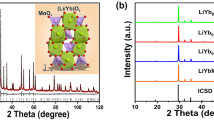
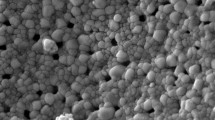
Abstract
Temperature determination is of fundamental importance for a wide variety of applications in scientific research, technological developments, biomedical applications, and control of many industrial processes. To supply all these needs, a variety of sensors and devices using different methods have been developed. In this work, we propose a new alternative for a luminescent thermometer based on the visible emission of the europium ion (Eu3+) in the Y2O3 matrix. The sharp emission peak observed at 612 nm was achieved by exciting the Y2O3:Eu3+ ceramic powders with a broadband LED light source centered at 395 nm. The temperature-sensing behavior was explored based on the valley-to-peak ratio (VPR) approach. Thermal sensing performance based on red-emitting level (5D0 → 7F2) as a function of the temperature, in the range of 298–573 K, has been considered to evaluate the thermometric parameters. The evaluated thermal sensitivity in Y2O3:Eu3+ is around 0.53% K−1 at 298 K in our experimental range. Results imply that the present phosphor Y2O3:Eu3+ exhibits high and stable sensitivity in a wide temperature range. Hence, this work demonstrates the basis for the manufacture of thermometer of low cost, using simple commercial LED as a source of excitation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Suo, X. Zhao, Z. Zhang, Y. Wang, J. Sun, M. Jin, C. Guo, Rational design of ratiometric luminescence thermometry based on thermally coupled levels for bioapplications. Laser Photon. Rev. 15, 2000319 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/lpor.202000319
S. Augustin, T. Fröhlich, Temperature dependence of the dynamic parametersof contact thermometers. Sensors 19, 2299 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/s19102299
C.D. Brites, P.P. Lima, N.J. Silva, A. Millán, V.S. Amaral, F. Palacio, L.D. Carlos, Thermometry at the nanoscale. Nanoscale 4, 4799–4829 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2NR30663H
X. Wang, Q. Liu, Y. Bu, C. Liu, T. Liu, X. Yan, Optical temperature sensing of rare-earth ion doped phosphors. RSC Adv. 5, 86219 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA16986K
C. Bradac, S.F. Lim, H. Chang, I. Aharonovich, Optical nanoscale thermometry: from fundamental mechanisms to emerging practical applications. Adv. Opt. Mater. 8, 2000183 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.202000183
J. Zhou, B. Rosal, D. Jaque, S. Uchiyama, D. Jin, Advances and challenges for fluorescence nanothermometry. Nat. Methods 17, 967–980 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-020-0957-y
E. Hemmer, F. Vetrone, Nanothermometry using upconverting nanoparticles, Chap 11, in Upconverting Nanomaterials: Perspectives, Synthesis, and Applications. ed. by C. Altavilla (CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton, 2017)
A.S. Souza, L.A.O. Nunes, I.G.N. Silva, F.A.M. Oliveira, L.L. da Luz, H.F. Brito, M.C.F.C. Felinto, R.A.S. Ferreira, S.A. Júnior, L.D. Carlos, O.L. Malta, Highly-sensitive Eu3+ratiometric thermometers based on excited state absorption with predictable calibration. Nanoscale 8, 5327–5333 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6nr00158k
N. Rakov, Y. Xing, G.S. Maciel, Optical thermometry operation within all three biological windows using Nd3+:Er3+:Y2O3 nanocomposite phosphors. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 3, 10479–10486 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.0c02397
I.E. Kolesnikov, A.A. Kalinichev, M.A. Kurochkin, D.V. Mamonova, E.Y. Kolesnikov, E. Lähderanta, M.D. Mikhailov, Bifunctional heater-thermometer Nd3+-doped nanoparticles with multiple temperature sensing parameters. Nanotechnology 30, 145501 (2019)
H. Suo, X.Q. Zhao, Z.Y. Zhang, C.F. Guo, Ultra-sensitive optical nano-thermometer LaPO4:Yb3+/Nd3+ based on thermoenhanced NIR-to-NIR emissions. Chem. Eng. J. 389, 124506 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124506
Y. Shi, F.M. Yang, C.Z. Zhao, Y. Huang, M.Z. Li, Q.J. Zhou, Q.Y. Li, Z.P. Li, J.M. Liu, T. Wei, Highly sensitive up- conversion thermometric performance in Nd3+ and Yb3+ sensitized Ba4La2Ti4Nb6O30 based on near-infrared emissions. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 124, 130–136 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2018.09.013
M. Runowski, P. Wozny, I.R. Martín, V. Lavín, S. Lis, Praseodymium doped YF3:Pr3+ nanoparticles as optical thermometer based on luminescence intensity ratio (LIR)−studies in visible and NIR range. J. Lumin. 214, 116571 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2019.116571
G. Jia, H. You, Y. Song, Y. Huang, M. Yang, H. Zhang, Facile synthesis and luminescence of uniform Y2O3 hollow spheres by a sacrificial template route. Inorg. Chem. 49, 7721–7725 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/ic100430g
Q. Dai, M.E. Foley, C.J. Breshike, A. Lita, G.F. Strouse, Ligand-passivated Eu: Y2O3 nanocrystals as a phosphor for white light emitting diodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 15475–15486 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja2039419
J. Zhou, R. Lei, H. Wang, C. Chen, B. Chen, E. Pan, S. Zhao, S. Xu, Er3+/Yb3+-codoped ZrO2 nanocrystals as ratiometric luminescence nanothermometers that cover three biological windows. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 3, 186–194 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.9b01895
Y. Zhou, F. Qin, Y. Zheng, Z. Zhang, W. Cao, Fluorescence intensity ratio method for temperature sensing. Opt. Lett. 40, 4544–4547 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.40.004544
S. Zhoua, X. Li, X. Weib, C. Duanb, M. Yin, A new mechanism for temperature sensing based on the thermal population of 7F2 state in Eu3+. Sens. Actuators B 231, 641–645 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.03.082
L. Li, W. Xu, L. Zheng, F. Qin, Y. Zhou, Z. Liang, Z. Zhang, W. Cao, Valley-to-peak intensity ratio thermometry based on the red upconversion emission of Er3+. Opt. Exp. 24, 13244–13249 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.24.013244
N. Rakov, G.S. Maciel, Exploring the 4I13/2 → 4I15/2 radiative transition from Er3+ in Y2O3 for temperature sensing. J. Lumin. 199, 293–297 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2018.03.020
Y. Gao, S. Murai, K. Shinozaki, J. Qiu, K. Tanaka, Phase-selective distribution of Eu2+ and Eu3+ in oxide and fluoride crystals in glass-ceramics for warm white-light-emitting diodes. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 1, 961–971 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaelm.9b00129
Y. Gao, J. Qiu, D. Zhou, Investigation of optical properties: Eu with Al codoping in aluminum silicate glasses and glass-ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 100, 2901–2913 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.14807
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), and Fundação de Amparo à Ciência e Tecnologia do Estado de Pernambuco (FACEPE) Brazilian Agencies. SAV thanks CNPq for the junior post-doctoral fellowship (Process Number 160920/2019-1). This work was also carried out under the support of the National Institute of Photonics (INFO) and PRONEX—Center of Excellence Program supported by the mentioned Brazilian agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rakov, N., Vieira, S.A. & Gomes, A.S.L. Highly sensitive optical thermometry operation using Eu3+:Y2O3 powders excited under low-intensity LED light source at 395 nm. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 23285–23292 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06813-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06813-6