Abstract
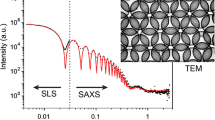
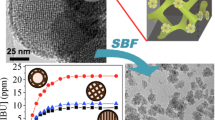
Hollow silica–polyelectrolyte composite nanoparticles were prepared using templates of spherical polyelectrolyte brushes which consist of a polystyrene (PS) core and a densely grafted linear poly(acrylic acid) shell. The obtained hollow particles were systematically studied by small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) in combination with other characterization methods such as transmission electron microscopy and dynamic light scattering. The hollow structure formed by dissolving the PS core was confirmed by the reduction of electron density to zero in the cavity through fitting SAXS data. SAXS revealed both the inward and outward expansions of the hollow silica–polyelectrolyte composite particles upon increasing pH from 3 to 9, while further increasing pH led to the partial dissolution of silica layer and even destruction of the hollow structure. SAXS was confirmed to be a unique and powerful characterization method to observe hollow silica nanoparticles, which should be ideal candidates for controlled drug delivery.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu J, Chen M, Fang X, Wu L (2011) Fabrication and application of inorganic hollow spheres. Chem Soc Rev 40(11):5472–5491
Zhao Y, Jiang L (2009) Hollow micro/nanomaterials with multilevel interior structures. Adv Mater 21(36):3621–3638
Si Y, Chen M, Wu L (2016) Syntheses and biomedical applications of hollow micro-/nano-spheres with large-through-holes. Chem Soc Rev 45(3):690–714
Li Y, Shi J (2014) Hollow-structured mesoporous materials: chemical synthesis: functionalization and applications. Adv Mater 26(20):3176–3205
Podsiadlo P, Kwon SG, Koo B, Lee B, Prakapenka VB, Dera P, Zhuravlev KK, Krylova G, Shevchenko EV (2013) How “Hollow” are hollow nanoparticles? J Am Chem Soc 135(7):2435–2438
Khanal A, Inoue Y, Yada M, Nakashima K (2007) Synthesis of Silica Hollow Nanoparticles Templated by Polymeric Micelle with Core–Shell–Corona Structure. J Am Chem Soc 129(6):1534–1535
Tang F, Li L, Chen D (2012) Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: synthesis biocompatibility and drug delivery. Adv Mater 24(12):1504–1534
Zhu Y, Shi J, Shen W, Dong X, Feng J, Ruan M, Li Y (2005) Stimuli-responsive controlled drug release from a hollow mesoporous silica sphere/polyelectrolyte multilayer core-shell structure. Angew Chem 117(32):5213–5217
Zhang Y, Hsu BYW, Ren C, Li X, Wang J (2015) Silica-based nanocapsules: synthesis, structure control and biomedical applications. Chem Soc Rev 44(1):315–335
Park C, Oh K, Lee SC, Kim C (2007) Controlled release of guest molecules from mesoporous silica particles based on a pH-responsive polypseudorotaxane motif. Angew Chem Int Ed 46(9):1455–1457
Guerrero-Martinez A, Perez-Juste J, Liz-Marzan LM (2010) Recent progress on silica coating of nanoparticles and related nanomaterials. Adv Mater 22(11):1182–1195
Cao SS, Zhang Y, Zhou LL, Chen JR, Fang L, Fei D, Zhu HJ, Ge Y (2014) Stimuli-responsive controlled release and molecular transport from hierarchical hollow silica/polyelectrolyte multilayer formulations. J Mater Chem B 2(41):7243–7249
Amstad E, Reimhult E (2012) Nanoparticle actuated hollow drug delivery vehicles. Nanomedicine 7(1):145–164
Lou XW, Archer LA, Yang Z (2008) Hollow micro-/nanostructures: synthesis and applications. Adv Mater 20(21):3987–4019
Wang Y, Wang J, Han H, Liu J, Zhao H, Shen M, Xu Y, Xu J, Li L, Guo X (2016) Self-assembled micelles of N-phthaloylchitosan-g-poly (N-vinylcaprolactam) for temperature-triggered non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug delivery. J Mater Sci 51(3):1591–1599. doi:10.1007/s10853-015-9482-2
Caruso F, Caruso RA, Mohwald H (1998) Nanoengineering of inorganic and hybrid hollow spheres by colloidal templating. Science 282(5391):1111–1114
Chen M, Wu LM, Zhou SX, You B (2006) A method for the fabrication of monodisperse hollow silica spheres. Adv Mater 18(6):801–806
Deng ZW, Chen M, Zhou SX, You B, Wu LM (2006) A novel method for the fabrication of monodisperse hollow silica spheres. Langmuir 22(14):6403–6407
Tissot I, Novat C, Lefebvre F, Bourgeat-Lami E (2001) Hybrid latex particles coated with silica. Macromolecules 34(17):5737–5739
Han L, Che SN (2013) Anionic surfactant templated mesoporous silicas (AMSs). Chem Soc Rev 42(9):3740–3752
Zou H, Wu SS, Ran QP, Shen J (2008) A simple and low-cost method for the preparation of monodisperse hollow silica spheres. J Phys Chem C 112(31):11623–11629
Chen KM, Zhu Y, Li L, Lu Y, Guo XH (2010) Recyclable spherical polyelectrolyte brushes containing magnetic nanoparticles in core. Macromol Rapid Commun 31(16):1440–1443
Balmer JA, Mykhaylyk OO, Armes SP, Fairclough JPA, Ryan AJ, Gummel J, Murray MW, Murray KA, Wiliams NSJ (2011) Time-Resolved Small-Angle X-ray Scattering Studies of Polymer-Silica Nanocomposite Particles: initial Formation and Subsequent Silica Redistribution. J Am Chem Soc 133(4):826–837
Grunder R, Urban G, Ballauff M (1993) Small-angle X-ray-analysis of latex-particles with core-shell morphology. Colloid Polym Sci 271(6):563–572
Ballauff M, Bolze J, Dingenouts N, Hickl P, Pötschke D (1996) Small-angle X-ray scattering on latexes. Macromol Chem Phys 197(10):3043–3066
Ballauff M (2011) Analysis of polymer colloids by small-angle X-ray and neutron scattering: contrast variation. Adv Eng Mater 13(8):793–802
Dingenouts N, Bolze J, Pötschke D, Ballauff M (1999) Analysis of polymer latexes by small-angle X-ray scattering. In: Polymer latexes—epoxide resins—polyampholytes. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–47. doi:10.1007/3-540-68384-4_1
Wang W, Li L, Henzler K, Lu Y, Wang J, Han H, Tian Y, Wang Y, Zhou Z, Lotze G, Narayanan T, Ballauff M, Guo X (2017) Protein immobilization onto cationic spherical polyelectrolyte brushes studied by small angle X-ray scattering. Biomacromol 18(5):1574–1581
Wang W, Li L, Yu X, Han H, Guo X (2014) Distribution of magnetic nanoparticles in spherical polyelectrolyte brushes as observed by small-angle X-ray scattering. J Polym Sci Part B: Polym Phys 52(24):1681–1688
Wang W, Chu F, Li L, Han H, Tian Y, Wang Y, Yuan Z, Zhou Z, Guo X (2016) Interactions among spherical poly(acrylic acid) brushes: observation by rheology and small angle X-ray scattering. J Polym Sci Part B: Polym Phys 54(3):405–413
Wang S, Chen K, Xu Y, Yu X, Wang W, Li L, Guo X (2013) Protein immobilization and separation using anionic/cationic spherical polyelectrolyte brushes based on charge anisotropy. Soft Matter 9(47):11276–11287
Tian Y, Li L, Han H, Wang W, Wang Y, Ye Z, Guo X (2016) Modification of spherical polyelectrolyte brushes by layer-by-layer self-assembly as observed by small angle X-ray scattering. Polymers 8(4):145
de Robillard Q, Guo X, Ballauff M, Narayanan T (2000) Spatial correlation of spherical polyelectrolyte brushes in salt-free solution as observed by small-angle X-ray scattering. Macromolecules 33(24):9109–9114
Ruckdeschel P, Dulle M, Honold T, Forster S, Karg M, Retsch M (2016) Monodisperse hollow silica spheres: an in-depth scattering analysis. Nano Res 9(5):1366–1376
Chen ZH, Kim C, Zeng XB, Hwang SH, Jang J, Ungar G (2012) Characterizing size and porosity of hollow nanoparticles: SAXS, SANS, TEM, DLS, and adsorption isotherms compared. Langmuir 28(43):15350–15361
Guo X, Weiss A, Ballauff M (1999) Synthesis of spherical polyelectrolyte brushes by photoemulsion polymerization. Macromolecules 32(19):6043–6046
Huang SB, Yu XJ, Dong YM, Li L, Guo XH (2012) Spherical polyelectrolyte brushes: ideal templates for preparing pH-sensitive core-shell and hollow silica nanoparticles. Colloids Surf A 415:22–30
Ballauff M (2003) Nanoscopic polymer particles with a well-defined surface: synthesis, characterization, and properties. Macromol Chem Phys 204(2):220–234
Dingenouts N, Norhausen C, Ballauff M (1998) Observation of the volume transition in thermosensitive core–shell latex particles by small-angle X-ray scattering. Macromolecules 31(25):8912–8917
Seelenmeyer S, Deike I, Rosenfeldt S, Norhausen C, Dingenouts N, Ballauff M, Narayanan T, Lindner P (2001) Small-angle x-ray and neutron scattering studies of the volume phase transition in thermosensitive core–shell colloids. J Chem Phys 114(23):10471–10478
Wang W, Li L, Han H, Tian Y, Zhou Z, Guo X (2015) Tunable immobilization of protein in anionic spherical polyelectrolyte brushes as observed by small-angle X-ray scattering. Colloid Polym Sci 293(10):2789–2798
Ballauff M (2007) Spherical polyelectrolyte brushes. Prog Polym Sci 32(10):1135–1151
Pedersen JS, Gerstenberg MC (1996) Scattering Form Factor of Block Copolymer Micelles. Macromolecules 29(4):1363–1365
Rosenfeldt S, Wittemann A, Ballauff M, Breininger E, Bolze J, Dingenouts N (2004) Interaction of proteins with spherical polyelectrolyte brushes in solution as studied by small-angle x-ray scattering. Phys Rev E 70(6 Pt 1):061403
Dingenouts N, Bolze J, Potschke D, Ballauff M (1999) Analysis of polymer latexes by small-angle X-ray scattering. Polym Latexes Epoxide Resins Polyampholytes 144:1–47
Henzler K, Rosenfeldt S, Wittemann A, Harnau L, Finet S, Narayanan T, Ballauff M (2008) Directed motion of proteins along tethered polyelectrolytes. Phys Rev Lett 100(15):158301
Henzler K, Wittemann A, Breininger E, Ballauff M, Rosenfeldt S (2007) Adsorption of bovine hemoglobin onto spherical polyelectrolyte brushes monitored by small-angle X-ray scattering and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Biomacromol 8(11):3674–3681
Guo X, Ballauff M (2000) Spatial dimensions of colloidal polyelectrolyte brushes as determined by dynamic light scattering. Langmuir 16(23):8719–8726
Acknowledgements
We gratefully thank the financial support from the NSFC Grants (51273063 and 21476143), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, 111 Project Grant (B08021), Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility, and the China Scholarship Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, H., Li, L., Yang, Q. et al. Characterization of hollow silica–polyelectrolyte composite nanoparticles by small-angle X-ray scattering. J Mater Sci 53, 3210–3224 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1747-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1747-5