Abstract
Background
The subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (S-ICD) system is an established therapy for the prevention of sudden cardiac death (SCD) and an alternative to a transvenous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) system in selected patients. S-ICDs are usually implanted under general anesthesia. The purpose of the present study was to describe the technical feasibility and safety of local anesthesia with conscious sedation as an alternative to general anesthesia during S-ICD implantation using the intermuscular technique.
Methods
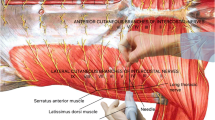
We conducted a retrospective, single-center study on patients undergoing S-ICD implantation using the intermuscular technique at our center between February 2016 and May 2018. All procedures were performed under controlled sedation with propofol and midazolam. Local anesthesia was used for all procedures.
Results
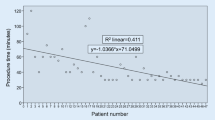
Twenty-two patients (17 men and 5 women) with a mean age of 51.1 ± 16.2 years were included. The indication for S-ICD implantation was primary prevention in 18 (81.8%) patients. The mean dose of midazolam and propofol administered was 7.8 ± 2.3 mg and 72.7 ± 37.4 mg, respectively. The procedural success rate was 100%, with no apneic or hypoxic episodes or other complications requiring therapeutic intervention. None of the patients required conversion to general anesthesia. All patients were comfortable with the position and appearance of the device.
Conclusions
Our findings suggest that local anesthesia with conscious sedation using propofol and midazolam is a safe and feasible option for S-ICD implantation procedures using an intermuscular technique.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ASA:
-
American Society of Anesthesiologists
- AST:
-
Automated screening tool
- CIED:
-
Cardiac implantable electronic device
- DFT:
-
Defibrillation threshold
- ICD:
-
Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
- IVF:
-
Idiopathic ventricular fibrillation
- J:
-
Joule
- M:
-
Musculus
- RASS:
-
Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale
- SCD:
-
Sudden cardiac death
- S-ICD:
-
Subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
- VF:
-
Ventricular fibrillation
References
Priori SG, Blomström-Lundqvist C, Mazzanti A, Blom N, Borggrefe M, Camm J, et al. 2015 ESC guidelines for the Management of Patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death: the task force for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC). Europace. 2015;17:1601–87.
Mirowski M, Reid PR, Mower MM, Watkins L, Gott VL, Schauble JF, et al. Termination of malignant ventricular arrhythmias with an implanted automatic defibrillator in human beings. N Engl J Med. 1980;303:322–4.
The Antiarrhythmics versus Implantable Defibrillators (AVID) Investigators. A comparison of antiarrhythmic-drug therapy with implantable defibrillators in patients resuscitated from near-fatal ventricular arrhythmias. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:1576–83.
Moss AJ, Hall WJ, Cannom DS, Daubert JP, Higgins SL, Klein H, et al. Multicenter automatic defibrillator implantation trial (MADIT) investigators. Improved survival with an implanted defibrillator in patients with coronary disease at high risk for ventricular arrhythmia. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:1933–40.
Moss AJ, Zareba W, Hall WJ, Klein H, Wilber DJ, Cannom DS, et al. Multicenter automatic defibrillator implantation trial II (MADIT II) investigators. Prophylactic implantation of a defibrillator in patients with myocardial infarction and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:877–83.
Bardy GH, Lee KL, Mark DB, Poole JE, Packer DL, Boineau R, et al. Sudden Cardiac Death in Heart Failure Trial (SCD-HeFT) Investigators. Amiodarone or an implantable cardio- verter-defibrillator for congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:225–37.
Poole JE, Gold MR. Who should receive the subcutaneous implanted defibrillator? The subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) should be considered in all ICD patients who do not require pacing. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2013;6(6):1236–44.
Lewis GF, Gold MR. Safety and efficacy of the subcutaneous implantable defibrillator. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;67:445–54.
Burke MC, Gold MR, Knight BP, Barr CS, Theuns DAMJ, Boersma LVA, et al. Safety and efficacy of the totally subcutaneous implantable defibrillator: 2-year results from a pooled analysis of the IDE study and EFFORTLESS registry. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65:1605–15.
Olde Nordkamp LR, Dabiri Abkenari L, Boersma LV, Maass AH, de Groot JR, van Oostrom AJ, et al. The entirely subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator: initial clinical experience in a large Dutch cohort. JAm Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:1933–9.
Jarman JW, Lascelles K, Wong T, Markides V, Clague JR, Till J. Clinical experience of entirely subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillators in children and adults: cause for caution. Eur HeartJ. 2012;33:1351–9.
Lambiase PD, Barr C, Theuns DA, Knops R, Neuzil P, Johansen JB, et al. Worldwide experience with a totally subcutaneous implantable defibrillator: early results from the EFFORTLESS S-ICD Registry. Eur Heart J. 2014;35(25):1657–65. EFFORTLESS Investigators.
Essandoh MK, Otey AJ, Abdel-Rasoul M, Stein EJ, Turner KR, Joseph NC, et al. Monitored anesthesia care for subcutaneous cardioverter-defibrillator implantation: a single-center experience. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2016;30(5):1228–33. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jvca.2016.06.007.
Essandoh MK, Mark GE, Aasbo JD, Joyner CA, Sharma S, Decena BF, et al. Anesthesia for subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator implantation: Perspectives from the clinical experience of a U.S. panel of physicians. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1111/pace.13364.
Knops RE, Olde Nordkamp LR, de Groot JR, Wilde AA. Two-incision technique for implantation of the subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. Heart Rhythm. 2013;10(8):1240–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2013.05.016. Epub 2013 May.
Winter J, Siekiera M, Shin DI, Meyer C, Kröpil P, Clahsen H, et al. Intermuscular technique for implantation of the subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator: long-term performance and complications. Europace. 2017;19(12):2036–41. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/euw297.
Ueshima H, Hiroshi O. A successful case of S-ICD implantation performed under the transversus thoracic muscle plane block. J Clin Anesth. 2016;32:253–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinane.2016.02.031.
Ueshima H, Kitamura A. Blocking of multiple anterior branches of inter costal nerves (Th2-6) using a transversus thoracic muscle plane block. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2015;40:388. https://doi.org/10.1097/AAP.0000000000000245.
Ueshima H, Hara E, Otake H. Successful cases of S-ICD implantation performed under the serratus plane block. J Clin Anesth. 2016;33:147–8.
Miller MA, Bhatt HV, Weiner M, Brouwer TF, Mittnacht AJ, Shariat A, et al. Implantation of the subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator with truncal plane blocks. Heart Rhythm. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2018.02.014.
Peyrol M, Barraud J, Cautela J, Maille B, Laine M, Bonello L, et al. Controlled sedation with midazolam and analgesis with nalbuphine to alleviate pain in patients undergoing subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator implantation. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2017;49(2):191–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-017-0255-5.
Afzal MR, Mehta D, Evenson C, Pinkhas D, Badin A, Patel D, et al. Perioperative management of oral anticoagulation in patients undergoing implantation of subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator. Heart Rhythm. 2018;15(4):520–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2017.11.010.
Sessler DI, Sigl JC, Kelley SD, Chamoun NG, Manberg PJ, Saager L, et al. Hospital stay and mortality are increased in patients having a “triple low” of low blood pressure, low bispectral index, and low minimum alveolar concentration of volatile anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 2012;116(6):1195–203. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e31825683dc.
Markewitz A. Annual report 2015 of the German cardiac pacemaker and defibrillator register-part 2: implantable cardioverter-defibrillators: cardiac pacemaker working group at the IQTIG - institute for quality assurance and transparency in health care. Herzschrittmacherther Elektrophysiol. 2018;29(1):100–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00399-017-0547-6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the ethics committee of the faculty of medicine of the University of Duisburg-Essen (Reference no. 17-7701-BO), Germany.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaya, E., Jánosi, R.A., Azizy, O. et al. Conscious sedation during subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator implantation using the intermuscular technique. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 54, 59–64 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-018-0445-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-018-0445-9