Abstract
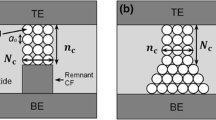
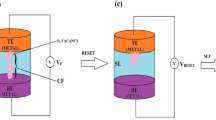
This paper investigates the impact of contact resistance on the memory window in phase-change random access memories (PCRAMs) using \(\hbox {Ge}_{2}\hbox {Se}_{2}\hbox {Te}_{5}\) (GST). We discuss the increase of contact resistance, as device is scaled down to a nanometer size and the effects of contact resistivity changes with respect to the resistance window between the set and reset states. In a contact area of \(400 \,\hbox {nm}^{2}\), the contact resistance in the set state occupies more than 80 % of the total resistance, and the occupied area increases as the contact area is scaled upward. The memory window is significantly degraded as the set resistance increases because of the increasing contact resistance. To maintain the memory window with more than two orders of magnitude of the resistance in a \(100 \,\hbox {nm}^{2}\) area, the contact resistance should be decreased to less than 60 % of that of a \(400\, \hbox {nm}^{2}\) area by reducing contact resistivity or by some other method. We examine the reduction of contact resistance achieved by adopting a three-dimensional contact structure, and we propose this structure as a candidate for the scaled PCRAM.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pirovano, A., Lacaita, A.L., Benvenuti, A., Pellizzer, F., Hudgens, S. Bez, R.: Scaling analysis of phase-change memory technology. IEDM Tech. Dig., 29.6.1–29.6.4 (2003)
Yin, Y., Sone, H., Hosaka, S.: Simulation of proposed confined-chalcogenide phase-change random access memory for low reset current by finite element modeling. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 45, 6177–6181 (2006)
Burr, G.W., Breitwisch, M.J., Franceschini, M., Garetto, D., Gopalakrishnan, K., Jackson, B., Kurdi, B., Lam, C., Lastras, L.A., Padilla, A., Rajendran, B., Raoux, S., Shenoy, R.S.: Phase change memory technology. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 28, 223–262 (2010)
Kim, E.H., Kang, N.S., Yang, H.J., Sutou, Y., Song, Y.H.: Novel device structure for phase change memory toward low-current operation. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 54, 094302 (2015)
Ahn, S.J., Song, Y.j., Jeong, H., Kim, B.C., Kang, Y.S., Ahn, D.H., Kwon, Y.W., Nam, S.W., Jeong, G.T., Kang, H.K., Chung, C.H.: Reliability perspectives for high density PRAM manufacturing. IEDM, 12.6.1–12.06.4 (2011)
Im, D.H., Lee, J.I., Cho, S.L., An, H.G., Kim, D.H., Kim, I.S., Park, H., Ahn, D.H., Horii, H., Park, S.O., Chung, U.I., Moon, J.T.: A unified 7.5 nm dash-type confined cell for high performance PRAM device. IEDM Tech. Dig., 1–4 (2008)
Wong, H.S.P., Raoux, S., Kim, S.B., Liang, J., Reifenberg, J.P., Rajendran, B., Asheghi, M., Goodson, K.E.: Phase change memory. Proc. IEEE 98, 2201–2227 (2010)
Kim, I.S., Cho, S.L., Im, D.H., Cho, E.H., Kim, D.H., Oh, G.H., Ahn, D.H., Park, S.O., Nam, S.W., Moon, J.T., Chung, C.H.: High performance PRAM cell scalable to sub-20nm technology with below \(\text{4F}^{2}\) cell size, extendable to DRAM applications. VLSI Tech., 203–204 (2010)
Reifenberg, J.P., Chang, K.W., Panzer, M.A., Kim, S.B., Rowlette, J.A., Asheghi, M., Wong, H.S.P., Goodson, K.E.: Thermal boundary resistance measurements for phase-change memory devices. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 31, 56–58 (2010)
Ferrari, G., Ghetti, A., Ielmini, D., Redaelli, A., Pirovano, A.: Multiphysics modeling of PCM devics for scaling investigation. In Proceedings of SISPAD International Conference, 265–268 (2010)
Kencke, D.L., Karpov, I.V., Johnson, B.G., Lee, S.J., Kau, D.C., Hudgens, S.J., Reifenberg, J.P., Savransky, S.D., Zhang, J., Giles, M.D., Spadini, G.: The role of interfaces in damascene phase-change memory. IEDM Tech. Dig., 323–326 (2007)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning (NRF-2015R1A2A2A01007289).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, Js., Choi, Cm., Shindo, S. et al. Impact of contact resistance on memory window in phase-change random access memory (PCRAM). J Comput Electron 15, 1570–1576 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-016-0905-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10825-016-0905-3