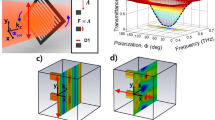
Abstract
In this letter we present a switchable THz notch filter. The filter contains a liquid crystal layer that acts as a half wave retarder in one state and as an isotropic layer in the other state. The device combines three unique properties: it can be switched electrically, it provides a filter depth of 35 dB at 350 GHz and it can be tuned over wide frequency range from 350 GHz to 700 GHz.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.H. Siegel, “Terahertz Technology,” IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech., vol. 50, 2002, pp. 910–928.
P.U. Jepsen, D.G. Cooke, and M. Koch, “Terahertz Spectroscopy and Imaging - Modern Techniques and Applications,” Laser Photonics Rev., Oct. 2010, pp. 1–43.
C. Jördens, M. Scheller, S. Wietzke, D. Romeike, C. Jansen, T. Zentgraf, K. Wiesauer, V. Reisecker, and M. Koch, “Terahertz Spectroscopy to Study the Orientation of Glass Fibres in Reinforced Plastics,” Comp. Sci. Technol., vol. 70, Mar. 2010, pp. 472–477.
C. Jansen, S. Wietzke, H. Wang, M. Koch, and G. Zhao, “Terahertz Spectroscopy on Adhesive Bonds,” Polymer Testing, vol. 30, 2011, pp. 150–154.
S. Wietzke, C. Jansen, F. Rutz, F. Mittleman, and M. Koch, “Determination of Additive Content in Polymeric Compounds with Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy,” Polymer Testing, vol. 26, 2007, pp. 614–618.
N. Krumbholz, T. Hochrein, N. Vieweg, T. Hasek, K. Kretschmer, M. Bastian, M. Mikulics, and M. Koch, “Monitoring polymeric compounding processes inline with THz time-domain spectroscopy,” Polym Test, vol. 28, 2009, pp. 30–35.
C. Jastrow, K. Münter, R. Piesiewicz, T. Kürner, T. Koch, and T. Kleine-Ostmann, “300 GHz Transmission System,” Electron. Lett., vol. 44, 2008, p. 213.
T. Kleine-Ostmann and T. Nagatsuma, “A Review on Terahertz Communications Research,” J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves, vol. 32, Jan. 2011, pp. 143–171.
J. Federici and L. Moeller, “Review of terahertz and subterahertz wireless communications,” J. Appl. Phys., vol. 107, 2010, p. 111101.
C. Jansen, S. Wietzke, V. Astley, D.M. Mittleman, and M. Koch, “Mechanically Flexible Polymeric Compound One-Dimensional Photonic Crystals for Terahertz Frequencies,” Appl. Phys. Lett, vol. 96, 2010, p. 111108.
L. Fekete, J.Y. Hlinka, F. Kadlec, P. Kužel, and P. Mounaix, “Active Optical Control of the Terahertz Reflectivity of High-Resistivity Semiconductors,” Opt. Lett., vol. 30, 2005, pp. 1992–1994.
J. Liu, R. Mendis, and D.M. Mittleman, “The transition from a TEM-like mode to a plasmonic mode in parallel-plate waveguides,” Appl. Phys. Lett., vol. 98, 2011, p. 231113.
K. Nielsen, H.K. Rasmussen, P.U. Jepsen, and O. Bang, “Porous-core honeycomb bandgap THz fiber.,” Opt.Lett., vol. 36, Mar. 2011, pp. 666–668.
C. Jördens, K.L. Chee, I.A.I. Al-Naib, I. Pupeza, S. Peik, G. Wenke, and M. Koch, “Dielectric Fibres for Low-Loss Transmission of Millimetre Waves and its Application in Couplers and Splitters,” J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves, vol. 31, Sep. 2010, pp. 214–220.
B. Scherger, M. Scheller, C. Jansen, M. Koch, and K. Wiesauer, “Terahertz lenses made by compression molding of micropowders.,” Appl.Opt., vol. 50, May. 2011, pp. 2256–62.
H. Nĕmec, P. Kuzel, L. Duvillaret, A. Pashkin, M. Dressel, and M.T. Sebastian, “Highly tunable photonic crystal filter for the terahertz range.,” Opt. Lett., vol. 30, Mar. 2005, pp. 549–51.
T. Kleine-Ostmann, K. Pierz, G. Hein, P. Dawson, and M. Koch, “Audio Signal Transmission over THz Communication Channel using Semiconductor Modulator,” Electron. Lett., vol. 40, 2004, p. 124.
R. Kersting, G. Strasser, and K. Unterrainer, “Terahertz Phase Modulator,” Electron. Lett., vol. 36, 2000, pp. 1156–1158.
T.T. Tan, R.P. Pan, Y.C. Wang, and P.C. L, “THz Time-Domain Spectroscopic Studies of a Ferroelectric Liquid Crystal in the SmA* and SmC* Phases,” Ferroelectrics, vol. 1, 2008, pp. 72–77.
M. Oh-e, H. Yokoyama, M. Koeberg, E. Hendry, and M. Bonn, “High-Frequency Dielectric Relaxation of Liquid Crystals : THz Time-Domain Spectroscopy of Liquid Crystal Colloids,” Opt. Express, vol. 14, 2006, pp. 11433–11440.
C.S. Yang, C.J. Lin, R.P. Pan, C.T. Que, K. Yamamoto, M. Tani, and C.L. Pan, “The Complex Refractive Indices of the Liquid Crystal Mixture E7 in the Terahertz Frequency Range,” J. Opt. Soc. Am. B, vol. 27, 2010, pp. 1866–1873.
N. Vieweg, M.K. Shakfa, B. Scherger, M. Mikulics, and M. Koch, “THz Properties of Nematic Liquid Crystals,” J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves, vol. 31, 2010, pp. 1312–1320.
N. Vieweg and M. Koch, “Terahertz Properties of Liquid Crystals with Negative Dielectric Anisotropy,” Appl. Opt., vol. 49, Oct. 2010, pp. 5764–5767.
N. Vieweg, M.K. Shakfa, and M. Koch, “BL037: A Nematic Mixture with High Terahertz Birefringence,” Opt. Commun., vol. 284, 2011, pp. 1887–1889.
N. Vieweg, C. Jansen, M.K. Shakfa, M. Scheller, N. Krumbholz, R. Wilk, M. Mikulics, and M. Koch, “Molecular Properties of Liquid Crystals in the Terahertz Frequency Range.,” Opt. Express, vol. 18, Mar. 2010, pp. 6097–107.
T.R. Tsai, C.Y. Chen, R.P. Pan, C.L. Pan, and X.C. Zhang, “Electrically Controlled Room Temperature Terahertz Phase Shifter with Liquid Crystal,” IEEE Microwave Wireless Comp. Lett., vol. 14, 2004, pp. 77–79.
C.Y. Chen, T.R. Tsai, C.L. Pan, and R.P. Pan, “Room Temperature Terahertz Phase Shifter based on Magnetically Controlled Birefringence in Liquid Crystals,” Appl. Phys. Lett., vol. 83, 2003, pp. 4497–4499.
C.F. Hsieh, Y.C. Lai, R.P. Pan, and C.L. Pan, “Polarizing Terahertz Waves with Nematic Liquid Crystals,” Opt. Lett., vol. 33, 2008, pp. 1174–1176.
R. Wilk, N. Vieweg, O. Kopschinski, and M. Koch, “Liquid Crystal Based Electrically Switchable Bragg Structure for THz Waves,” Opt. Express, vol. 17, Apr. 2009, pp. 7377–7382.
Z. Ghattan, T. Hasek, R. Wilk, M. Shahabadi, and M. Koch, “Sub-Terahertz On – Off Switch based on a Two-Dimensional Photonic Crystal Infiltrated by Liquid Crystals,” Opt. Comm., vol. 281, 2008, pp. 4623–4625.
I.C. Khoo, D.H. Werner, X. Liang, and A. Diaz, “Nanosphere Dispersed Liquid Crystals for Tunable Negative – Zero – Positive Index of Refraction in the Optical and Terahertz Regimes,” Opt. Lett., vol. 31, 2006, pp. 2592–2594.
C.Y. Chen, C.L. Pan, C.F. Hsieh, Y.F. Lin, and R.P. Pan, “Liquid-Crystal-Based Terahertz Tunable Lyot Filter,” Appl. Phys. Lett, vol. 88, 2006, p. 101107.
S.A. Jewell, E. Hendry, and J.R. Sambles, “Resonant Absorption of THz Radiation Using Nematic Liquid Crystals,” Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst., vol. 494, 2008, pp. 320–327.
S. a Jewell, E. Hendry, T.H. Isaac, and J.R. Sambles, “Tuneable Fabry–Perot etalon for terahertz radiation,” New Journal of Physics, vol. 10, Mar. 2008, p. 033012.
Acknowledgement
Nico Vieweg thanks the Studienstiftung des deutschen Volkes and the Braunschweig international graduate school of metrology for funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vieweg, N., Born, N., Al-Naib, I. et al. Electrically Tunable Terahertz Notch Filters. J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves 33, 327–332 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-012-9877-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-012-9877-y