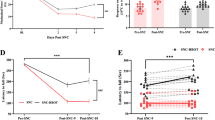
Abstract
Neuropathic pain (NP) is characterized by persistent pain, tactile allodynia, or hyperalgesia. Peripheral nerve injury contributes to rapid progress of inflammatory response and simultaneously generates neuropathic pain. Hydrogen (H2) has anti-inflammation, anti-apoptosis, and anti-oxidative stress effects. Therefore, we hypothesized that H2 treatment could alleviate allodynic and hyperalgesic behaviors and the release of inflammatory factors in rats with neuropathic pain. Peripheral neuropathic pain was established by chronic constriction injury of sciatic nerve in rats. H2 was given twice through intraperitoneal injection at a daily dose of 10 mL/kg during days 1–7 after the operation. Hyperalgesia and allodynia were tested, pro-inflammatory factors of dorsal root ganglia (DRG) and the spinal cord were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) during days 1–14 after the operation, and heme oxygenase (HO)-1 messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein expression and activities were measured at day 14 after sciatic nerve injury in rats. After Sn (IV) protoporphyrin IX dihydrochloride (SnPP)-IX, hemin, and carbon monoxide-releasing molecule (CORM)-2 had been given for chronic constriction injury (CCI) in rats, the above indicators were assessed. We found that H2 clearly inhibited hyperalgesia and allodynia in neuropathic pain and also attenuated the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, and high-mobility group box (HMGB) 1. H2 improved HO-1 mRNA and protein expression and activities in the process of pain. SnPP-IX reversed the inhibitory effect of H2 on hyperalgesia and allodynia and on pro-inflammatory cytokines in DRG and the spinal cord. The antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of H2 were involved in the activation of HO-1/CO signaling during neuropathic pain in rats.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Da, S.K., A.F. Paszcuk, G.F. Passos, E.S. Silva, A.F. Bento, and F.C. Meotti. 2011. Activation of cannabinoid receptors by the pentacyclic triterpene alpha, beta-amyrin inhibits inflammatory and neuropathic persistent pain in mice. Pain 152: 1872–87.
Lavertu, G., S.L. Cote, and Y. de Koninck. 2014. Enhancing K-Cl co-transport restores normal spinothalamic sensory coding in a neuropathic pain model. Brain 137: 724–38.
Bijjem, K.R., S.S. Padi, and S.P. Lal. 2013. Pharmacological activation of heme oxygenase (HO)-1/carbon monoxide pathway prevents the development of peripheral neuropathic pain in Wistar rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Archives of Pharmacology 386: 79–90.
Nadeau, S., M. Filali, J. Zhang, B.J. Kerr, S. Rivest, D. Soulet, Y. Iwakura, J.P. de Rivero Vaccari, R.W. Keane, and S. Lacroix. 2011. Functional recovery after peripheral nerve injury is dependent on the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1beta and TNF: implications for neuropathic pain. Journal of Neuroscience 31: 12533–42.
Watkins, L.R., M.R. Hutchinson, E.D. Milligan, and S.F. Maier. 2007. “Listening” and “talking” to neurons: implications of immune activation for pain control and increasing the efficacy of opioids. Brain Research Reviews 56: 148–69.
Verri, W.J., T.M. Cunha, C.A. Parada, S. Poole, F.Q. Cunha, and S.H. Ferreira. 2006. Hypernociceptive role of cytokines and chemokines: targets for analgesic drug development? Pharmacology and Therapeutics 112: 116–38.
Scholz, J., and C.J. Woolf. 2007. The neuropathic pain triad: neurons, immune cells and glia. Nature Neuroscience 10: 1361–8.
Vale, M.L., J.B. Marques, C.A. Moreira, F.A. Rocha, S.H. Ferreira, S. Poole, F.Q. Cunha, and R.A. Ribeiro. 2003. Antinociceptive effects of interleukin-4, -10, and -13 on the writhing response in mice and zymosan-induced knee joint incapacitation in rats. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 304: 102–8.
Fan, W., F. Huang, Z. Wu, X. Zhu, D. Li, and H. He. 2011. Carbon monoxide: a gas that modulates nociception. Journal of Neuroscience Research 89: 802–7.
Rosa, A.O., J. Egea, S. Lorrio, A.I. Rojo, A. Cuadrado, and M.G. Lopez. 2008. Nrf2-mediated haeme oxygenase-1 up-regulation induced by cobalt protoporphyrin has antinociceptive effects against inflammatory pain in the formalin test in mice. Pain 137: 332–9.
Egea, J., A.O. Rosa, S. Lorrio, B.L. Del, A. Cuadrado, and M.G. Lopez. 2009. Haeme oxygenase-1 overexpression via nAChRs and the transcription factor Nrf2 has antinociceptive effects in the formalin test. Pain 146: 75–83.
Maicas, N., M.L. Ferrándiz, I. Devesa, R. Motterlini, M.I. Koenders, W.B. van den Berg, and M.J. Alcaraz. 2010. The CO-releasing molecule CORM-3 protects against articular degradation in the K/BxN serum transfer arthritis model. European Journal of Pharmacology 634: 184–91.
Chen, H.G., K.L. Xie, H.Z. Han, W.N. Wang, D.Q. Liu, G.L. Wang, and Y.H. Yu. 2013. Heme oxygenase-1 mediates the anti-inflammatory effect of molecular hydrogen in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. International Journal of Surgery 11: 1060–6.
Ohsawa, I., M. Ishikawa, K. Takahashi, M. Watanabe, K. Nishimaki, K. Yamagata, K. Katsura, Y. Katayama, S. Asoh, and S. Ohta. 2007. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nature Medicine 13: 688–94.
Xie, K., W. Fu, W. Xing, A. Li, H. Chen, H. Han, Y. Yu, and G. Wang. 2012. Combination therapy with molecular hydrogen and hyperoxia in a murine model of polymicrobial sepsis. Shock 38: 656–63.
Xie, K., Y. Yu, Y. Pei, L. Hou, S. Chen, L. Xiong, and G. Wang. 2010. Protective effects of hydrogen gas on murine polymicrobial sepsis via reducing oxidative stress and HMGB1 release. Shock 34: 90–7.
Xie, K., Y. Yu, Z. Zhang, W. Liu, Y. Pei, L. Xiong, L. Hou, and G. Wang. 2010. Hydrogen gas improves survival rate and organ damage in zymosan-induced generalized inflammation model. Shock 34: 495–501.
Chen, Q., P. Chen, S. Zhou, X. Yan, J. Zhang, X. Sun, H. Yuan, and W. Yu. 2013. Hydrogen-rich saline attenuated neuropathic pain by reducing oxidative stress. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences 40: 857–63.
Bao, Y.H., Q.H. Zhou, R. Chen, H. Xu, L.L. Zeng, X. Zhang, W. Jiang, and D.P. Du. 2014. Gabapentin enhances the morphine anti-nociceptive effect in neuropathic pain via the interleukin-10-heme oxygenase-1 signalling pathway in rats. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience 54: 137–46.
Bennett, G.J., and Y.K. Xie. 1998. A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 33: 87–107.
Hayashida, K., M. Sano, I. Ohsawa, K. Shinmura, K. Tamaki, K. Kimura, J. Endo, T. Katayama, A. Kawamura, S. Kohsaka, S. Makino, S. Ohta, S. Ogawa, and K. Fukuda. 2008. Inhalation of hydrogen gas reduces infarct size in the rat model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 373: 30–5.
Chaplan, S.R., F.W. Bach, J.W. Pogrel, J.M. Chung, and T.L. Yaksh. 1994. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 53: 55–63.
Bianchi, M., P. Sacerdote, P. Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P. Mantegazza, and A.E. Panerai. 1992. Central effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 alpha on nociceptive thresholds and spontaneous locomotor activity. Neuroscience Letters 148: 76–80.
Andersson, U., and K.J. Tracey. 2011. HMGB1 is a therapeutic target for sterile inflammation and infection. Annual Review of Immunology 29: 139–62.
Hervera, A., S. Leanez, R. Motterlini, and O. Pol. 2013. Treatment with carbon monoxide-releasing molecules and an HO-1 inducer enhances the effects and expression of micro-opioid receptors during neuropathic pain. Anesthesiology 118: 1180–97.
Su, L., C. Wang, Y.H. Yu, Y.Y. Ren, K.L. Xie, and G.L. Wang. 2011. Role of TRPM8 in dorsal root ganglion in nerve injury-induced chronic pain. BMC Neuroscience 12: 120.
Kawaguchi, M., Y. Satoh, Y. Otsubo, and T. Kazama. 2014. Molecular hydrogen attenuates neuropathic pain in mice. PLoS One 9: e100352.
Khalil, Z., T. Liu, and R.D. Helme. 1999. Free radicals contribute to the reduction in peripheral vascular responses and the maintenance of thermal hyperalgesia in rats with chronic constriction injury. Pain 79: 31–7.
Zhang, F., X. Feng, R. Dong, H. Wang, J. Liu, W. Li, J. Xu, and B. Yu. 2011. Effects of clonidine on bilateral pain behaviors and inflammatory response in rats under the state of neuropathic pain. Neuroscience Letters 505: 254–9.
DeLeo, J.A., and R.P. Yezierski. 2001. The role of neuroinflammation and neuroimmune activation in persistent pain. Pain 90: 1–6.
Grace, P.M., P.E. Rolan, and M.R. Hutchinson. 2011. Peripheral immune contributions to the maintenance of central glial activation underlying neuropathic pain. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity 25: 1322–32.
Sacerdote, P., S. Franchi, S. Moretti, M. Castelli, P. Procacci, V. Magnaghi, and A.E. Panerai. 2013. Cytokine modulation is necessary for efficacious treatment of experimental neuropathic pain. Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology 8: 202–11.
Sacerdote, P., S. Franchi, A.E. Trovato, A.E. Valsecchi, A.E. Panerai, and M. Colleoni. 2008. Transient early expression of TNF-alpha in sciatic nerve and dorsal root ganglia in a mouse model of painful peripheral neuropathy. Neuroscience Letters 436: 210–3.
Muthuraman, A., and N. Singh. 2012. Neuroprotective effect of saponin rich extract of Acorus calamus L. in rat model of chronic constriction injury (CCI) of sciatic nerve-induced neuropathic pain. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 142: 723–31.
Jaggi, A.S., and N. Singh. 2010. Differential effect of spironolactone in chronic constriction injury and vincristine-induced neuropathic pain in rats. European Journal of Pharmacology 648: 102–9.
Kukkar, A., N. Singh, and A.S. Jaggi. 2013. Neuropathic pain-attenuating potential of aliskiren in chronic constriction injury model in rats. Journal of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System 14: 116–23.
Kawasaki, Y., Z.Z. Xu, X. Wang, J.Y. Park, Z.Y. Zhuang, P.H. Tan, Y.J. Gao, K. Roy, G. Corfas, E.H. Lo, and R.R. Ji. 2008. Distinct roles of matrix metalloproteases in the early- and late-phase development of neuropathic pain. Nature Medicine 14: 331–6.
Uceyler, N., A. Tscharke, and C. Sommer. 2007. Early cytokine expression in mouse sciatic nerve after chronic constriction nerve injury depends on calpain. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity 21: 553–60.
Perrin, F.E., S. Lacroix, M. Aviles-Trigueros, and S. David. 2005. Involvement of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, macrophage inflammatory protein-1alpha and interleukin-1beta in Wallerian degeneration. Brain 128: 854–66.
Ruohonen, S., M. Khademi, M. Jagodic, H.S. Taskinen, T. Olsson, and M. Roytta. 2005. Cytokine responses during chronic denervation. Journal of Neuroinflammation 2: 26.
Kawasaki, Y., L. Zhang, J.K. Cheng, and R.R. Ji. 2008. Cytokine mechanisms of central sensitization: distinct and overlapping role of interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in regulating synaptic and neuronal activity in the superficial spinal cord. Journal of Neuroscience 28: 5189–94.
Zhang, R.X., A. Li, B. Liu, L. Wang, K. Ren, H. Zhang, B.M. Berman, and L. Lao. 2008. IL-1ra alleviates inflammatory hyperalgesia through preventing phosphorylation of NMDA receptor NR-1 subunit in rats. Pain 135: 232–239.
Milligan, E.D., C. Twining, M. Chacur, J. Biedenkapp, K. O’Connor, S. Poole, K. Tracey, D. Martin, S.F. Maier, and L.R. Watkins. 2003. Spinal glia and proinflammatory cytokines mediate mirror-image neuropathic pain in rats. Journal of Neuroscience 23: 1026–40.
Shibasaki, M., M. Sasaki, M. Miura, K. Mizukoshi, H. Ueno, S. Hashimoto, Y. Tanaka, and F. Amaya. 2010. Induction of high mobility group box-1 in dorsal root ganglion contributes to pain hypersensitivity after peripheral nerve injury. Pain 149: 514–21.
Tong, W., W. Wang, J. Huang, N. Ren, S.X. Wu, and Y.Q. Li. 2010. Spinal high-mobility group box 1 contributes to mechanical allodynia in a rat model of bone cancer pain. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 395: 572–6.
Lawrence, S., L. Willmott, E. Milligan, S. Winch, B. White, and M. Parker. 2012. Autonomy versus futility? Barriers to good clinical practice in end-of-life care: a Queensland case. Medical Journal of Australia 196: 404–5.
Steiner, A.A., L.G. Branco, F.Q. Cunha, and S.H. Ferreira. 2001. Role of the haeme oxygenase/carbon monoxide pathway in mechanical nociceptor hypersensitivity. British Journal of Pharmacology 132: 1673–82.
Motterlini, R., J.E. Clark, R. Foresti, P. Sarathchandra, B.E. Mann, and C.J. Green. 2002. Carbon monoxide-releasing molecules: characterization of biochemical and vascular activities. Circulation Research 90: E17–E24.
Guillen, M.I., J. Megias, V. Clerigues, F. Gomar, and M.J. Alcaraz. 2008. The CO-releasing molecule CORM-2 is a novel regulator of the inflammatory process in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47: 1323–8.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81372033 to Yonghao Yu; 81101409 and 81471842 to KeliangXie) and the Natural Science Foundation of the Tianjin Science Committee (Nos. 13JCQNJC11400 to KeliangXie).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yajun Chen, Hongguang Chen and Keliang Xie contributed equally to this work.
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(JPEG 6631 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Chen, H., Xie, K. et al. H2Treatment Attenuated Pain Behavior and Cytokine Release Through the HO-1/CO Pathway in a Rat Model of Neuropathic Pain. Inflammation 38, 1835–1846 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0161-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0161-x