Abstract
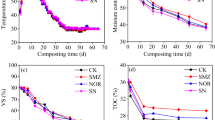
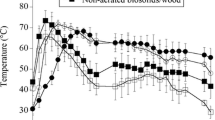
In this study, the effects of dietary inclusion of antibiotics on emissions of greenhouse gases (GHG: CO2, CH4 and N2O) from cattle manure during composting were investigated. Manure was collected at the end of two feeding trials in 2005 and 2006 in which feedlot cattle were assigned to one of five dietary groups: (1) Control: no antibiotics added; (2) TYL11: tylosin at 11 mg kg−1 feed; (3) CTC11: chlortetracycline at 11 mg kg−1 feed; (4) CTC44: chlortetracycline at 44 mg kg−1 feed; and CTC44SMZ44: chlortetracycline and sulfamethazine, each at 44 mg kg−1 feed. Open windrows were constructed and the rate of GHG emission was measured periodically. In both years, CO2 surface emissions were higher (P < 0.05) for treatments CTC11 and CTC44SMZ44 than for the Control. The CO2 emission rates in 2005 were lower (P < 0.05) than in 2006, reflecting lower total carbon (TC) content in the manure in 2005 (138 ± 2 g kg−1) than in 2006 (245 ± 2 g kg−1). The rate of CH4 emission varied from 0.006 to 0.232 g C m−2 day−1. Average values from all four antibiotic treatments were similar (P > 0.05) to the Control in both years. The N2O emission rates were higher (P > 0.05) with CTC44SMZ44 (2005), TYL11 (2006) and CTC11 (2006) than with Control. While antibiotics do alter GHG emissions from composted feedlot manure, the mechanisms responsible are not clear and warrant further investigation.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CTC:
-
Chlortetracycline
- GHG:
-
Greenhouse gases
- SMZ:
-
Sulfamethazine
- TYL:
-
Tylosin
References
Arikan OA, Sikora LJ, Mulbry W, Khan SU, Rice C, Foster GD (2006) The fate and effect of oxytetracycline during the anaerobic digestion of manure from therapeutically treated calves. Process Biochem 41:1637–1643
Arikan OA, Sikora LJ, Mulbry W, Khan SU, Foster GD (2007) Composting rapidly reduces levels of extractable oxytetracycline in manure from therapeutically treated beef calves. Bioresour Technol 98:169–176
Arikan OA, Mulbry W, Ingram D, Millner P (2009a) Minimally managed composting of beef manure at the pilot scale: effect of manure pile construction on pile temperature profiles and on the fate of oxytetracycline and chlortetracycline. Bioresour Technol 100:4447–4453
Arikan OA, Mulbry W, Rice C (2009b) Management of antibiotic residues from agricultural sources: use of composting to reduce chlortetracycline residues in beef manure from treated animals. J Hazard Mater 164:483–489
Boxall ABA, Blackwell P, Cavallo R, Kay P, Tolls J (2002) The sorption and transport of a sulphonamide antibiotics in soil systems. Toxicol Lett 131:19–28
Cessna AJ, Larney FJ, Kuchta SL, Hao X, Entz T, Topp E, McAllister TA (2010) Veterinary antimicrobials in feedlot manure: dissipation during composting and effects on composting processes. J Environ Qual (submitted)
Chelliapan S, Wilby T, Sallis PJ (2006) Performance of an up-flow anaerobic stage reactor (UASA) in the treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater containing macrolide antibiotics. Water Res 40:506–516
Davis JG, Truman CC, Kim SC, Ascough JC, Carlson K (2006) Antibiotic transport via runoff and soil loss. J Environ Qual 35:2250–2260
Dolliver H, Gupta S, Noll S (2008) Antibiotic degradation during manure composting. J Environ Qual 37:1245–1253
Elmund K, Morrison SM, Grant DW (1971) Role of excreted chlortetracycline in modifying the decomposition process in feedlot water. Bull Ecol Contam Toxicol 6:129–132
Hao X, Chang C, Larney FJ, Travis GR (2001) Greenhouse gas emissions during cattle feedlot manure composting. J Environ Qual 30:376–386
Hao X, Chang C, Larney FJ (2004) Carbon, nitrogen balances, and greenhouse gas emission during cattle feedlot manure composting. J Environ Qual 33:37–44
Hutchinson GL, Mosier AR (1981) Improved soil cover method for field measurement of nitrous oxide fluxes. Soil Sci Soc Am J 45:311–316
Kay P, Blackwell PA, Boxall ABA (2004) Fate of veterinary antibiotics in a macroporous tile drained soil. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:1136–1144
Kemper N (2008) Veterinary antibiotics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment. Ecol Indic 8:1–13
Kotzerke A, Sharma S, Schauss K, Heuer H, Thiele-Bruhn S, Smalla K, Wilke B-M, Schloter M (2008) Alterations in soil microbial activity and N-transformation processes due to sulfadiazine loads in pig-manure. Environ Pollut 153:315–322
Kuchta SL, Cessna AJ, Elliott JA, Peru KM, Headley JV (2009) Transport of lincomycin to surface and ground water from manure-amended cropland. J Environ Qual 38:1719–1727
Kumar K, Gupta SC, Chander Y, Singh AK (2005) Antibiotic use in agriculture and its impact on the terrestrial environment. Adv Agron 87:1–54
Lallai A, Mura G, Onnis N (2002) The effects of certain antibiotics on biogas production in the anaerobic digestion of pig waste slurry. Bioresour Technol 82:205–208
Larney FJ, Hao X (2007) Composting as a management alternative for beef feedlot manure in southern Alberta, Canada. Bioresour Technol 98:3221–3227
Liu F, Ying G-G, Tao R, Zhao J-L, Yang J-F, Zhao L-F (2009) Effects of six selected antibiotics on plant growth and soil microbial and enzymatic activities. Environ Pollut 157:1636–1642
Marounek M, Suchorska O, Savka O (1999) Effect of substrate and feed antibiotics on in vitro productions of volatile fatty acids and methane in caecal contents of chickens. Anim Feed Sci Technol 80:223–230
Martínez-Carballo E, González-Barreiro C, Scharf S, Gans O (2007) Environmental monitoring study of selected veterinary antibiotics in animal manure and soils in Austria. Environ Pollut 148:570–579
Massé DI, Lu D, Masse L, Droste RL (2000) Effect of antibiotics on psychrophilic anaerobic digestion of swine manure slurry in sequencing batch reactors. Bioresour Technol 75:205–211
Sarmah AK, Meyer MT, Boxall ABA (2006) A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere 65:725–759
SAS Institute (2005) SAS OnlineDoc® 9.1.3. Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc
Schauss K, Focks A, Leininger S, Kotzerke A, Heuer H, Thiele-Bruhn S, Sharma S, Wilke B-M, Matthies M, Smalla K, Munch JC, Amelung W, Kaupenjohann M, Schloter M, Schleper C (2009) Dynamics and functional relevance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in two agricultural soils. Environ Microbiol 11:446–456
Sponza DT, Demirden P (2007) Treatability of sulfamerazine in sequential upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor (UASB)/completely stirred tank reactor (CSTR) processes. Separ Purif Technol 56:108–117
Stone JJ, Clay SA, Zhu Z, Wong KL, Porath LR, Spellman GM (2009) Effect of antimicrobial compounds tylosin and chlortetracycline during batch anaerobic swine manure digestion. Water Res 43:4740–4750
Warman PR (1980) The effect of Amprolium and Aureomycin on the nitrification of poultry manure-amended soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44:1333–1334
Warman PR, Thomas RL (1981) Chlortetracycline in soil amended with poultry manure. Can J Soil Sci 61:161–163
Zielezny Y, Groeneweg J, Vereecken H, Tappe W (2006) Impact of sulfadiazine and chlorotetracycline on soil bacterial community structure and respiratory activity. Soil Biol Biochem 38:2372–2380
Acknowledgments
This project was funded by Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada (AAFC) and the AAFC Environmental Technology Assessment for Agriculture (ETAA) program. Technical assistance was provided by G. Travis, B. Hill, P. Caffyn, J. Hoffman, A. Olson, P. DeMaere and W. Smart. This is Lethbridge Research Centre contribution number 38710013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, X., Xu, S., Larney, F.J. et al. Inclusion of antibiotics in feed alters greenhouse gas emissions from feedlot manure during composting. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 89, 257–267 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-010-9391-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-010-9391-3