Abstract
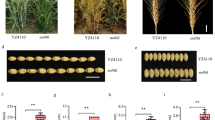
Oryza longistaminata (AA genome) is a wild rice species that is phenotypically inferior to cultivated rice but possesses useful alleles that can be used to improve agronomically important traits. Interspecific hybrids that are derived from cultivated rice and wild rice species with AA genome are important contributors of genetic diversity in rice. To illustrate the potential of wild rice relatives as a source of novel alleles for rice improvement, a total of 40 chromosome segment substitution lines (CSSLs) of O. longistaminata in the background of the elite japonica cultivar Taichung 65 were developed and evaluated for yield and various yield-related traits. A number of CSSLs carrying putative quantitative trait loci (QTLs) controlling different yield-related traits were identified during both dry and wet seasons. In particular, 10 major putative QTLs controlling early heading date, plant height, tiller number, panicle length, number of primary branches per panicle, grain number per panicle, grain width, and grain thickness were identified. Interestingly, one of the CSSL lines, LTSL26, with major putative QTLs on chromosomes 1 and 8 that increase grain number per panicle, showed pleiotropic effects on other traits such as plant height, days to flowering, tiller number, number of branches per panicle, and grain length. These results suggest that O. longistaminata is a good source of new alleles that can be used to improve yield-related traits in cultivated rice varieties.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali ML, Sanchez PL, Yu SB, Lorieux M, Eizenga GC (2010) Chromosome segment substitution lines: a powerful tool for the introgression of valuable genes from Oryza wild species into cultivated rice (O. sativa). Rice 3:218–234
Ando T, Yamamoto T, Shimizu T, Ma XF, Shomura A, Takeuchi Y, Lin SY, Yano M (2008) Genetic dissection and pyramiding of quantitative traits for panicle architecture by using chromosomal segment substitution lines in rice. Theor Appl Genet 116:881–890
Brar DS, Khush GS (1997) Alien introgression in rice. Plant Mol Biol 35:35–47
Brar DS, Khush GS (2002) Transferring of genes from wild species into rice. In: Kang MS (ed) Quantitative genetics, genomics and plant breeding. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 197–217
Brar DS, Khush GS (2003) Utilization of wild species in rice. In: Nanda JS, Sharma SD (eds) Monograph on genus Oryza. Science Pub. Inc., Enfield, pp 283–309
Brar DS, Khush GS (2006) Cytogenetic manipulation and germplasm enhancement of rice (Oryza sativa L.). In: Singh RJ, Jauhar PP (eds) Genetic resources, chromosome engineering and crop improvement. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 115–158
Brar DS, Singh K (2011) Oryza. In: Kole C (ed) Wild crop relatives: genomics and breeding resources: cereals. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 321–366
Chen Z, Hu F, Xu P, Li J, Deng X, Zhou J (2009) QTL analysis for hybrid sterility and plant height in interspecific populations derived from a wild rice relative, Oryza longistaminata. Breed Sci 59:441–445
Chu YE, Oka HI (1970) Introgression across isolating barriers in wild and cultivated Oryza species. Evolution 24:344–355
Doi K, Iwata N, Yosimura A (1997) The construction of chromosome substitution lines of African rice (Oryza glaberrima Steud.) in the background of Japonica rice (O. sativa L.). Rice Genet Newsl 14:39–41
Ebitani T, Takeuchi Y, Nonoue Y, Yamamoto T, Takeuchi K, Yano M (2005) Construction and evaluation of chromosome segment substitution lines carrying overlapping chromosome segments of indica rice cultivar “Kasalath” in a genetic background of japonica elite cultivar ‘Koshihikari’. Breed Sci 55:65–73
Furuta T, Uehara K, Angeles-Shim RB, Shim J, Ashikari M, Takashi T (2014) Development and evaluation of chromosome segment substitution lines (CSSLs) carrying chromosome segments derived from Oryza rufipogon in the genetic background of Oryza sativa L. Breed Sci 63:468–475
Gichuhi E, Himi E, Takahashi H, Maekawa M (2012) Oryza longistaminata’s chromosome segments are responsible for agronomically important traits for environmentally smart rice. In: Proceedings of the 2012 JKUAT scientific, technological and industrialization conference-science, technology and innovation for sustainable development. Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology, Nairobi, Kenya, pp 723–726
Gutierrez AG, Carabali SJ, Giraldo OX, Martinez CP, Correa F, Prado G, Tohme J, Lorieux M (2010) Identification of a Rice stripe necrosis virus resistance locus and yield component QTLs using Oryza sativa × O. glaberrima introgression lines. BMC Plant Biol 10(1):6
http://plants.ensembl.org/Oryza_longistaminata/Info/Annotation/. Accessed 29 Jan 2015
Jena KK (2010) The species of the genus Oryza and transfer of useful genes from wild species into cultivated rice, O. sativa. Breed Sci 60:518–523
Kanya JI, Hauser TP, Kinyamario JI, Amugune NO (2012) Hybridization potential between cultivated rice, Oryza sativa and African rice Oryza longistaminata. Int J Agric Res 7(6):291–302
Khush GS, Bacalangco E, Ogawa T (1990) A new gene for resistance to bacterial blight from O. longistaminata. Rice Genet Newsl 7:121–122
Kobayashi N, Ikeda R, Domingo IT, Vaughan DA (1993) Resistance to infection of rice tungro viruses and vector resistance in wild species of rice (Oryza spp.). Jpn J Breed 43:377–378
Kobayashi N, Ikeda R, Vaughan DA (1994) Screening wild species of rice (Oryza spp.) for resistance to rice tungro disease. JARQ-Jpn Agric Res Q 28(4):230–236
Li J, Xiao J, Grandillo S, Jiang L, Wan Y, Deng Q, Yuan L, McCouch SR (2004) QTL detection for rice grain quality traits using an interspecific backcross population derived from cultivated Asian rice (O. sativa L.) and African rice (O. glaberrima S.). Genome 47:697–704
Marathi B, Jena KK (2015) Floral traits to enhance outcrossing for higher hybrid seed production in rice: present status and future prospects. Euphytica 201:1–14
Marathi B, Ramos J, Hechanova SL, Oane RH, Jena KK (2015) SNP genotyping and characterization of pistil traits revealing a distinct phylogenetic relationship among the species of Oryza. Euphytica 201:131–148
McCouch SR, Sweeney M, Li J, Jiang H, Thomson M, Septiningsih E (2007) Through the genetic bottleneck: O. rufipogon as a source of trait-enhancing alleles for O. sativa. Euphytica 154:317–339
Moncada P, Martinez CP, Borrero J, Chatel M, Gauch H, Guimaraes E, Tohme J, McCouch SR (2001) Quantitative trait loci for yield and yield components in an Oryza sativa × Oryza rufipogon BC2F2 population evaluated in an upland environment. Theor Appl Genet 102:41–52
Neff MM, Neff JD, Chory J, Pepper AE (1998) dCAPs, a simple technique for the genetic analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms: experimental applications in Arabidopsis thaliana genetics. Plant J 14(3):387–392
Reintar RIS (2007) Molecular characterization of introgression from O. longistaminata A. Chev. et Roehr. into rice (Oryza sativa L.). Dissertation, University of the Philippines, Los Baños (UPLB)
Ronald PC, Albano B, Tabien R, Abenes L, Wu KS, McCouch SR, Tanksley SD (1992) Genetic and physical analysis of the rice bacterial blight disease resistance locus, Xa21. Mol Gen Genet 236(1):113–120
Sanchez PL, Sobrizal Ikeda K, Yasui H, Yoshimura A (2003) Identifying late heading genes in rice using Oryza glumaepatula introgression lines. In: Khush GS, Brar DS, Hardy B (eds) Advances in rice genetics, proceedings of the fourth international rice genetics symposium. International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, pp 153–154
Sanchez PL, Wing RA, Brar DS (2013) The wild relatives of rice: genomes and genomics. In: Zhang Q, Wing RA (eds) Genetics and genomics of rice, plant genetics and genomics: crops and models 5. Springer, New York, pp 9–25
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9:671–675
Septiningsih EM, Prasetyono J, Lubis E, Thai TH, Tjubaryat T, Moeljopawiro S, McCouch SR (2003) Identification of quantitative trait loci for yield and yield components in an advanced backcross population derived from the Oryza sativa variety IR64 and the wild relative O. rufipogon. Theor Appl Genet 107:1419–1432
Shan X, Lui Z, Dong Z, Wang Y, Chen Y, Lin X, Long L, Han F, Dong Y, Lui B (2005) Mobilization of the Active MITE transposons mPing and Pong in rice by introgression from wild rice (Zizania latifolia Griseb.). Mol Biol Evol 22:976–990
Shim RA, Angeles ER, Ashikari M, Takashi T (2010) Development and evaluation of Oryza glaberrima Steud. chromosome segment substitution lines (CSSLs) in the background of O. sativa L. cv. Koshihikari. Breed Sci 60:613–619
Shim RA, Vinarao R, Marathi B, Jena K (2014) Molecular analysis of Oryza latifolia Desv. (CCDD Genome)-derived introgression lines and identification of value-added traits for rice (O. sativa L.) improvement. J Hered 105(5):676–689
Soriano IR, Schmit V, Brar DS, Prot JC, Reversat G (1999) Resistance to rice knot nematode Meloidogyne graminicola identified in Oryza longistaminata and O. glaberrima. Nematology 1(4):395–398
Statistical Tools for Agricultural Research (STAR), version 1.0 (2013) Biometrics and Breeding Informatics, PBGB Division, International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines
Susanto U, Aswidinnoor H, Koswara J, Aetiawan A, Lopena V, Torrizo L, Virk PS (2008) QTL mapping of yield, yield components and morphological traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using SSR markers. Bull Agron 36(3):188–195
Swamy BPM, Sarla N (2008) Yield enhancing quantitative trait loci (QTLs) from wild species. Biotechnol Adv 26(1):106–120
Swamy BPM, Kaladhar K, Ramesha MS, Viraktamath VC, Sarla N (2011) Molecular mapping of QTLs for yield and related traits in Oryza sativa cv Swarna × O. nivara (IRGC 81848) backcross population. Rice Sci 18(3):178–186
Takai T, Nonoue Y, Yamamoto S, Yamanouchi U, Matsubara K, Liang Z, Lin H, Ono N, Uga Y, Yano M (2007) Development of chromosome segment substitution lines derived from backcross between indica donor rice cultivar ‘Nona Bokra” and japonica recipient cultivar ‘Koshihikari’. Breed Sci 57:257–261
Varma CMK, Gouda PK, Saikumar S, Shenoy V, Shashidhar HE, Neelamraju S (2012) Transgressive segregation for yield traits in Oryza sativa IR58025B × Oryza meridionalis Ng. BC2F3 population under irrigated and aerobic conditions. J Crop Sci Biotechnol 15(3):231–238
Wang YM, Dong ZY, Zhang ZJ, Lin XY, Shen Y, Zhou D, Lui B (2005) Extensive de novo genomic variation in rice induced by introgression from wild rice (Zizania latifolia Griseb.). Genetics 170:1945–1956
Xiao J, Li J, Grandillo S, Ahn SN, Yuan L, Tanksley S, McCouch SR (1998) Identification of trait-improving quantitative trait loci alleles from wild rice relative, O. rufipogon. Genetics 150:899–909
Yang H, Hu L, Hurek T, Reinhold-Hurek B (2010) Global characterization of the root transcriptome of a wild species of rice, Oryza longistaminata, by deep sequencing. BMC Genom 11:705–712
Zhang F, Li T, Shan Q, Guo Y, Xu P, Hui F, Tao D (2008) Weed suppression ability of Oryza longistaminata and Oryza sativa. Allelopathy J 22(2):345–352
Zhang H, Zhao Q, Sun ZZ, Zhang CQ, Feng Q, Tang SZ, Liang GH, Gu MH, Han B, Liu QQ (2011) Development and high-throughput genotyping of substitution lines carrying the chromosome segments of indica 93-11 in the background of japonica Nipponbare. J Genet Genom 38(12):603–611
Zhao J, Li J, Xu P, Zhou J, Hu F, Deng X, Deng W, Tao D (2012) A new gene controlling hybrid sterility between Oryza sativa and Oryza longistaminata. Euphytica 187:339–344
Acknowledgments
Our sincere thanks go to the members of the Novel Gene Resources Laboratory (previously Wide Hybridization Laboratory), particularly to Mr. Eleazar “Boyet” Manalaysay, who helped in the production of LTSLs and in the evaluation of the materials. This research is supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Ronpaku Program in collaboration with the International Rice Research Institute, Philippines; Nagoya University, Japan, and the Science and Technology Research Program for Agriculture, Forestry, Fisheries and Food Industry; and is partially supported by JST, CREST.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramos, J.M., Furuta, T., Uehara, K. et al. Development of chromosome segment substitution lines (CSSLs) of Oryza longistaminata A. Chev. & Röhr in the background of the elite japonica rice cultivar, Taichung 65 and their evaluation for yield traits. Euphytica 210, 151–163 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-016-1685-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-016-1685-3