Abstract
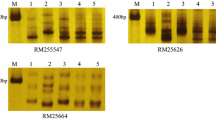
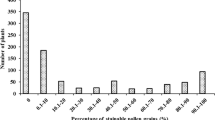
The genetic relationship among three cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS) systems, consisting of WA, Dissi, and Gambiaca, was studied. The results showed that the maintainers of one CMS system can also maintain sterility in other cytoplasmic backgrounds. The F1 plants derived from crosses involving A and R lines of the respective cytoplasm and their cross-combination with other CMS systems showed similar pollen and spikelet fertility values, indicating that similar biological processes govern fertility restoration in these three CMS systems. The results from an inheritance study showed that the pollen fertility restoration in all three CMS systems was governed by two independent and dominant genes with classical duplicate gene action. Three F2 populations, generated from the crosses between the parents of good-performing rice hybrids, that possess WA, Dissi, and Gambiaca CMS cytoplasm, were used to map the Rf genes. For the WA-CMS system, Rf3 was located at a distance of 2.8 cM from RM490 on chromosome 1 and Rf4 was located at 1.6 cM from RM1108 on chromosome 10. For the Dissi-CMS system, Rf3 was located on chromosome 1 at 1.9 cM from RM7466 and Rf4 on chromosome 10 was located at 2.3 cM from RM6100. The effect of Rf3 on pollen fertility appeared to be stronger than the effect of Rf4. In the Gambiaca-CMS system, only one major locus was mapped on chromosome 1 at 2.1 cM from RM576. These studies have led to the development of marker-assisted selection (MAS) for selecting putative restorer lines, new approaches to alloplasmic line breeding, and the transfer of Rf genes into adapted cultivars through a backcrossing program in an active hybrid rice breeding program.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi H, Nakamura A, Yokozeki-Misono Y, Inagaki A, Takahashi H, Mori K, Fujimura T (2004) Positional cloning of the rice Rf-1 gene, a restorer of BT-type cytoplasmic male sterility that encodes a mitochondria targeting PPR protein. Theor Appl Genet 108:1449–1457
Bentolila S, Alfonso AA, Hanson MR (2002) A pentatricopeptide repeat-containing gene restores fertility to cytoplasmic male sterile plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:10887–10892
Bharaj TS, Bains SS, Sidhu GS, Gagneja MR (1991) Genetics of fertility restoration of ‘wild abortive’ cytoplasmic male sterility in rice, Oryza sativa L. Euphytica 56:199–203
Bharaj TS, Virmani SS, Khush GS (1995) Chromosomal location of fertility restoring genes for ‘wild abortive’ cytoplasmic male sterility using primary trisomics in rice. Euphytica 83:169–173
Bi X, De Palma J, Oane R, Khush GS, Bennett J (2003) Molecular approaches for fixing the heterozygosity of hybrid rice. In: Virmani SS, Mao CX, Hardy B (eds) Hybrid rice for food security, poverty alleviation, and environmental protection. Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Hybrid Rice, Hanoi, Vietnam, 14–17 May 2002. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines, pp 135–150
Brown G, Formanova N, Jin H, Wargachuk R, Dendy C, Patil P, Laforest M, Cheung WY, Landry BS (2003) The radish Rfo restorer gene of Ogura cytoplasmic male sterility encodes a protein with multiple pentatricopeptide repeats. Plant J 35:262–272
Chase C, Babay-Laughnan S (2004) Cytoplasmic male sterility and fertility restoration by nuclear genes. In: Daniell H, Chase C (eds) Molecular biology and biotechnology of plant organelles. Kluwer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 593–622
Chaudhary RC, Virmani SS, Khush GS (1981) Pattern of pollen abortion in some cytoplasmic male sterile lines of rice (O. sativa L.). Oryza 18:140–142
Cui X, Wise RP, Schnable PS (1996) The rf2 nuclear restorer gene of male-sterile T-cytoplasm maize. Science 272:1334–1336
Govinda Raj K, Virmani SS (1988) Genetics of fertility restoration of ‘WA’ type cytoplasmic male sterility in rice. Crop Sci 28:787–792
Hanson MR, Bentolila S (2004) Interactions of mitochondrial and nuclear genes that affect male gametophytic development. Plant Cell 16:S154–S169
Huang QY, He QY, Jing RC, Zhu RS, Zhu YG (2000) Mapping of the nuclear fertility restorer gene for HL cytoplasmic male sterility in rice using microsatellite markers. Chin Sci Bull 45(5):430–432
Ichikawa N, Kishimoto N, Inagaki A, Nakamura A, Koshino Y, Yokozecki Y, Oka HI, Samoto S, Akagi H, Higo K, Shinjyo C, Fujimura T, Shimada H (1997) A rapid PCR-based selection of a rice line containing the Rf-1 gene, which is involved in restoration of the cytoplasmic male sterility. Mol Breed 3:195–202
Ikehashi H (1991) Genetics of hybrid sterility in wide hybridization in rice (O. sativa L.). In: Bajaj YPS (ed) Biotechnology in agriculture and forestry. 14. Rice. Springer, Berlin, pp 113–127
IRRI (1986) Annual report for 1985. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines
Jing R, Li X, Yi P, Zhu Y (2001) Mapping fertility restoring genes of rice WA cytopasmic male sterility using SSLP markers. Bot Bull Acad Sin 42:167–171
Komori T, Yamamoto T, Takemori N, Kashihara M, Matsushima H, Nitta N (2003) Fine genetic mapping of the nuclear gene, Rf-1, that restores the BT-type cytoplasmic male sterility in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by PCR-based markers. Euphytica 129:241–247
Komori T, Ohta S, Murai N, Takakura Y, Kuraya Y, Suzuki S, Hiei Y, Imaeki H, Nitta N (2004) Map-based cloning of a fertility restorer gene, Rf-1, in rice (Oryza sativa L). Plant J 37:315–325
Lander ES, Green P, Daly MY, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural population. Genomics 1:174–181
Li YC, Yuan LP (1986) IRRI (ed) Genetic analysis of fertility restoration in male sterile lines of rice. In: Rice genetics. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines, pp 617–632
Li ZB, Zhu YG (1988) Rice male sterile cytoplasm and fertility restoration. In: Smith WH, Bostian LR, Cervantes E (eds) Hybrid rice. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines, pp 85–102
Li Z, Shao WH, Zhu YK, Li RJ, Liu ZL, Wan JM (1982) The study and practice of hybrid rice. Shanghai Press, Shanghai, China
Lin SC, Yuan LP (1980) IRRI (ed) Hybrid rice breeding in China. In: Innovative approaches to rice breeding. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines, pp 35–51
Liu XQ, Xu X, Tan YP, Li SQ, Hu J, Huang JY, Yang DC, Li YS, Zhu YG (2004) Inheritance and molecular mapping of two fertility-restoring loci for Honglian gametophytic cytoplasmic male sterility in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Gen Genomics 271:586–594
Ma GH, Yuan LP (2003) Hybrid rice achievements and development in China. In: Virmani SS, Mao CX, Hardy B (eds) Hybrid rice for food security, poverty alleviation, and environmental protection. Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Hybrid Rice, Hanoi, Vietnam, 14–17 May 2002. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines, pp 247–256
McCouch SR, Teytelman L, Xu Y, Lobos KB, Clare K, Walton M, Fu B, Maghiran R, Li Z, Xing Y, Zhang Q, Kono I, Yano M, Jellstrom RF, Declerck G, Schneider D, Cartinhour S, Ware D, Stein L (2002) Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.). DNA Res 9:199–207
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nuclic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Nelson JC (1997) QGENE, software for marker-based genomic analysis and breeding. Mol Breed 3:239–245
Pradhan SB, Jachuck PJ (1999) Genetics of fertility restoration of elite lines for different cytoplasmic male sterile sources in rice. Oryza 36(4):374–376
Rao YS (1988) Cytohistology of cytoplasmic male sterile lines in hybrid rice. In: Smith WH, Bostian LR, Cervantes E (eds) Hybrid rice. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines, pp 115–128
Sattari M, Kathiresan A, Gregorio G, Hernandez JE, Nas TM, Virmani SS (2007) Development and use of a two-gene marker-aided selection system for fertility restorer genes in rice. Euphytica 153:35–42
Shinjyo C (1969) Cytoplasmic-genetic male sterility in cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.). II. The inheritance of male sterility. Jpn J Genet 44:149–156
Shinjyo C (1975) Genetical studies of cytoplasmic male sterility and fertility restoration in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Sci Bull Coll Agric Univ Ryukyus 22:1–57
Tan XL, Vanavichit A, Amornsilpa S, Trangoonrung S (1998) Genetic analysis of rice CMS-WA fertility restoration based on QTL mapping. Theor Appl Genet 96:994–999
Temnykh S, De Clerck G, Lukashova A, Lipovich L, Carthinour S, McCouch SR (2001) Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.): frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genome Res 11:1441–1452
Teng LS, Shen ZT (1994) Inheritance of fertility restoration for cytoplasmic male sterility in rice. Rice Genet Newsl 11:95–97
Virmani SS (2003) Advances in hybrid rice research and development in the tropics. In: Virmani SS, Mao CX, Hardy B (eds) Hybrid rice for food security, poverty alleviation, and environmental protection. Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Hybrid Rice, Hanoi, Vietnam, 14–17 May 2002. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines, pp 7–20
Virmani SS, Govinda Raj K, Casal C, Dalmacio RD, Aurin PA (1986) Current knowledge and future outlook on cytoplasmic genetic male sterility and fertility restoration in rice. In: IRRI (ed) Rice genetics. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines, pp 633–647
Virmani SS, Wan BH (1988) Development of CMS lines in hybrid rice breeding. In: Smith WH, Bostian LR, Cervantes E (eds) Hybrid rice. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines, pp 103–114
Virmani SS, Toledo RS (2000) Development and use of tropical rice hybrids. In: Redona ED, Gaspar MG (eds) Hybrid rice in the Philippines: Progress and new horizons. Philippine Rice Research Institute (PhilRice), Maligaya, Science City of Muñoz, Nueva Ecija, Philippines
Wang Z, Zou Y, Li X, Zhang Q, Chen L, Wu H, Su D, Chen Y, Guo J, Luo D, Long Y, Zhong Y, Liu YG (2006) Cytoplasmic male sterility of rice with Boro II cytoplasm is caused by a cytotoxic peptide and is restored by two related PPR motif genes via distinct modes of mRNA silencing. Plant Cell 18:676–687
Yao FY, Xu CG, Yu SB, Li JX, Gao YJ, Li XH, Zhang Q (1997) Mapping and genetic analysis of two fertility restorer loci in the wild abortive cytoplasmic male sterility system of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 98:183–187
Young JB, Virmani SS (1984) Inheritance of fertility restoration in a rice cross. Rice Genet Newsl 1:102–103
Yuan LP (1977) The execution and theory of developing hybrid rice. Chin Agric Sci 1:27–31
Yuan LP, Virmani SS (1988) Status of hybrid rice research and development. In: Smith WH, Bostian LR, Cervantes E (eds) Hybrid rice. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines, pp 7–24
Zhang G, Bharaj TS, Virmani SS, Huang N (1997) Mapping of the Rf-3 nuclear fertility-restoring gene for WA cytoplasmic male sterility in rice using RAPD and RFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 94:27–33
Zhang QY, Liu YG, Mei MT (2002) Molecular mapping of the fertility restorer gene Rf4 for WA cytoplasmic male sterility. Acta Genet Sin 29:1001–1004
Zhou T (1983) Analysis of R genes in hybrid indica rice of WA type. Acta Agron Sin 9:241–247
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a graduate program scholarship from IRRI and the Ministry of Agriculture of the Islamic Republic of Iran. The authors thank Dr. Bill Hardy for editing the manuscript and T. M. Nas for technical assistance during the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sattari, M., Kathiresan, A., Gregorio, G.B. et al. Comparative genetic analysis and molecular mapping of fertility restoration genes for WA, Dissi, and Gambiaca cytoplasmic male sterility systems in rice. Euphytica 160, 305–315 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9498-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9498-z