Summary
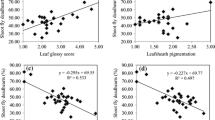
Sorghum shoot fly, Atherigona soccata (Rondani) is an important pest of sorghum in Asia, Africa, and Mediterranean Europe, and host plant resistance is an important component for the management of this pest. The levels of resistance in the cultivated germplasm are low to moderate, and therefore, it is important to identify genotypes with different mechanisms of resistance to pyramid the resistance genes. We studied the antixenosis for oviposition, antibiosis, and tolerance components of resistance in a diverse array of shoot fly-resistant and -susceptible genotypes. The main plants and tillers of SFCR 151, ICSV 705, SFCR 125, and, IS 18551 experienced lower shoot fly deadhearts at 28 days after seedling emergence, produced more number of productive tillers. The insects fed on these genotypes also exhibited longer larval period (10.1–11.0 days compared to 9.3 days on Swarna), lower larval survival and adult emergence (54.7–67.8 and 46.7–52.2% compared to 73.3 and 60.6% on Swarna, respectively), and lower growth and adult emergence indices as compared to the susceptible check, Swarna. Physico-chemical traits such as leaf glossiness, trichome density, and plumule and leaf sheath pigmentation were found to be associated with resistance, and chlorophyll content, leaf surface wetness, seedling vigor, and waxy bloom with susceptibility to shoot fly and explained 88.5% of the total variation in deadhearts. Step-wise regression indicated that 90.4% of the total variation in deadhearts was due to leaf glossiness and trichome density. The direct and indirect effects, correlation coefficients, multiple and step-wise regression analysis suggested that deadhearts, plants with eggs, leaf glossiness, trichomes on the abaxial surface of the leaf, and leaf sheath pigmentation can be used as marker traits to select for resistance to shoot fly, A. soccata in sorghum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal, B.L. & C.V. Abraham, 1985. Breeding sorghum for resistance to shoot fly and midge. In: Proceedings of the International Sorghum Entomology Workshop, 15–21 July 1984, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas, USA, p. 371. International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics, Patancheru 502324, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Blum, A., 1968. Anatomical phenomena in seedlings of sorghum varieties resistant to the sorghum shoot fly (Atherigona varia soccata). Crop Sci 9: 508–510.
Blum, A., 1967. Varietal resistance of sorghum to the sorghum shoots fly (Atherigona varia soccata). Crop Sci 7: 461–462.
Blum, A., 1972. Sorghum breeding for shoot fly resistance in Israel. In: M.G. Jotwani & W.R. Young (Eds.), Control of Sorghum Shoot Fly, pp. 180–191. Oxford & IBH Publishing Co., New Delhi, India.
Borad, P.K. & V.P. Mittal, 1983. Assessment of losses caused by pest complex to sorghum hybrid, CSH 5. In: B.H. Krishnamurthy Rao & K.S.R.K. Murthy (Eds.), Crop Losses due to Insect Pests, Special Issue of Indian Journal of Entomology, pp. 271–278. Entomological Society of India, Rajendranagar, Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Dahms, R.G., 1969. Theoretical effects of antibiosis on insect population dynamics. United States Department of Agriculture, ERO, Beltsville, p. 5.
Deeming, J.C., 1971. Some species of Atherigona Rondani (Diptera: Muscidae) from northern Nigeria, with special reference to those injurious to cereal crops. Bull Entomol Res 61: 133–190.
Dhillon, M.K., 2004. Effects of cytoplasmic male-sterility on expression of resistance to sorghum shoot fly, Atherigona soccata (Rondani). Ph.D. Thesis, 382 pp. Department of Entomology, Chaudhary Charan Singh Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar 125004, Haryana, India.
Doggett, H., K.J. Starks & S.A. Eberhart, 1970. Breeding for resistance to the sorghum shoot fly. Crop Sci 10: 528–531.
Gibson, P.T. & R.K. Maiti, 1983. Trichomes in segregating generations of sorghum matings. I. Inheritance of presence and density. Crop Prot 23: 73–75.
Jain, K.K. & M.P. Bhatnagar, 1962. Studies on varietal resistance to the jowar shoot fly. Indian J Genet 22: 224–229.
Jotwani, M.G., 1978. Investigations on Insect Pests of Sorghum and Millets With Special Reference to Host Plant Resistance. In: Final Technical Report (1972–1977), p. 114. Research Bulletin of the Division of Entomology, Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi, India.
Jotwani, M.G., 1982. Factors reducing sorghum yields – Insect pests. In: L.R. House, L.K. Mughogho & J.M. Peacock (Eds.), Sorghum in Eighties, Proceeding of the International Symposium on Sorghum, 2–7 November, 1981, pp. 251–255. International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics, Patancheru 502 324, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Kamatar, M.Y. & P.M. Salimath, 2003. Morphological traits of sorghum associated with resistance to shoot fly, Atherigona soccata Rondani. Indian J Plant Prot 31: 73–77.
Karanjkar, R.R., R.D. Chandurwar & S.T. Borikar, 1992. Correlations and path analysis of shoot fly resistance in sorghum. J Res Maharashtra Agric Univ 17: 389–391.
Maiti, R.K. & F.R. Bidinger, 1979. A simple approach to the identification of shoot fly tolerance in sorghum. Indian J Plant Prot 7: 135–140.
Maiti, R.K., 1980. Role of ‘glossy trichome’ trait in sorghum crop improvement. In: Annual Meeting, All India Sorghum Improvement Workshop, 12–14 May, 1980, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India, pp. 1–14.
Maiti, R.K. & P.T. Gibson, 1983. Trichomes in segregating generations of sorghum matings. II. Association with shoot fly resistance. Crop Sci 23: 76–79.
Maiti, R.K., K.E.P. Rao, P.S. Raju & L.R. House, 1984. The glossy trait in sorghum: Its characteristics and significance in crop improvement. Field Crops Res 9: 279–289.
Maiti, R.K., F.R. Bidinger, K.V. Seshu Reddy, P. Gibson & J.C. Davies, 1980. Nature and Occurrence of Trichomes in Sorghum Lines With Resistance to Sorghum Shoot Fly. Joint Progress Report 3, Sorghum Physiology and Sorghum Entomology, pp. 1–33. International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics, Patancheru 502324, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Mate, S.N., B.A. Phadanwis & S.S. Mehetre, 1988. Studies on growth and physiological factors in relation to shoot fly attack on sorghum. Indian J Agric Res 22: 81–84.
Meksongsee, B., M. Chawanapong, U. Sangkasuwan & P. Poonyathaworn, 1981. The biology and control of the sorghum shoot fly, Atherigona soccata Rondani, in Thailand. Insect Sci Applic 2: 111–116.
Nwanze, K.F., R.J. Pring, P.S. Sree, D.R. Butler, Y.V.R. Reddy & P. Soman, 1992. Resistance in sorghum to the shoot fly, Atherigona soccata: Epicuticular wax and wetness of the central whorl leaf of young seedlings. Ann Appl Biol 120: 373–382.
Nwanze, K.F., Y.V.R. Reddy & P. Soman, 1990. The role of leaf surface wetness in larval behavior of the sorghum shoot fly, Atherigona soccata. Entomol Exp Applic 56: 187–195.
Ogwaro, K. & E.D. Kokwaro, 1981. Development and morphology of the immature stages of the sorghum shoot fly, Atherigona soccata Rondani. Insect Sci Applic 1: 365–372.
Omori, T., B.L. Agrawal & L.R. House, 1983. Componential analysis of the factors influencing shoot fly resistance in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench). JARQ 17: 215–218.
Pont, A.C. & J.C. Deeming, 2001. A shoot-fly Atherigona tritici sp. n. (Diptera: Muscidae), attacking wheat Triticum aestivum in Egypt. Bull Entomol Res 91: 297–300.
Pont, A.C., 1972. A review of the Oriental species of Atherigona Rondani (Diptera: Muscidae) of economic importance. In: M.G. Jotwani & W.R. Young (Eds.), Control of Sorghum Shoot Fly, pp. 27–104. Oxford and IBH Publishing Co., New Delhi, India.
Raina, A.K., H.Z. Thindwa, S.M. Othieno & R.T. Corkhill, 1981. Resistance in sorghum to sorghum shoot fly: Larval development and adult longevity and fecundity on selected cultivars. Insect Sci Applic 2: 99–103.
Raina, A.K., H.Z. Thindwa, S.M. Othieno & L.W. Douglass, 1984. Resistance in sorghum to shoot fly (Diptera: Muscidae) and oviposition on selected cultivars. J Econ Entomol 77: 648–651.
Rana, B.S., B.U. Singh & N.G.P. Rao, 1985. Breeding for shoot fly and stem borer resistance in sorghum. In: Proceedings of the International Sorghum Entomology Workshop, 15–21 July, 1984, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas, USA, pp. 347–359. International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics, Patancheru 502324, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Rana, B.S., D.P. Tripathi, K. Balakotaiah, R. Damodar & N.G.P. Rao, 1975. Genetic analysis of some exotic × Indian crosses in sorghum selection for shoot fly resistance. Indian J Genet 35: 350–355.
Rao, M. & S. Gowda, 1967. A short note on the bionomics and control of jowar fly. Sorghum Newslett 10: 55–57.
Sharma, G.C., M.G. Jotwani, B.S. Rana & N.G.P. Rao, 1977. Resistance to the sorghum shoot fly, Atherigona soccata (Rond.) and its genetic analysis. J Entomol Res 1: 1–12.
Sharma, H.C., K.F. Nwanze & V. Subramanian, 1997. Mechanisms of resistance to insects and their usefulness in sorghum improvement. In: H.C. Sharma, Faujdar Singh & K.F. Nwanze (Eds.), Plant Resistance to Insects in Sorghum, pp. 81–100. International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics, Patancheru 502324, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Sharma, H.C., S.L. Taneja, N. Kameswara Rao & K.E. Prasada Rao 2003. Evaluation of sorghum germplasm for resistance to insect pests. Information Bulletin No. 63, 177 pp. International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics, Patancheru 502324, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Shivankar, V.I., S. Ram & M.P. Gupta, 1989. Tolerance in some sorghum germplasm to shoot fly (Atherigona soccata Rondani). Indian J Entomol 51: 593–596.
Singh, R. & K.L. Narayana, 1978. Influence of different varieties of sorghum on the biology of sorghum shoot fly. Indian J Agric Sci 48: 8–12.
Singh, S.P. & M.G. Jotwani, 1980a. Mechanisms of resistance in sorghum to shoot fly. I. Ovipositional non-preference. Indian J Entomol 42: 353–360.
Singh, S.P. & M.G. Jotwani, 1980b. Mechanisms of resistance in sorghum to shoot fly. II. Antibiosis. Indian J Entomol 42: 240–247.
Soto, P.E., 1974. Ovipositional preference and antibiosis in relation to resistance to sorghum shoot fly. J Econ Entomol 67: 265–267.
Taneja, S.L. & K. Leuschner, 1985. Resistance screening and mechanisms of resistance in sorghum to shoot fly. In: Proceedings of the International Sorghum Entomology Workshop, 15–21 July, 1984, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas, USA, pp. 115–129. International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics, Patancheru 502324, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Unnithan, G.C. & K.V.S. Reddy, 1985. Oviposition and infestation of the sorghum shoot fly, Atherigona soccata Rondani, on certain sorghum cultivars in relation to their relative resistance and susceptibility. Insect Sci Applic 6: 409–412.
Wiseman, B.R. & W.P. Morrison, 1981. Components for management of field corn and grain sorghum insects and mites in the United States. USDA Agricultural Research Service ARMS-18, Government Printing Office, Washington, DC, USA.
Zein el Abdin, A.M., 1981. Review of sorghum shoot fly research in the Sudan. Insect Sci Applic 2: 55–58.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhillon, M.K., Sharma, H.C., Singh, R. et al. Mechanisms of resistance to shoot fly, Atherigona soccata in sorghum. Euphytica 144, 301–312 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-005-7400-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-005-7400-4