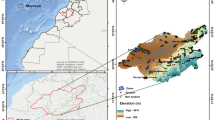
Abstract
Soil erosion by water and other anthropogenic activities in the semi-arid and humid region is noticed as a major issue in the reduction in natural land by the loss of soil nutrients. The seven standard parameters were suggested in the literature for the assessment of soil erosion hazard, viz. soil loss, sediment yield, run-off potential, land capability class, drainage density, sediment transport index, and slope. In the present study, the combination of intelligent vulnerability prediction, multi-criteria decision-making, and geographic information system techniques provides an effective approach to identify the soil erosion hazard in the semi-arid and humid region. It makes this process more effective and efficient as the vulnerability of soil erosion hazard can be predicted by the proposed trained models for any locations that have the streamlined values of above seven parameters as suggested in this paper. The standard machine learning classifiers such as k-nearest neighbour, decision tree, random forest (RF), multinomial naive bays, adaptive boosting, and gradient adaptive boosting (GAB) have been applied on the spatial data set of “Pairi” river watershed found in “Chhattisgarh”, India. There are five categories of soil abrasion, viz. “very low”, “low”, “medium”, “high”, and “very high”, in this data set that represents an index of soil erosion hazard. The experimental results have given 91.5140% and 90.5525% accuracy using RF and GAB, respectively, whereas a much better log-loss measure, i.e. 0.27, is obtained by the GAB in comparison of 0.93 with RF. The results have been verified by visiting the ground truth locations.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnihotri, D., Verma, K., & Tripathi, P. (2016). Computing symmetrical strength of n-grams: A two pass filtering approach in automatic classification of text documents. SpringerPlus, 5(1), 942. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-2573-y.
Agnihotri, D., Verma, K., & Tripathi, P. (2017). Variable global feature selection scheme for automatic classification of text documents. Expert Systems with Applications, 81, 268–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2017.03.057.
Agnihotri, D., Verma, K., & Tripathi, P. (2018a). An automatic classification of text documents based on correlative association of words. Journal of Intelligent Information Systems, 50(3), 549–572. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10844-017-0482-3.
Agnihotri, D., Verma, K., Tripathi, P., & Singh, B. K. (2018b). Soft voting technique to improve the performance of global filter based feature selection in text corpus. Applied Intelligence,. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-018-1349-1.
Alkharabsheh, M. M., Alexandridis, T., Bilas, G., Misopolinos, N., & Silleos, N. (2013a). Impact of land cover change on soil erosion hazard in Northern Jordan using remote sensing and GIS. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 19, 912–921.
Alkharabsheh, M. M., Alexandridis, T., Bilas, G., Misopolinos, N., & Silleos, N. (2013b). Impact of land cover change on soil erosion hazard in Northern Jordan using remote sensing and GIS. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 19, 912–921.
Ayalew, G. (2015). Geographical information system (GIS) based land capability classification of East Amhara region Ethiopia. Journal of Environmental and Earth Science, 5(1), 80–87.
Borrelli, P., Panagos, P., Märker, M., Modugno, S., & Schütt, B. (2017). Assessment of the impacts of clear-cutting on soil loss by water erosion in Italian forests: First comprehensive monitoring and modelling approach. Catena, 149, 770–781.
Briak, H., Moussadek, R., Aboumaria, K., & Mrabet, R. (2016). Assessing sediment yield in Kalaya gauged watershed (Northern Morocco) using GIS and SWAT model. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 4(3), 177–185.
Chen, W., Li, W., Chai, H., Hou, E., Li, X., & Ding, X. (2016). Gis-based landslide susceptibility mapping using analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and certainty factor (CF) models for the Baozhong region of Baoji City, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(1), 63.
Chowdhury, A., Jha, M. K., & Chowdary, V. (2010). Delineation of groundwater recharge zones and identification of artificial recharge sites in West Medinipur district, West Bengal, using RS, GIS and MCDM techniques. Environmental Earth Sciences, 59(6), 1209.
Ganasri, B., & Ramesh, H. (2016a). Assessment of soil erosion by RUSLE model using remote sensing and GIS—A case study of Nethravathi Basin. Geoscience Frontiers, 7(6), 953–961.
Ganasri, B., & Ramesh, H. (2016b). Assessment of soil erosion by RUSLE model using remote sensing and GIS—A case study of Nethravathi Basin. Geoscience Frontiers, 7(6), 953–961.
Gigović, L., Pamučar, D., Lukić, D., & Marković, S. (2016). Gis-fuzzy dematel MCDA model for the evaluation of the sites for ecotourism development: A case study of Dunavski ključ region, Serbia. Land Use Policy, 58, 348–365.
Guo, H., Jiapaer, G., Bao, A., Li, X., Huang, Y., Ndayisaba, F., et al. (2017). Effects of the Tarim Rivers middle stream water transport dike on the fractional cover of desert riparian vegetation. Ecological Engineering, 99, 333–342.
Hornero, J., Manzano, M., Ortega, L., & Custodio, E. (2016). Integrating soil water and tracer balances, numerical modelling and GIS tools to estimate regional groundwater recharge: Application to the Alcadozo Aquifer System (SE Spain). Science of the Total Environment, 568, 415–432.
Huang, W., Ho, H. C., Peng, Y., & Li, L. (2016). Qualitative risk assessment of soil erosion for karst landforms in Chahe town, Southwest China: A hazard index approach. Catena, 144, 184–193.
Jaiswal, R., Ghosh, N., Galkate, R., & Thomas, T. (2015a). Multi criteria decision analysis (MCDA) for watershed prioritization. Aquatic Procedia, 4, 1553–1560.
Jaiswal, R., Ghosh, N. C., Lohani, A., & Thomas, T. (2015b). Fuzzy AHP based multi crteria decision support for watershed prioritization. Water Resources Management, 29(12), 4205–4227.
Jaiswal, R., Thomas, T., Galkate, R., Ghosh, N., & Singh, S. (2014). Watershed prioritization using Saaty’s AHP based decision support for soil conservation measures. Water Resources Management, 28(2), 475–494.
Jhariya, D. C., Kumar, T., Dewangan, R., Pal, D., & Dewangan, P. K. (2017). Assessment of groundwater quality index for drinking purpose in the Durg district, Chhattisgarh using geographical information system (GIS) and multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) techniques. Geological Society of India, 89(4), 453–459.
Jhariya, D. C., Kumar, T., Gobinath, M., Diwan, P., & Kishore, N. (2016). Assessment of groundwater potential zone using remote sensing, GIS and multi criteria decision analysis techniques. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 88(4), 481–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-016-0511-9.
Jhariya, D. C., Kumar, T., & Pandey, H. K. (2018). Watershed prioritization based on soil and water hazard model using remote sensing, geographical information system and multi-criteria decision analysis approach. Geocarto International. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2018.1510039.
Kachouri, S., Achour, H., Abida, H., & Bouaziz, S. (2015a). Soil erosion hazard mapping using analytic hierarchy process and logistic regression: A case study of Haffouz watershed, central Tunisia. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 8(6), 4257–4268.
Kachouri, S., Achour, H., Abida, H., & Bouaziz, S. (2015b). Soil erosion hazard mapping using analytic hierarchy process and logistic regression: A case study of Haffouz watershed, central Tunisia. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 8(6), 4257–4268.
Kachouri, S., Achour, H., Abida, H., & Bouaziz, S. (2015c). Soil erosion hazard mapping using analytic hierarchy process and logistic regression: A case study of Haffouz watershed, central Tunisia. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 8(6), 4257–4268.
Kachouri, S., Achour, H., Abida, H., & Bouaziz, S. (2015d). Soil erosion hazard mapping using analytic hierarchy process and logistic regression: A case study of Haffouz watershed, central Tunisia. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 8(6), 4257–4268.
Kazemi, H., & Akinci, H. (2018). A land use suitability model for rainfed farming by multi-criteria decision-making analysis (MCDA) and geographic information system (GIS). Ecological Engineering, 116, 1–6.
Kumar, T., Gautam, A. K., & Jhariya, D. (2016a). Multi-criteria decision analysis for planning and management of groundwater resources in Balod District, India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(8), 649.
Kumar, T., Gautam, A. K., & Jhariya, D. C. (2016b). Multi-criteria decision analysis for planning and management of groundwater resources in Balod District, india. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(8), 649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5462-3.
Kumar, T., Gautam, A. K., & Kumar, T. (2014a). Appraising the accuracy of GIS-based multi-criteria decision making technique for delineation of groundwater potential zones. Water Resources Management, 28(13), 4449–4466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0663-6.
Kumar, T., Gautam, A. K., & Kumar, T. (2014b). Appraising the accuracy of GIS-based multi-criteria decision making technique for delineation of groundwater potential zones. Water Resources Management, 28(13), 4449–4466.
Kumar, T., & Jhariya, D. (2015). Land quality index assessment for agricultural purpose using multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA). Geocarto International, 30(7), 822–841. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2014.997304.
Kumar, T., & Jhariya, D. C. (2017). Identification of rainwater harvesting sites using SCS-CN methodology, remote sensing and geographical information system techniques. Geocarto International, 32(12), 1367–1388. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2016.1213772.
Machiwal, D., Katara, P., & Mittal, H. (2015a). Estimation of soil erosion and identification of critical areas for soil conservation measures using RS and GIS-based universal soil loss equation. Agricultural Research, 4(2), 183–195.
Machiwal, D., Katara, P., & Mittal, H. (2015b). Estimation of soil erosion and identification of critical areas for soil conservation measures using RS and GIS-based universal soil loss equation. Agricultural Research, 4(2), 183–195.
Marzen, M., Iserloh, T., de Lima, J. L., Fister, W., & Ries, J. B. (2017). Impact of severe rain storms on soil erosion: Experimental evaluation of wind-driven rain and its implications for natural hazard management. Science of the Total Environment, 590, 502–513.
Mekonnen, M., Melesse, A. M., & Keesstra, S. D. (2016). Spatial runoff estimation and mapping of potential water harvesting sites: A GIS and remote sensing perspective, Northwest Ethiopia. In A. Melesse & W. Abtew (Eds.), Landscape dynamics, soils and hydrological processes in varied climates, Springer Geography. Cham: Springer.
Nasiri, H., Boloorani, A. D., Sabokbar, H. A. F., Jafari, H. R., Hamzeh, M., & Rafii, Y. (2013). Determining the most suitable areas for artificial groundwater recharge via an integrated PROMETHEE II-AHP method in GIS environment (case study: Garabaygan Basin, Iran). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(1), 707–718.
Noori, H., Siadatmousavi, S. M., & Mojaradi, B. (2016a). Assessment of sediment yield using RS and GIS at two sub-basins of Dez watershed, Iran. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 4(3), 199–206.
Noori, H., Siadatmousavi, S. M., & Mojaradi, B. (2016b). Assessment of sediment yield using RS and GIS at two sub-basins of Dez Watershed, Iran. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 4(3), 199–206.
Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Michel, V., Thirion, B., Grisel, O., et al. (2011a). Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 12, 2825–2830.
Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Michel, V., Thirion, B., Grisel, O., et al. (2011b). Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 12, 2825–2830.
Pham, T. G., Degener, J., & Kappas, M. (2018a). Integrated universal soil loss equation (USLE) and geographical information system (GIS) for soil erosion estimation in A Sap basin: Central Vietnam. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 6(2), 99–110.
Pham, T. G., Degener, J., & Kappas, M. (2018b). Integrated universal soil loss equation (USLE) and geographical information system (GIS) for soil erosion estimation in A Sap basin: Central Vietnam. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 6(2), 99–110.
Pramanik, M. K. (2016). Site suitability analysis for agricultural land use of Darjeeling district using AHP and GIS techniques. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 2(2), 56.
Rahman, M. R., Shi, Z., & Chongfa, C. (2009a). Soil erosion hazard evaluation an integrated use of remote sensing, GIS and statistical approaches with biophysical parameters towards management strategies. Ecological Modelling, 220(13–14), 1724–1734.
Rahman, M. R., Shi, Z., & Chongfa, C. (2009b). Soil erosion hazard evaluation: an integrated use of remote sensing, GIS and statistical approaches with biophysical parameters towards management strategies. Ecological Modelling, 220(13–14), 1724–1734.
Rahman, M. R., Shi, Z., Chongfa, C., & Dun, Z. (2015). Assessing soil erosion hazard-a raster based GIS approach with spatial principal component analysis (SPCA). Earth Science Informatics, 8(4), 853–865.
Ramakrishnan, D., Bandyopadhyay, A., & Kusuma, K. (2009). SCS-CN and GIS-based approach for identifying potential water harvesting sites in the Kali Watershed, Mahi River Basin, India. Journal of Earth System Science, 118(4), 355–368.
Rizeei, HM., Pradhan, B., & Saharkhiz, M. A. (2017). Surface runoff estimation and prediction regarding LULC and climate dynamics using coupled LTM, optimized ARIMA and distributed-GIS-based SCS-CN models at tropical region. In Global civil engineering conference (pp. 1103–1126). Springer.
Roşca, S., Bilasco, Ş., Păcurar, I., Oncu, M., Negrusier, C., & Petrea, D. (2015). Land capability classification for crop and fruit product assessment using GIS technology. Case Study: The Niraj River Basin (Transylvania Depression, Romania), Not Bot Horti Agrobo, 43(1), 235–242.
Roy, S., & Sahu, A. S. (2017). Potential interaction between transport and stream networks over the Lowland rivers in Eastern India. Journal of Environmental Management, 197, 316–330.
Rymszewicz, A., Bruen, M., O’Sullivan, J., Turner, J., Lawler, D., Harrington, J., et al. (2018). Modelling spatial and temporal variations of annual suspended sediment yields from small agricultural catchments. Science of The Total Environment, 619, 672–684.
Saaty, T. (1980). The analytic process: Planning, priority setting, resources allocation. New York: McGraw.
Saaty, T. L. (1990). How to make a decision: The analytic hierarchy process. European Journal of Operational Research, 48(1), 9–26.
Saaty, T. L. (2003). Decision-making with the AHP: Why is the principal eigenvector necessary. European Journal of Operational Research, 145(1), 85–91.
Saravanan, S., & Manjula, R. (2015). Geomorphology based semi-distributed approach for modeling rainfall-runoff modeling using GIS. Aquatic Procedia, 4, 908–916.
Satheeshkumar, S., Venkateswaran, S., & Kannan, R. (2017). Rainfall-runoff estimation using SCS-CN and GIS approach in the Pappiredipatti watershed of the Vaniyar Sub Basin, South India. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 3(1), 24.
Singh, L. K., Jha, M. K., & Chowdary, V. (2017). Multi-criteria analysis and GIS modeling for identifying prospective water harvesting and artificial recharge sites for sustainable water supply. Journal of Cleaner Production, 142, 1436–1456.
Singh, G., & Panda, R. K. (2017a). Grid-cell based assessment of soil erosion potential for identification of critical erosion prone areas using USLE, GIS and remote sensing: A case study in the Kapgari Watershed, India. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 5(3), 202–211.
Singh, G., & Panda, R. K. (2017b). Grid-cell based assessment of soil erosion potential for identification of critical erosion prone areas using USLE, GIS and remote sensing: A case study in the Kapgari Watershed, India. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 5(3), 202–211.
Subramanya, K. (2013). Engineering hydrology (4th ed.). New York: Tata McGraw-Hill Education.
Yalew, S. G., van Griensven, A., Mul, M. L., & van der Zaag, P. (2016). Land suitability analysis for agriculture in the Abbay basin using remote sensing, GIS and AHP techniques. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 2(2), 101.
Yao, L., Wei, W., Yu, Y., Xiao, J., & Chen, L. (2018). Rainfall-runoff risk characteristics of urban function zones in Beijing using the SCS-CN model. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 28(5), 656–668.
Zare, M., Panagopoulos, T., & Loures, L. (2017a). Simulating the impacts of future land use change on soil erosion in the Kasilian watershed, Iran. Land Use Policy, 67, 558–572.
Zare, M., Panagopoulos, T., & Loures, L. (2017b). Simulating the impacts of future land use change on soil erosion in the Kasilian watershed, Iran. Land Use Policy, 67, 558–572.
Zende, A. M., Patil, R. A., & Bhosale, G. M. (2018). Sediment yield estimation and soil conservation measures for Agrani River basin using geospatial techniques. Materials Today: Proceedings, 5(1), 550–556.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agnihotri, D., Kumar, T. & Jhariya, D. Intelligent vulnerability prediction of soil erosion hazard in semi-arid and humid region. Environ Dev Sustain 23, 2524–2551 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-00685-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-00685-2