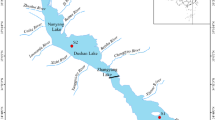
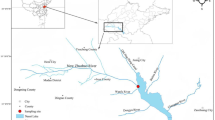
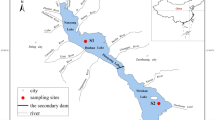
Abstract
Recently, reservoirs in southern China are witnessing incidents involving black water, which are harmful to the aquatic ecosystem. This study unravels the cause of the black water events by studying the occurrence and the ecological risks of contaminants (Pb, Cu, Cd, Zn, Ni, TFe, Mn, S, P, and DOC) in sediments of Tianbao reservoir. Due to the significantly high concentration of TFe, Mn, and P in the sediments, the study further used the thin film diffusion gradient (DGT) technology and high-resolution dialysis method to investigate the movement of Fe2+, Mn2+, S2−, and reactive P within the sediments. The ecological risk assessment (threshold effect level and probable effect level) showed that the sediments had a low concentration of Pb, Cu, Cd, Zn, and Ni. High organic matter from the Eucalyptus plantation surrounding the reservoir, as well as the intense thermal stratification of the reservoir, caused the hypolimnion to be hypoxic (DO < 2 mg/L). The diffusion fluxes at the water–sediment boundary (WSB) demonstrated a significant movement of Fe2+, Mn2+, and PO43− from the sediments into the overlying water, while the movement of S2− was in both directions due to hypoxia. A high correlation Fe–DOC (r = 0.9), Fe–S (r = 0.8), and Mn–S (r = 0.7) and the redox interaction of Fe2+, Mn2+, S2−, P, and DOC at the hypoxic WSB caused the production of black substances in the hypolimnion contributing to the so-called black water reservoir.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Akoto, O., Gyimah, E., Zhan, Z., et al. (2019). Evaluation of health risks associated with trace metal exposure in water from the Barekese reservoir in Kumasi, Ghana. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 7039. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1559033
Battin, T. J. (1998). Dissolved organic matter and its optical properties in a blackwater tributary of the upper Orinoco river, Venezuela. PII S0146–6380(98)00028-X 28:561–569. https://doi.org/10.1002/prop.2190400803
Berthon, J. F., & Zibordi, G. (2010). Optically black waters in the northern Baltic Sea. Geophysical Research Letters, 37, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010GL043227
Bisutti, I., Hilke, I., & Raessler, M. (2004). Determination of total organic carbon - An overview of current methods. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 23, 716–726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2004.09.003
Cheng, H., Li, K., Li, M., et al. (2014). Geochemical background and baseline value of chemical elements in urban soil in China. Earth Science Frontiers, 21, 265–306. https://doi.org/10.13745/j.esf.2014.03.028
Deng, M., Yang, X., Dai, X., et al. (2020). Heavy metal pollution risk assessments and their transportation in sediment and overlay water for the typical Chinese reservoirs. Ecological Indicators, 112, 106166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106166
Duan, H., Ma, R., Loiselle, S. A., et al. (2014). Optical characterization of black water blooms in eutrophic waters. Science of the Total Environment, 482–483, 174–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.02.113
Duval, B., & Ludlam, S. D. (2001). The black water chemocline of meromictic Lower Mystic Lake, Massachusetts, U.S.A. International Review of Hydrobiology, 86, 165–181. https://doi.org/10.1002/1522-2632(200104)86:2%3c165::AID-IROH165%3e3.0.CO;2-Y
He, C., Su, T., Liu, S., et al. (2020). Heavy metal, arsenic, and selenium concentrations in bird feathers from a region in southern China impacted by intensive mining of nonferrous metals. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 39, 371–380. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.4622
Hladyz, S., Watkins, S. C., Whitworth, K. L., & Baldwin, D. S. (2011). Flows and hypoxic blackwater events in managed ephemeral river channels. Journal of Hydrology, 401, 117–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.02.014
Huang, J., Amuzu-Sefordzi, B., & Li, M. (2015). Heavy metals and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) sedimentation in the Lianhua Mountain Reservoir, Pearl River Delta, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 111–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4466-x
Huang, J., Norgbey, E., Li, G., et al. (2019). Unraveling the feeding dynamics of Chinese mitten crab-based ecosystems using carbon and nitrogen stable isotope techniques. Journal of Consumer Protection and Food Safety, 14(3), 251–261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-019-01220-w
Huang, J., Norgbey, E., Nkrumah, P. N., et al. (2017). Detection of corn oil in adulterated olive and soybean oil by carbon stable isotope analysis. Journal of Consumer Protection and Food Safety, 12(3), 201–208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-017-1097-x
Jaishankar, M., Tseten, T., Anbalagan, N., et al. (2014). Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdisciplinary Toxicology, 7, 60–72. https://doi.org/10.2478/intox-2014-0009
Krachler, R., Krachler, R., Valda, A., & Keppler, B. K. (2019). Natural iron fertilization of the coastal ocean by “blackwater rivers.” Science of the Total Environment, 656, 952–958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.423
Krueger, K. M., Vavrus, C. E., Lofton, M. E., et al. (2020). Iron and manganese fluxes across the sediment-water interface in a drinking water reservoir. Water Research, 182, 116003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116003
Kummu, M., & Varis, O. (2007). Sediment-related impacts due to upstream reservoir trapping, the Lower Mekong River. Geomorphology, 85, 275–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.03.024
Li, K., Yang, M., Peng, J., et al. (2019a). Rapid control of black and odorous substances from heavily-polluted sediment by oxidation: Efficiency and effects. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 13(6), 1–11.
Li, R., Wu, Z., Li, L., et al. (2019b). Simulation of fish migration at different water depths based on backpropagation neural network. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 17, 437–449.
Li, Y., Luo, F., Guo, J., et al. (2018). Mechanism of “black-water” occurrence in the reservoirs with Eucalyptus plantation, southern China. Journal of Lake Science, 30, 15–24. https://doi.org/10.18307/2018.0102
Li, Y., Norgbey, E., Zhu, Y., et al. (2021). Iron, thermal stratification, Eucalyptus sp., and hypoxia: Drivers to water blackening in southern China reservoirs. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12500-0
Li, Y., Nwankwegu, A. S., Huang, Y., et al. (2020). Evaluating the phytoplankton, nitrate, and ammonium interactions during summer bloom in tributary of a subtropical reservoir. Journal of Environmental Management, 271, 110971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110971
Liao, J., Chen, J., Ru, X., et al. (2017). Heavy metals in river surface sediments affected with multiple pollution sources, South China: Distribution, enrichment and source apportionment. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 176, 9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.08.013
Liu, M., Zhang, Y., Shi, K., et al. (2019). Thermal stratification dynamics in a large and deep subtropical reservoir revealed by high-frequency buoy data. Science of the Total Environment, 651, 614–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.215
Luo, F., Li, Y., Norgbey, E., et al. (2020). A study on the occurrence of black water in reservoirs in Eucalyptus Plantation region. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09613-3
Marip, J. B., Yuan, X., Zhu, H., et al. (2020). Spatial distribution and environmental significance of phosphorus fractions in river sediments and its influencing factor from hongze and tiaoxi watersheds, Eastern China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165787
Marks, B., Peters, A., & McGough, D. (2017). Aquatic environmental risk assessment of manganese processing industries. Neurotoxicology, 58, 187–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NEURO.2016.04.011
Melaku, S., Dams, R., & Moens, L. (2005). Determination of trace elements in agricultural soil samples by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry: Microwave acid digestion versus aqua regia extraction. Analytica Chimica Acta, 543, 117–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2005.04.055
Murphy, J., & Riley, J. P. (1962). A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta, 27, 31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(00)88444-5
Norgbey, E., Huang, J., Hirsch, V., et al. (2020a). Unravelling the efficient use of waste lignin as a bitumen modifier for sustainable roads. Construction and Building Materials, 230, 116957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.116957
Norgbey, E., Li, Y., Ya, Z., et al. (2020b). High resolution evidence of iron-phosphorus-sulfur mobility at hypoxic sediment water interface: An insight to phosphorus remobilization using DGT-induced fluxes in sediments model. Science of the Total Environment, 724, 138204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138204
Norgbey, E., Li, Y., Zhu, Y., et al. (2021). Seasonal dynamics of iron and phosphorus in reservoir sediments in Eucalyptus plantation region. Ecological Processes, 10.https://doi.org/10.1186/s13717-021-00280-x
Nwankwegu, A. S., Li, Y., Huang, Y., et al. (2020a). Nitrate repletion during spring bloom intensifies phytoplankton iron demand in Yangtze River tributary, China. Environmental Pollution, 264, 114626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114626
Nwankwegu, A. S., Li, Y., Huang, Y., et al. (2020b). Nutrient addition bioassay and phytoplankton community structure monitored during autumn in Xiangxi Bay of Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Chemosphere, 247, 125960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.125960
Rong, N., Lu, W., Zhang, C., et al. (2020). In situ high-resolution measurement of phosphorus, iron and sulfur by diffusive gradients in thin films in sediments of black-odorous rivers in the Pearl River Delta region, South China. Environmental Research, 189.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109918
Shao, Y., Chen, Z., & Wu, L. (2019). Oxidative stress effects of soluble sulfide on human hepatocyte cell line lo2. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16091662
Sheng, Y., Qu, Y., Ding, C., et al. (2013). A combined application of different engineering and biological techniques to remediate a heavily polluted river. Ecological Engineering, 57, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2013.04.004
Shyla, B., Mahadevaiah, & Nagendrappa, G. (2011). A simple spectrophotometric method for the determination of phosphate in soil, detergents, water, bone and food samples through the formation of phosphomolybdate complex followed by its reduction with thiourea. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 78, 497–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2010.11.017
Soto-Neira, J., Zhu, Q., & Aller, R. C. (2011). A new spectrophotometric method to quantify dissolved manganese in marine pore waters. Marine Chemistry, 127, 56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2011.07.009
Tamura, H., Goto, K., Yotsuyanagi, T., & Nagayama, M. (1974). Spectrophotometric determination of iron(II) with 1,10-phenanthroline in the presence of large amounts of iron(III). Talanta, 21, 314–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/0039-9140(74)80012-3
Tue-Ngeun, O., Sandford, R. C., Jakmunee, J., et al. (2005). Determination of dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in freshwaters by sequential injection spectrophotometry with on-line UV photo-oxidation. Analytica Chimica Acta, 554, 17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2005.08.043
Valett, H. M., Baker, M. A., Morrice, J. A., et al. (2005). Biogeochemical and metabolic responses to the flood pulse in a semiarid floodplain. Ecology, 86, 220–234. https://doi.org/10.1890/03-4091
Wang, Y., Ding, S., Shi, L., et al. (2017). Simultaneous measurements of cations and anions using diffusive gradients in thin films with a ZrO-Chelex mixed binding layer. Analytica Chimica Acta, 972, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.04.007
Whitworth, K. L., & Baldwin, D. S. (2016). Improving our capacity to manage hypoxic blackwater events in lowland rivers: The blackwater risk assessment tool. Ecological Modelling, 320, 292–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2015.10.001
Whitworth, K. L., Kerr, J. L., Mosley, L. M., et al. (2013). Options for managing hypoxic blackwater in river systems: Case studies and framework. Environmental Management, 52, 837–850. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-013-0130-9
Xu, D., Wu, W., Ding, S., et al. (2012). A high-resolution dialysis technique for rapid determination of dissolved reactive phosphate and ferrous iron in pore water of sediments. Science of the Total Environment, 421–422, 245–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.01.062
Yan, R., Gao, Y., Li, L., & Gao, J. (2019). Estimation of water environmental capacity and pollution load reduction for urban lakeside of Lake Taihu, eastern China. Ecological Engineering, 139, 105587. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOLENG.2019.105587
Yuan, H., Tai, Z., Li, Q., & Liu, E. (2020). In-situ, high-resolution evidence from water-sediment interface for significant role of iron bound phosphorus in eutrophic lake. Science of the Total Environment, 706, 136040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136040
Zhang, Y., Han, Y., Yang, J., et al. (2017). Toxicities and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Taihu Lake, China, based on sediment quality guidelines. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 62, 31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.08.002
Zhang, Y., Yang, J., Simpson, S. L., et al. (2019). Application of diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) and simultaneously extracted metals (SEM) for evaluating bioavailability of metal contaminants in the sediments of Taihu Lake, China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 184, 109627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109627
Zhang, Z., Cao, R., Mamat, Z., et al. (2020). A study of synchronous measurement of liable phosphorous and iron based on ZrO-Chelex (DGT) in the sediment of the Chaiwopu Lake, Xinjiang, Northwest China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, 15057–15067. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07701-y
Zhou, J., He, Q., Hemme, C. L., et al. (2011). How sulphate-reducing microorganisms cope with stress: Lessons from systems biology. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 9, 452–466.
Zhuang, W., Ying, S. C., Frie, A. L., et al. (2019). Distribution, pollution status, and source apportionment of trace metals in lake sediments under the influence of the South-to-North Water Transfer Project, China. Science of the Total Environment, 671, 108–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.306
Funding
The National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFC0405203, 2016YFC0401703) and the National Science Foundation of China (52039003, 51779072, 51809102) supported this research. The Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment (2017ZX07204003) also supported this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: LY; methodology: EN, LY, ZY; formal analysis and investigation: LY, EN, AN; writing — original draft preparation: LY, EN; writing — review and editing: LN; funding acquisition: LY, EN; resources: PY, YH; supervision: RB, DA.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Norgbey, E., Li, Y., Zhu, Y. et al. Combined use of high-resolution dialysis, diffusive gradient in thin films (DGT) technique, and conventional methods to assess trace metals in reservoir sediments. Environ Monit Assess 193, 469 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09247-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09247-z