Abstract
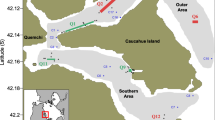
The environmental impacts of fish farming on benthic ecosystems beneath the fish cages have been widely addressed the past decades. However, the chronic release of nutrients can cause a shift in local primary productivity and a chronic increase in the sedimentation of organic material at a large spatial scale which could be reflected in benthic ecosystems. In this context, the indirect effects of aquaculture on the benthic ecosystem were studied in a semi-closed bay (Cephalonia, Ionian Sea) where a relatively large fish farm has been operating since 1982. Results from the present sampling were compared to historical data obtained in 1996 and 2001, in order to detect if nutrient release that could impact phytoplankton dynamics in the bay could indirectly alter benthic communities, as well. Macrofaunal communities have not shown deterioration but rather a small, yet statistically significant, improvement in diversity indices and ecological status indicators, and no significant change regarding bioturbation potential. This indicated that processes involved in nutrient consumption and transfer are highly effective in such an oligotrophic environment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birchenough, S. N. R., Parker, R. E., McManus, E., & Barry, J. (2012). Combining bioturbation and redox metrics: potential tools for assessing seabed function. Ecological Indicators, 12(1), 8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2011.03.015.
Borja, A., Franco, J., & Pérez, V. (2000). A marine biotic index to establish the ecological quality of soft-bottom benthos within European estuarine and coastal environments. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 40(12), 1100–1114. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-326X(00)00061-8.
Borja, Á., Rodríguez, J. G., Black, K., Bodoy, A., Emblow, C., Fernandes, T. F., Forte, J., Karakassis, I., Muxika, I., Nickell, T. D., Papageorgiou, N., Pranovi, F., Sevastou, K., Tomassetti, P., & Angel, D. (2009). Assessing the suitability of a range of benthic indices in the evaluation of environmental impact of fin and shellfish aquaculture located in sites across Europe. Aquaculture, 293(3–4), 231–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2009.04.037.
Clarke, K. R., & Gorley, R. N. (2015). PRIMER v7 : user manual/tutorial PRIMER-E: Plymouth. PRIMER-E Ltd.
Clarke, K. R., Gorley, R. N., Somerfield, P. J., & Warwick, R. M. (2014). Change in marine communities: an approach to statistical analysis and interpretation (3rd ed.). PRIMER-E Ltd.
Conides, A. (2006). Report on the trophic status of Argostoli bay (Cephalonia) in relation to fish farming. Athens: Ministry of rural development and food Hellenic Republic.
Danovaro, R., Dell’Anno, A., Fabiano, M., Pusceddu, A., & Tselepides, A. (2001). Deep-sea ecosystem response to climate changes: the eastern Mediterranean case study. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 16(9), 505–510.
de Paz, L., Patrício, J., Marques, J. C., Borja, A., & Laborda, A. J. (2008). Ecological status assessment in the lower Eo estuary (Spain). The challenge of habitat heterogeneity integration: a benthic perspective. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 56(7), 1275–1283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2008.04.027.
Dell’Anno, A., Mei, M. L., Pusceddu, A., & Danovaro, R. (2002). Assessing the trophic state and eutrophication of coastal marine systems: a new approach based on the biochemical composition of sediment organic matter. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 44(7), 611–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-326X(01)00302-2.
Dimitriou, P. D., Apostolaki, E. T., Papageorgiou, N., Reizopoulou, S., Simboura, N., Arvanitidis, C., & Karakassis, I. (2012). Meta-analysis of a large data set with Water Framework Directive indicators and calibration of a benthic quality index at the family level. Ecological Indicators, 20, 101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.02.008.
Dimitriou, P. D., Papageorgiou, N., Arvanitidis, C., Assimakopoulou, G., Pagou, K., Papadopoulou, K. N., Pavlidou, A., Pitta, P., Reizopoulou, S., Simboura, N., & Karakassis, I. (2015). One step forward: benthic pelagic coupling and indicators for environmental status. PLoS One, 10(10), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0141071.
Dippner, J. W., & Ikauniece, A. (2001). Long-term zoobenthos variability in the Gulf of Riga in relation to climate variability. Journal of Marine Systems, 30(3–4), 155–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-7963(01)00055-0.
Duarte, C. M., Holmer, M., Olsen, Y., Soto, D., Marbà, N., Guiu, J., Black, K., & Karakassis, I. (2009). Will the oceans help feed humanity? BioScience, 59(11), 967–976. https://doi.org/10.1525/bio.2009.59.11.8.
FAO. (2015). FAO Global Aquaculture Production statistics database updated to 2013: summary information. Food and Agriculture Oraganization of the United Nations, 2013(March 2015). doi: I4899E./1/08.15.
Fernandez-Gonzalez, V., Aguado-Giménez, F., Gairin, J. I., & Sanchez-Jerez, P. (2013). Exploring patterns of variation in amphipod assemblages at multiple spatial scales: natural variability versus coastal aquaculture effect. Aquaculture Environment Interactions, 3(2), 93–105. https://doi.org/10.3354/aei00054.
Frid, C. L. J., Harwood, K. G., Hall, S. J., & Hall, J. A. (2000). Long-term changes in the benthic communities on North Sea fishing grounds. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 57(5), 1303–1309. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmsc.2000.0900.
Gray, J. S., & Elliott, M. (2009). Ecology of marine sediments. 241. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s13398-014-0173-7.2.
Hedges, J. I., & Stern, J. H. (1984). Carbon and nitrogen determinations of carbonate-containing solids1. Limnology and Oceanography, 29(3), 657–663. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1984.29.3.0657.
Heilskov, A. C., & Holmer, M. (2001). Effects of benthic fauna on organic matter mineralization in fish-farm sediments: importance of size and abundance. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 58(2), 427–434. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmsc.2000.1026.
Holmer, M., Argyrou, M., Dalsgaard, T., Danovaro, R., Diaz-Almela, E., Duarte, C. M., Frederiksen, M., Grau, A., Karakassis, I., Marbà, N., Mirto, S., Pérez, M., Pusceddu, A., & Tsapakis, M. (2008). Effects of fish farm waste on Posidonia oceanica meadows: synthesis and provision of monitoring and management tools. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 56(9), 1618–1629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2008.05.020.
Husa, V., Kutti, T., Ervik, A., Sjøtun, K., Hansen, P. K., & Aure, J. (2014). Regional impact from fin-fish farming in an intensive production area (Hardangerfjord, Norway). Marine Biology Research, 10(3), 241–252. https://doi.org/10.1080/17451000.2013.810754.
Hyland, J., Balthis, L., Karakassis, I., Magni, P., Petrov, A., Shine, J., Vestergaard, O., & Warwick, R. (2005). Organic carbon content of sediments as an indicator of stress in the marine benthos. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 295, 91–103. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps295091.
Josefson, A., Norkko, J., & Norkko, a. (2012). Burial and decomposition of plant pigments in surface sediments of the Baltic Sea: role of oxygen and benthic fauna. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 455, 33–49. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps09661.
Kalantzi, I., & Karakassis, I. (2006). Benthic impacts of fish farming: meta-analysis of community and geochemical data. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 52(5), 484–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2005.09.034.
Karakassis, I., Hatziyanni, E., Tsapakis, M., & Plaiti, W. (1999). Benthic recovery following cessation of fish farming: a series of successes and catastrophes. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 184, 205–218. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps184205.
Karakassis, I., Tsapakis, M., Hatziyanni, E., Papadopoulou, K. N., & Plaiti, W. (2000). Impact of cage farming of fish on the seabed in three Mediterranean coastal areas. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 57(5), 1462–1471. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmsc.2000.0925.
Karakassis, I., Tsapakis, M., Hatziyanni, E., & Pitta, P. (2001). Diel variation of nutrients and chlorophyll in sea bream and sea bass cages in the Mediterranean. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 10(3), 278–283 http://www.psp-parlar.de/pdf/FEB696_pp278_283.pdf.
Karakassis, I., Pitta, P., & Krom, M. D. (2005). Contribution of fish farming to the nutrient loading of the Mediterranean. Scientia Marina, 69(2), 313–321. https://doi.org/10.3989/scimar.2005.69n2313.
Karlson, K., Rosenberg, R., & Bonsdorff, E. (2002). Temporal and spatial large-scale effects of eutrophication and oxygen deficiency on benthic fauna in Scandinavian and Baltic waters—a review. Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review, 40, 427–489. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203180594.ch8.
Keeley, N. B., Macleod, C. K., Hopkins, G. A., & Forrest, B. M. (2014). Spatial and temporal dynamics in macrobenthos during recovery from salmon farm induced organic enrichment: when is recovery complete? Marine Pollution Bulletin, 80(1–2), 250–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.12.008.
Kress, N., Herut, B., & Galil, B. S. (2004). Sewage sludge impact on sediment quality and benthic assemblages off the Mediterranean coast of Israel—a long-term study. Marine Environmental Research, 57(3), 213–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-1136(03)00081-3.
Kröncke, I., Zeiss, B., & Rensing, C. (2001). Long-term variability in macrofauna species composition off the island of Norderney (East Frisia, Germany) in relation to changes in climatic and environmental conditions. Senckenbergiana Maritima, 31(1), 65–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03042837.
Kutti, T., Ervik, A., & Hansen, P. K. (2007a). Effects of organic effluents from a salmon farm on a fjord system. I. Vertical export and dispersal processes. Aquaculture, 262(2–4), 367–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2006.10.010.
Kutti, T., Hansen, P. K., Ervik, A., Høisæter, T., & Johannessen, P. (2007b). Effects of organic effluents from a salmon farm on a fjord system. II. Temporal and spatial patterns in infauna community composition. Aquaculture, 262(2–4), 355–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2006.10.008.
Labrune, C., Grémare, A., Guizien, K., & Amouroux, J. M. (2007). Long-term comparison of soft bottom macrobenthos in the Bay of Banyuls-sur-Mer (north-western Mediterranean Sea): a reappraisal. Journal of Sea Research, 58(2), 125–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seares.2007.02.006.
Machias, A., Karakassis, I., Labropoulou, M., Somarakis, S., Papadopoulou, K. N., & Papaconstantinou, C. (2004). Changes in wild fish assemblages after the establishment of a fish farming zone in an oligotrophic marine ecosystem. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 60(4), 771–779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2004.03.014.
Machias, A., Karakassis, I., Giannoulaki, M., Papadopoulou, K. N., Smith, C. J., & Somarakis, S. (2005). Response of demersal fish communities to the presence of fish farms. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 288, 241–250. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps288241.
Machias, A., Giannoulaki, M., Somarakis, S., Maravelias, C. D., Neofitou, C., Koutsoubas, D., Papadopoulou, K. N., & Karakassis, I. (2006). Fish farming effects on local fisheries landings in oligotrophic seas. Aquaculture, 261(2), 809–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2006.07.019.
Macleod, C. K., Moltschaniwskyj, N. A., Crawford, C. M., & Forbes, S. E. (2007). Biological recovery from organic enrichment: some systems cope better than others. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 342, 41–53. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps342041.
Mirto, S., Bianchelli, S., Gambi, C., Krzelj, M., Pusceddu, A., Scopa, M., Holmer, M., & Danovaro, R. (2010). Fish-farm impact on metazoan meiofauna in the Mediterranean Sea: analysis of regional vs. habitat effects. Marine Environmental Research, 69(1), 38–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2009.07.005.
Moraitis, M., Papageorgiou, N., Dimitriou, P. D., Petrou, A., & Karakassis, I. (2013). Effects of offshore tuna farming on benthic assemblages in the eastern Mediterranean. Aquaculture Environment Interactions, 4(1), 41–51. https://doi.org/10.3354/aei00071.
Muxika, I., Borja, Á., & Bald, J. (2007). Using historical data, expert judgement and multivariate analysis in assessing reference conditions and benthic ecological status, according to the European Water Framework Directive. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 55(1–6), 16–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2006.05.025.
Nickell, L. A., Black, K. D., Hughes, D. J., Overnell, J., Brand, T., Nickell, T. D., Breuer, E., & Martyn Harvey, S. (2003). Bioturbation, sediment fluxes and benthic community structure around a salmon cage farm in Loch Creran, Scotland. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 285–286, 221–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0981(02)00529-4.
Papageorgiou, N., Kalantzi, I., & Karakassis, I. (2010). Effects of fish farming on the biological and geochemical properties of muddy and sandy sediments in the Mediterranean Sea. Marine Environmental Research, 69(5), 326–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2009.12.007.
Pavlidou, A., Simboura, N., Rousselaki, E., Tsapakis, M., Pagou, K., Drakopoulou, P., Assimakopoulou, G., Kontoyiannis, H., & Panayotidis, P. (2015). Methods of eutrophication assessment in the context of the water framework directive: examples from the Eastern Mediterranean coastal areas. Continental Shelf Research, 108, 156–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2015.05.013.
Piroddi, C., Bearzi, G., & Christensen, V. (2011). Marine open cage aquaculture in the eastern Mediterranean sea: a new trophic resource for bottlenose dolphins. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 440, 255–266. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps09319.
Pitta, P., Karakassis, I., Tsapakis, M., & Zivanovic, S. (1999). Natural vs. mariculture induced variability in nutrients and plankton in the eastern Mediterranean. Hydrobiologia, 391(1–3), 181–194.
Pitta, P., Apostolaki, E. T., Giannoulaki, M., & Karakassis, I. (2005). Mesoscale changes in the water column in response to fish farming zones in three coastal areas in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 65(3), 501–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2005.06.021.
Pitta, P., Apostolaki, E. T., Tsagaraki, T., Tsapakis, M., & Karakassis, I. (2006). Fish farming effects on chemical and microbial variables of the water column: a spatio-temporal study along the Mediterranean Sea. Hydrobiologia, 563(1), 99–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-1593-3.
Pitta, P., Tsapakis, M., Apostolaki, E. T., Tsagaraki, T., Holmer, M., & Karakassis, I. (2009). “Ghost nutrients” from fish farms are transferred up the food web by phytoplankton grazers. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 374, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps07763.
Price, C., Black, K., Hargrave, B., & Morris, J. (2015). Marine cage culture and the environment: effects on water quality and primary production. Aquaculture Environment Interactions, 6(2), 151–174. https://doi.org/10.3354/aei00122.
Queirós, A. M., Birchenough, S. N. R., Bremner, J., Godbold, J. A., Parker, R. E., Romero-Ramirez, A., Reiss, H., Solan, M., Somerfield, P. J., van Colen, C., van Hoey, G., & Widdicombe, S. (2013). A bioturbation classification of European marine infaunal invertebrates. Ecology and Evolution, 3(11), 3958–3985. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.769.
Rosenberg, R., Blomqvist, M., Nilsson, H. C., Cederwall, H., & Dimming, A. (2004). Marine quality assessment by use of benthic species-abundance distributions: a proposed new protocol within the European Union Water Framework Directive. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 49(9–10), 728–739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2004.05.013.
Simboura, N., & Zenetos, A. (2002). Benthic indicators to use in ecological quality classification of Mediterranean soft bottom marine ecosystems, including a new biotic index. Mediterranean Marine Science, 3(2), 77–111.
Simboura, N., Pavlidou, A., Bald, J., Tsapakis, M., Pagou, K., Zeri, C., Androni, A., & Panayotidis, P. (2016). Response of ecological indices to nutrient and chemical contaminant stress factors in Eastern Mediterranean coastal waters. Ecological Indicators, 70(2016), 89–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.05.018.
Solan, M., Batty, P., Bulling, M. T., & Godbold, J. A. (2008). How biodiversity affects ecosystem processes: implications for ecological revolutions and benthic ecosystem function. Aquatic Biology, 2(3), 289–301. https://doi.org/10.3354/ab00058.
Tsagaraki, T. M., Pitta, P., Frangoulis, C., Petihakis, G., & Karakassis, I. (2013). Plankton response to nutrient enrichment is maximized at intermediate distances from fish farms. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 493(Turley 1999), 31–42. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps10520.
Tsapakis, M., Pitta, P., & Karakassis, I. (2006). Nutrients and fine particulate matter released from sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) farming. Aquatic Living Resources, 19, 69–75.
Wilson, A., Magill, S., & Black, K. D. (2009). Review of environmental impact assessment and monitoring in salmon aquaculture. Aquaculture, 455–535.
World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS). (2017). WoRMS editorial board. http://www.marinespecies.org.
Yentsch, C. S., & Menzel, D. W. (1963). A method for the determination of phytoplankton chlorophyll and phaeophytin by fluorescence. Deep Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 10(3), 221–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/0011-7471(63)90358-9.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the two anonymous reviewers for critically revising the manuscript. We also thank our colleagues: Ms. Anastasia Tsiola, Dr. Ioanna Kalantzi, Ms. Eleni Rousselaki, Mr. Santi Diliberto, Dr. Nikos Lampadariou, and the crew members of R/V Filia for their help with the sampling. Thanks are also due to Dr. Nafsika Papageorgiou, Dr. Athanasios Samaras, and Mr. Antonios Geropoulos for their comments on the manuscript.
Funding
This work is part of the PhD Thesis of I. Tsikopoulou who was funded by HYPOXIA (EU/GSRT Aristeia II), LifeWatchGreece Research Infrastructure (GSRT/ESFRI Projects/NSFR), and AQUASPACE (EU, HORIZON 2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsikopoulou, I., Moraitis, M.L., Tsapakis, M. et al. Can intensive fish farming for 20 years induce changes in benthic ecosystems on a scale of waterbody? An assessment from Cephalonia bay (Ionian Sea). Environ Monit Assess 190, 469 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6846-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6846-5