Abstract
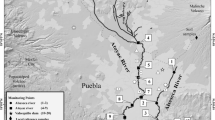
The objective of this research is to characterize the variability of trace metals in the Rio Santa watershed based on synoptic sampling applied at a large scale. To that end, we propose a combination of methods based on the collection of water, suspended sediments, and riverbed sediments at different points of the watershed within a very limited period. Forty points within the Rio Santa watershed were sampled between June 21 and July 8, 2013. Forty water samples, 36 suspended sediments, and 34 riverbed sediments were analyzed for seven trace metals. The results, which were normalized using the USEPA guideline for water and sediments, show that the Rio Santa water exhibits Mn concentrations higher than the guideline at more than 50% of the sampling points. As is the second highest contaminating element in the water, with approximately 10% of the samples containing concentrations above the guideline. Sediments collected in the Rio Santa riverbed were heavily contaminated by at least four of the tested elements at nearly 85% of the sample points, with As presenting the highest normalized concentration, at more than ten times the guideline. As, Cd, Fe, Pb, and Zn present similar concentration trends in the sediment all along the Rio Santa.
The findings indicate that care should be taken in using the Rio Santa water and sediments for purposes that could affect the health of humans or the ecosystem. The situation is worse in some tributaries in the southern part of the watershed that host both active and abandoned mines and ore-processing plants.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackermann, F. (1980). A procedure for correcting the grain size effect in heavy metal analyses of estuarine and coastal sediments. Environmental Technology Letters, 1(11), 518–527. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593338009384008.
Angove, M. J., Johnson, B. B., & Wells, J. D. (1998). The influence of temperature on the adsorption of cadmium (II) and cobalt (II) on kaolinite. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 204(1), 93–103. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.1998.5549.
Baraer, M., Mark, B. G., McKENZIE, J. M., Condom, T., Bury, J., Huh, K-I., et. al (2012) "Glacier recession and water resources in Peru's Cordillera Blanca." Journal of Glaciology, 58(207), 134–150.
Benin, A. L., Sargent, J. D., Dalton, M., & Roda, S. (1999). High concentrations of heavy metals in neighborhoods near ore smelters in northern Mexico. Environmental Health Perspectives, 107(4), 279–284. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.99107279.
Bradl, H., Kim, C., Kramar, U., & Stüben, D. (2005). Heavy metals in the environment: origin, interaction and remediation. In H. Bradl (Ed.), (Vol. Volume 6, pp. 28–164): Elsevier-Academic press.
Brunel, C. (2005). Dynamique Des Elements Traces Metalliques (Pb, Zn Et Cd) Sur Un Petit Bassin Versant Contamine Par Des Dechets Miniers–Cas Du Bassin Versant Amont Du Lez (Ariege, Pyrenees). Sciences de l’Univers, de l’Espace et de l’Environnement. University Toulouse III - Paul Sabatier.
Burns, P., & Nolin, A. (2014). Using atmospherically-corrected Landsat imagery to measure glacier area change in the Cordillera Blanca, Peru from 1987 to 2010. Remote Sensing of Environment, 140, 165–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2013.08.026.
Bury, J., Mark, B. G., Carey, M., Young, K. R., McKenzie, J. M., Baraer, M., French, A., & Polk, M. H. (2013). New geographies of water and climate change in Peru: coupled natural and social transformations in the Santa River watershed. Annals of the Association of American Geographers, 103(2), 363–374. https://doi.org/10.1080/00045608.2013.754665.
Bury, J. T., Mark, B. G., McKenzie, J. M., French, A., Baraer, M., Huh, K. I., Zapata Luyo, M. A., & Gómez López, R. J. (2011). Glacier recession and human vulnerability in the Yanamarey watershed of the Cordillera Blanca, Peru. Climatic Change, 105(1–2), 179–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-010-9870-1.
Carey, M., Baraer, M., Mark, B. G., French, A., Bury, J., Young, K. R., & McKenzie, J. M. (2014). Toward hydro-social modeling: merging human variables and the social sciences with climate-glacier runoff models (Santa River, Peru). Journal of Hydrology, 518(PA), 60–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.11.006.
de-Groot, A. J., Zschuppel, K. H., & Salomons, W. (1982). Standardization of methods of analysis for heavy metals in sediments. Hydrobiologia, 91(1), 689–695.
de Popovici, G. C. (2012). Estudio Hidrobiológico en la Cuenca Superior del Río Santa, Ancash-Perú. http://www.macaglochapoperu.com/ESTUDIOHIDROLOGICO.pdf. Accessed 4 April 2017.
Environnement Canada (2007). Ministère du Développement durable de l’Environnement et des Parcs du Québec. Critères pour l’évaluation de la qualité des sédiments au Québec et cadres d’application : prévention, dragage et restauration. http://planstlaurent.qc.ca/fileadmin/publications/diverses/Qualite_criteres_sediments_f.pdf. Accessed 4 April 2017.
Facundo, M. J. (2011). Extracción química secuencial de metales pesados en el estudio de alteración química de relaves de mina en Ticapampa (Huaraz, Perú). Boletín Geológico y Minero, 122(2), 221–234.
Fernandez, A., Mark, B. G., & Wigmore, O. (2012). Unpublished data.
Fortner, S. K., Mark, B. G., McKenzie, J. M., Bury, J., Trierweiler, A., Baraer, M., Burns, P. J., & Munk, L. A. (2011). Elevated stream trace and minor element concentrations in the foreland of receding tropical glaciers. Applied Geochemistry, 26(11), 1792–1801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.06.003.
Gaines, P. (2014). Mercury chemical stability. http://www.inorganicventures.com/mercury-chemical-stability.
Galewski, N. (2010). Campesino community participation in watershed management. Georgia Institute of Technology. https://smartech.gatech.edu/bitstream/handle/1853/34753/galewski_nancy_m_201008_master.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y . Accessed 4 April 2017.
Goldberg, S. (1986). Chemical modeling of arsenate adsorption on aluminum and iron oxide minerals. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 50(5), 1154–1157. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1986.03615995005000050012x.
Hall, S., Chakraborty, J., & Ruch, R. (1996). Chemical exposure and toxic responses. Raton, Fl., USA: CRC Press.
Järup, L. (2003). Hazards of heavy metal contamination. British Medical Bulletin, 68(1), 167–182. https://doi.org/10.1093/bmb/ldg032.
Jones, C. A., Nimick, D. A., & McCleskey, R. B. (2004). Relative effect of temperature and pH on diel cycling of dissolved trace elements in Prickly Pear Creek, Montana. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 153(1–4), 95–113. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000019934.64939.f0.
Kaser, G., Ames, A., & Zamora, M. (1990). Glacier fluctuations and climate in the Cordillera Blanca, Peru. Annals of Glaciology, 14, 136–140. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0260305500008430.
Kaser, G., & Georges, C. (1999). On the mass balance of low latitude glaciers with particular consideration of the Peruvian Cordillera Blanca. Geografiska Annaler: Series A. Physical Geography, 81(4), 643–651.
Kaser, G., Juen, I., Georges, C., Gómez, J., & Tamayo, W. (2003). The impact of glaciers on the runoff and the reconstruction of mass balance history from hydrological data in the tropical Cordillera Bianca, Perú. Journal of Hydrology, 282(1–4), 130–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(03)00259-2.
Li, H., Shi, A., Li, M., & Zhang, X. (2013). Effect of pH, temperature, dissolved oxygen, and flow rate of overlying water on heavy metals release from storm sewer sediments. Journal of Chemistry, 2013.
Lofts, S., Chapman, P. M., Dwyer, R., McLaughlin, M. J., Schoeters, I., Sheppard, S. C., et al. (2007). Critical loads of metals and other trace elements to terrestrial environments. Environmental Science and Technology, 41(18), 6326–6331. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0726106.
Lynch, B. D. (2012). Vulnerabilities, competition and rights in a context of climate change toward equitable water governance in Peru’s Rio Santa Valley. Global Environmental Change, 22(2), 364–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2012.02.002.
Machesky, M. L. (1990) Influence of temperature on ion adsorption by hydrous metal oxides. In ACS symposium series, (Vol. 416, pp. 282–292): Oxford University Press.
Mark, B. G. (2008). Tracing tropical Andean glaciers over space and time: some lessons and transdisciplinary implications. Global and Planetary Change, 60(1–2), 101–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2006.07.032.
McKenzie, R. (1980). The adsorption of lead and other heavy metals on oxides of manganese and iron. Soil Research, 18(1), 61–73. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR9800061.
McKinney, D., Anderson, G., & Byers, A. (2011). Adaptation to climate change: a case study–Glacial retreat and adaptation options in Peru’s Rio Santa basin. United States Agency for International Development (USAID) Report.
McNulty, B. A., Farber, D. L., Wallace, G. S., Lopez, R., & Palacios, O. (1998). Role of plate kinematics and plate-slip-vector partitioning in continental magmatic arcs: evidence from the Cordillera Blanca, Peru. Geology, 26(9), 827–830. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(1998)026<0827:ROPKAP>2.3.CO;2.
MINEM (1998). Estudio de evaluación ambiental territorial y de planeamiento para reducción o eliminación de la contaminación de origen minero en la cuenca del río Santa. Ministerio De Energia y Minas. http://www.minem.gob.pe/minem/archivos/file/DGAAM/publicaciones/evats/santa/Santa.pdf. Accessed 3 April 2017.
Murcott, S. (2012). Arsenic contamination in the world, an international sourcebook. London: IWA Publishing.
Myers, J. S. (1975). Vertical crustal movements of the Andes in Peru. Nature, 254(5502), 672–674. https://doi.org/10.1038/254672a0.
Nriagu, J. O., & Pacyna, J. M. (1988). Quantitative assessment of worldwide contamination of air, water and soils by trace metals. Nature, 333(6169), 134–139. https://doi.org/10.1038/333134a0.
Parker, S. R., Gammons, C. H., Poulson, S. R., & DeGrandpre, M. D. (2007). Diel variations in stream chemistry and isotopic composition of dissolved inorganic carbon, upper Clark Fork River, Montana, USA. Applied Geochemistry, 22(7), 1329–1343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2007.02.007.
Perada, M. (2010). Determinación De Plomo En Aguas Del Río Santa. Facultad de Ciencias de la Salud: Universidad Católica Los Ángeles De Chimbote.
Petford, N., & Atherton, M. P. (1992). Granitoid emplacement and deformation along a major crustal lineament: the Cordillera Blanca, Peru. Tectonophysics, 205(1–3), 171–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(92)90425-6.
Rojas Vargas, R. A. (1981). Estudio de contaminación y preservación del río Santa. Direccion General del Medio Ambiente del Ministerio de Salud. http://bases.bireme.br/cgi-bin/wxislind.exe/iah/online/?IsisScript=iah/iah.xis&src=google&base=REPIDISCA&lang=p&nextAction=lnk&exprSearch=143500&indexSearch=ID. Accessed 4 April 2017. In.
Romero, A. A., Flores, S. L., & Pacheco, W. W. (2010). Estudio de la calidad de agua de la cuenca del río Santa. Revista del Instituto de Investigaciones FIGMMG, 13(25), 61–69.
Saeedi, M., Li, L. Y., Karbassi, A. R., & Zanjani, A. J. (2013). Sorbed metals fractionation and risk assessment of release in river sediment and particulate matter. [Research support, non-U.S. Gov’t]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(2), 1737–1754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2664-3.
Simons, G. W. H., Bastiaanssen, W. G. M., & Immerzeel, W. W. (2015). Water reuse in river basins with multiple users: a literature review. Journal of Hydrology, 522, 558–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.01.016.
Smolders, A. J. P., Lock, R. A. C., Van der Velde, G., Medina Hoyos, R. I., & Roelofs, J. G. M. (2003). Effects of mining activities on heavy metal concentrations in water, sediment, and macroinvertebrates in different reaches of the Pilcomayo River, South America. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 44(3), 314–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-002-2042-1.
Suresh, G., Sutharsan, P., Ramasamy, V., & Venkatachalapathy, R. (2012). Assessment of spatial distribution and potential ecological risk of the heavy metals in relation to granulometric contents of Veeranam lake sediments, India. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 84, 117–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.06.027.
Thomas, R. P., Ure, A. M., Davidson, C. M., Littlejohn, D., Rauret, G., Rubio, R., & López-Sánchez, J. F. (1994). Three-stage sequential extraction procedure for the determination of metals in river sediments. Analytica Chimica Acta, 286(3), 423–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2670(94)85088-7.
USEPA (1996). Method 1669—sampling ambient water for trace metals at EPA water quality criteria levels. US Environmental Protection Agency. Office of Water, Washington, DC.
USEPA. (2006). EPA Region III BTAG. Freshwater Sediment Screening: Benchmarks.
USEPA (2009). Drinking water contaminants. http://water.epa.gov/drink/contaminants/index.cfm#Inorganic.
USEPA (2012). Edition of the drinking water standards and health advisories. Office of Water, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC.
Vergara, W., Deeb, A., & Leino, I. (2011). Assessment of the impacts of climate change on mountain hydrology: development of a methodology through a case study in the Andes of Peru: World Bank Publications, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1596/978-0-8213-8662-0.
Walsh, E. A. (2013). The origin and distribution of trace metals in the Rio Santa watershed, Peru. McGill University, Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences.
WHO. (2011). Guidelines for drinking-water quality, fourth edition. In Chapter 8—chemical aspects.
Zhang, C., Wang, L., Li, G., Dong, S., Yang, J., & Wang, X. (2002). Grain size effect on multi-element concentrations in sediments from the intertidal flats of Bohai Bay, China. Applied Geochemistry, 17(1), 59–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(01)00079-8.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank École de technologie supérieure in Canada for its support in carrying out the research under the best possible conditions.
Funding
We are grateful for the funding provided by the National Science Foundation (BCS-0752175), the Geochemistry and Geodynamics Research Centre of Québec (GEOTOP), the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), McGill University, and the Climate, Water and Carbon Program at The Ohio State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guittard, A., Baraer, M., McKenzie, J.M. et al. Trace-metal contamination in the glacierized Rio Santa watershed, Peru. Environ Monit Assess 189, 649 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6353-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6353-0