Abstract
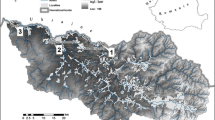
The lower Don River in the south of the European part of Russia was studied to determine the concentration, spatial distribution, and sources of 19 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediments. Total PAH concentrations ranged from 14.2 to 529 ng/g-dw. Sedimentary PAH concentrations were higher in the delta of the Don River and in the estuaries of rivers Sal and Aksai compared to the main channel of the Don. Analysis of the PAHs sources showed that PAHs came mostly from pyrogenic sources as a result of incomplete combustion of coal. Bioluminescent bacterial sensors were used for ecotoxicological assessment of surface sediments. The surface sediments of all the investigated stations of lower reaches of the Don River were toxic and genotoxic. The maximum concentration of PAHs and the high genotoxicity effect caused by the presence of genotoxicants were found in the surface sediments of the same stations. Significant correlations between the concentrations of individual PAHs in sediments and the genotoxic effect were found. Correlation between genotoxicity of surface sediments and concentration of phenanthrene and benz(k)fluoranthene was the most significant both with and without application of metabolic activation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aichner, B., Bussian, B., Lehnik-Habrink, P., & Hein, S. (2013). Levels and spatial distribution of persistent organic pollutants in the environment: a case study of German forest soils. Environmental science & technology, 47(22), 12703–12714.
Akyüz, M., & Cabuk, H. (2010). Gas-particle partitioning and seasonal variation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the atmosphere of Zonguldak, Turkey. Science of the total environment, 408(22), 5550–5558.
Aouadene, A., Di Giorgio, C., Sarrazin, L., Moreau, X., De Jong, L., Garcia, F., Thiery, A., Botta, A., & De Méo, M. (2008). Evaluation of the genotoxicity of river sediments from industrialized and unaffected areas using a battery of short-term bioassays. Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis. doi:10.1002/em.20384.
Behymer, T. D., & Hites, R. A. (1985). Photolysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons adsorbed on simulated atmospheric particulates. Environmental science & technology, 19, 1004–1006.
Belkin, S. (2003). Microbial whole-cell sensing systems of environmental pollutants. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 6(3), 206–212.
Bihari, N., Fafandel, M., Hamer, B., & Kralj-Bilen, B. (2006). PAH content, toxicity and genotoxicity of coastal marine sediments from the Rovinj area, Northern Adriatic, Croatia. Science of The Total Environment. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.12.001.
Boitsov, S., Petrova, V., Jensen, H. K., Kursheva, A., Litvinenko, I., & Klungsøyr, J. (2013). Sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in marine sediments from southern and northern areas of the Norwegian continental shelf. Marine environmental research, 87–88, 73–84.
Boonyatumanond, R., Wattayakorn, G., Togo, A., & Takada, H. (2006). Distribution and origins of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in riverine, estuarine, and marine sediments in Thailand. Marine pollution bulletin, 52, 942–956.
Burgess, R. M., Ahrens, M. J., & Hickey, C. W. (2003). Geochemistry of PAHs in aquatic environments: source, persistence and distribution. In P. E. T. Douben (Ed.), PAHs: an ecotoxicological perspective (pp. 35–45). West Sussex, United Kingdom: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Cachot, J., Geffard, O., Augagneur, S., Lacroix, S., Le Menach, K., Peluhet, L., Couteau, J., Denier, X., Devier, M. H., Pottier, D., & Budzinski, H. (2006). Evidence of genotoxicity related to high PAH content of sediments in the upper part of the Seine estuary (Normandy, France). Aquatic Toxicology, 79(3), 257–267.
Christensen, E. R., & Bzdusek, P. A. (2005). PAHs in sediments of the Black River and the Ashtabula River, Ohio: source apportionment by factor analysis. Water Research, 39, 511–524.
Fernandes, M. B., & Brooks, P. (2003). Characterization of carbonaceous combustion residues: II. Non-polar organic compounds. Chemosphere, 53, 447–458.
Havelcová, M., Melegy, A., & Rapant, S. (2014). Geochemical distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils and sediments of El-Tabbin, Egypt. Chemosphere, 95, 63–74.
Hiller, E., Sirotiak, M., Jurkovic, L., & Zemanová, L. (2009). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments from three water reservoirs, Slovakia. Bulletin of environmental contamination and toxicology, 83, 444–448.
Jahin, H. S., Barsoum, B. N., Tawfic, T. A., & Headley, J. V. (2009). Occurrence and distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Egyptian aquatic environment. Journal of environmental science and health, Part A: Toxic/hazardous substances & environmental engineering. doi:10.1080/10934520903139969.
Kamens, R. M., Guo, Z., Fulcher, J. N., & Bell, D. A. (1988). The influence of humidity, sunlight, and temperature on the daytime decay of polyaromatic hydrocarbons on atmospheric soot particles. Environmental science & technology, 22, 103–108.
Koyama, J., Uno, S., & Cono, K. (2004). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contamination and recovery characteristics in some organisms after the Nakhodka oil spill. Marine pollution bulletin, 49, 1054–1061.
Li, G., Xia, X., Yang, Z., Wang, R., & Voulvoulis, N. (2006). Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River, China. Environmental pollution, 144, 985–993.
Lin, D., & Zhu, L. (2004). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: pollution and source analysis of a black tea. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 52(26), 8268–8271.
Liu, Y., Chen, L., Jianfu, Z., Qinghui, H., Zhiliang, Z., & Hongwen, G. (2008). Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments of rivers and an estuary in Shanghai, China. Environmental pollution, 154(2), 298–305.
Liu, Y., Beckingham, B., Ruegner, H., Li, Z., Ma, L., Schwientek, M., Xie, H., Zhao, J., & Grathwohl, P. (2013). Comparison of sedimentary PAHs in the rivers of Ammer (Germany) and Liangtan (China): differences between early- and newly-industrialized countries. Environmental science & technology. doi:10.1021/es3031566.
Lyla, S., Manokaran, S., & Khan, A. (2012). Petroleum hydrocarbon distribution in continental shelf region of southeast coast of India. International Journal of Sediment Research. doi:10.1016/S1001-6279(12)60017-1.
Ma, L. L., Chu, S. G., Wang, X. T., Cheng, H. X., Liu, X. F., & Xu, X. B. (2005). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the surface soils from outskirts of Beijing, China. Chemosphere, 58, 1355–1363.
Ma, X. Y., Wang, X. C., Ngo, H. H., Guo, W., Wu, M. N., & Wang, N. (2014). Bioassay based luminescent bacteria: interferences, improvements, and applications. Science of The Total Environment. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.028.
Man, Y. B., Chow, K. L., Kang, Y., & Wong, M. H. (2013). Mutagenicity and genotoxicity of Hong Kong soils contaminated by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and dioxins/furans. Mutation Research. doi:10.1016/j.mrgentox.2013.01.004.
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E. F., & Sambrook, J. (1982). Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.
Moreno-González, R., Campillo, J. A., & León, V. M. (2013). Influence of an intensive agricultural drainage basin on the seasonal distribution of organic pollutants in seawater from a Mediterranean coastal lagoon (Mar Menor, SE Spain). Marine pollution bulletin, 77, 400–411.
Nguyen, H. T., Kim, K. H., Ma, C. J., & Oh, J. M. (2010). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon concentration levels on the Korean peninsula between 2006 and 2008. ScientificWorld Journal, 10, 20–37.
Quante, M., Ebinghaus, R., & Flöser, G. (2011). Persistent pollution—past, present and future. Berlin, Germany: Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Robertson, A. (1998). Arctic monitoring, assessment programme. Arctic Pollution Issues, Oslo: AMAP Assessment Report.
Rocher, V., Azimi, S., Moilleron, R., & Chebbo, G. (2004). Hydrocarbons and heavy metals in the different sewer deposits in the ‘Le Marais’ catchment (Paris, France): stocks, distributions and origins. The Science of the total environment, 323, 107–122.
Sauer, T. C., Michel, J., Hayes, M. O., & Aurand, D. V. (1998). Hydrocarbon characterization and weathering of oiled intertidal sediments along the Saudi Arabian Coast two years after the Gulf War oil spill. Environment International. doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(97)00120-7.
Sazykina, M. A., Chistyakov, V. A., & Sazykin, I. S. (2012). Genotoxicity of Don River surface sediments (2001–2007). Water Resources, 39, 118–124.
Sazykina, М.А., Chistyakov, V.A., Voinova, N.V. (2002). A method for determining the genotoxicity of chemicals. RU Patent, application 2179581 C1, 17.07.2000.
Schwarz, K., Gocht, T., & Grathwohl, P. (2011). Transport of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in highly vulnerable karst systems. Environmental Pollution. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2010.09.026.
Slezakova, K., Pires, J. C., Castro, D., Alvim-Ferraz, M. C., Delerue-Matos, C., Morais, S., & Pereira, M. C. (2013). PAH air pollution at a Portuguese urban area: carcinogenic risks and sources identification. Environmental science and pollution research international, 20(6), 3932–3945.
Soclo, H. H., Garrigues, P., & Ewald, M. (2000). Origin of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in coastal marine sediments: case studies in Cotonou (Benin) and Aquitaine (France) areas. Marine pollution bulletin, 40, 387–396.
Unlü, S., & Alpar, B. (2009). Evolution of potential ecological impacts of the bottom sediment from the Gulf of Gemlik; Marmara Sea, Turkey. Bulletin of environmental contamination and toxicology, 83, 903–906.
Vollmer, A. C., Belkin, S., Smulski, D. R., VanDyk, T. K., & LaRossa, R. A. (1997). Detection of DNA damage by use of Escherichia coli carrying recA′::lux, uvrA′::lux, or alkA′::lux reporter plasmids. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 63(7), 2566–2571.
Wang, X. T., Chu, S. G., Ma, L. L., Sun, Y. Z., Li, X. H., & Xu, X. B. (2004). Contamination of priority polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water from Guanting reservoir and the Yongding river, China. Bulletin of environmental contamination and toxicology, 72(1), 194–201.
Wang, X. C., Sun, S., Ma, H. Q., & Liu, Y. (2006). Sources and distribution of aliphatic and polyaromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of Jiaozhou Bay, Qingdao, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 52(2), 129–138.
White, P. A., & Claxton, L. (2004). Mutagens in contaminated soil: a review. Mutation Research. doi:10.1016/j.mrrev.2004.09.003.
Woutersen, M., Belkin, S., Brouwer, B., van Wezel, A. P., & Heringa, M. B. (2011). Are luminescent bacteria suitable for online detection and monitoring of toxic compounds in drinking water and its sources? Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 400(4), 915–929.
Yang, Y., Ligouis, B., Pies, C., Grathwohl, P., & Hofmann, T. (2008). Occurrence of coal and coal-derived particle-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in a river floodplain soil. Environmental Pollution. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2007.02.020.
Yang, Y., Van Metre, P. C., Mahler, B. J., Wilson, J. T., Ligouis, B., Razzaque, M. M., Schaeffer, D. J., & Werth, C. J. (2010). Influence of coal-tar sealcoat and other carbonaceous materials on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon loading in an urban watershed. Environmental science & technology. doi:10.1021/es902657h.
Yin, C. Q., Jiang, X., Yang, X. L., Bian, Y. R., & Wang, F. (2008). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils in the vicinity of Nanjing. China. Chemosphere. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.05.041.
Yunker, M. B., Macdonald, R. W., Vingarzan, R., Mitchell, R. H., Goyette, D., & Sylvestre, S. (2002). PAHs in the Fraser River Basin: a critical appraisal of PAH ratios as indicators of PAH source and composition. Organic geochemistry, 33, 489–515.
Zakaria, M. P., Takada, H., Tsutsumi, S., Ohno, K., Yamada, J., Kouno, E., & Kumata, H. (2002). Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in rivers and estuaries in Malaysia: a widespread input of petrogenic PAHs. Environmental science & technology, 36, 1907–1918.
Zedeck, M. S. (1980). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: a review. Journal of environmental pathology and toxicology, 3, 537–567.
Zhang, H. B., Luo, Y. M., Wong, M. H., Zhao, Q. G., & Zhang, G. L. (2006). Distributions and concentrations of PAHs in Hong Kong Soils. Environmental pollution, 141, 107–114.
Zhang, D., Ding, A., Cui, S., Hu, C., Thornton, S. F., Dou, J., Sun, Y., & Huang, W. E. (2013a). Whole cell bioreporter application for rapid detection and evaluation of crude oil spill in seawater caused by Dalian oil tank explosion. Water Research. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2012.11.038.
Zhang, H., Sun, L., Sun, T., Li, H., & Luo, Q. (2013b). Spatial distribution and seasonal variation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) contaminations in surface water from the Hun River, Northeast China. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 185, 1451–1462.
Acknowledgments
The study was funded by the Southern Federal University (grant no. 213.01-07-2014/12 PCVG), the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation (grant no. 1894), and the leading scientific school of the Russian Federation (grant no. NS-2449.2014.4).
Ethical statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sazykin, I.S., Sazykina, M.A., Khammami, M.I. et al. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments of lower reaches of the Don River (Russia) and their ecotoxicologic assessment by bacterial lux-biosensors. Environ Monit Assess 187, 277 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4406-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4406-9