Abstract
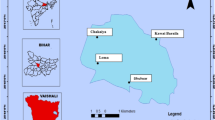
Metal concentrations were determined in surface sediments and transplanted mussels in a shallow semi-enclosed bay, Pagassitikos Gulf, Aegean Sea. Cu, Zn, Pb, Hg, and As levels in sediments were enriched close to point sources of pollution, i.e., Volos Port and cement plant. Fe, Mn, Cr, and Ni spatial distributions in sediments were rather uniform with increasing concentrations towards deeper sites, suggesting natural enrichment, whereas levels found in the port, although elevated, were not the highest in the study area. Spatial variations in concentrations of most metals in mussels transplanted nearshore were generally in accordance to those in sediments, with the highest Fe, Mn, Cr, Ni, and Cu levels in the port and the highest Hg levels close to the cement plant. Concentrations of metals in sediments and transplanted mussels were comparable to those reported in Mediterranean areas. Results indicate that pollution point sources contribute to anthropogenic metal enrichment in the study area.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aloupi, M., & Angelidis, M. O. (2002). The significance of coarse sediments in metal pollution studies in the coastal zone. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 133, 121–131.
Andral, B., Stanisiére, J. Y., Sauzade, D., Damier, E., Thebault, H., Galgani, F., et al. (2004). Monitoring chemical contamination levels in the Mediterranean based on the use of mussel caging. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 49, 704–712.
Andral, B., Galgani, F., Tomasino, C., Bouchoucha, M., Blottiere, C., Scarpato, A., et al. (2011). Chemical contamination baseline in the Western Basin of the Mediterranean Sea based on transplanted mussels. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 61, 261–271.
Ansari, T. M., Marr, I. L., & Tariq, N. (2004). Heavy metals in marine pollution perspective—a mini review. Journal of Applied Sciences, 4, 1–20.
Casado-Martínez, M. C., Forja, J. M., & DelValls, T. A. (2009). A multivariate assessment of sediment contamination in dredged materials from Spanish ports. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163, 1353–1359.
Damiens, G., Gnassia-Barelli, M., Loquès, F., Roméo, M., & Salbert, V. (2007). Integrated biomarker response index as a useful tool for environmental assessment evaluated using transplanted mussels. Chemosphere, 66, 574–583.
Deudero, S., Box, A., Tejada, S., & Tintoré, J. (2009). Stable isotopes and metal contamination in caged marine mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 58, 1025–1031.
Devier, M.-H., Augagneur, S., Budzinski, H., Le Menach, K., Mora, P., Narbonne, J.-F., et al. (2005). One-year monitoring survey of organic compounds (PAHs, PCBs, TBT), heavy metals and biomarkers in blue mussels from the Arcachon Bay, France. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 7, 224–240.
Esen, E., Kucuksezgin, F., & Uluturhan, E. (2010). Assessment of trace metal pollution in surface sediments of Nemrut Bay, Aegean Sea. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 160, 257–266.
Förstner, U., & Salomons, W. (1980). Trace metal analysis on polluted sediments. Part I: assessment of sources and intensities. Environmental Technology Letters, 1, 494–505.
Galanopoulou, S., Vgenopoulos, A., & Conispoliatis, N. (2009). Anthropogenic heavy metal pollution in the surficial sediments of the Keratsini Harbor, Saronikos Gulf, Greece. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 202, 121–130.
Georgakopoulou-Gregoriadou, E., Voutsinou-Taliadouri, F., Gotsis-Skretas, O., & Psyllidou-Giouranovits, R. (1997). Water quality assessment through organochlorine and biological analyses in a semi-enclosed embayment (Pagassitikos Gulf, Hellas). Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 6, 154–159.
Goldberg, E. D. (1975). The mussel watch. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 6, 111–113.
Hunt, C. D., & Slone, E. (2010). Long-term monitoring using resident and caged mussels in Boston Harbor yield similar spatial and temporal trends in chemical contamination. Marine Environmental Research, 70, 343–357.
Joksimovic, D., Tomic, I., Stankovic, R., Jovic, M., & Stankovic, S. (2011). Trace metal concentrations in Mediterranean blue mussel and surface sediments and evaluation of the mussels quality and possible risks of high human consumption. Food Chemistry, 127, 632–637.
Karageorgis, A., Sioulas, A., & Anagnostou, C. (2002). Use of surface sediments in Pagassitikos Gulf, Greece, to detect anthropogenic influence. Geo-Marine Letters, 21, 200–211.
Karageorgis, A. P., Katsanevakis, S., & Kaberi, H. (2009). Use of enrichment factors for the assessment of heavy metal contamination in the sediments of Koumoundourou Lake, Greece. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 204, 243–258.
Kress, N., Herut, B., & Galil, B. S. (2004). Sewage sludge impact on sediment quality and benthic assemblages off the Mediterranean coast of Israel—a long-term study. Marine Environmental Research, 57, 213–233.
Landi, S., & Fagioli, F. (1994). The adaptation of the dichromate digestion method for total mercury determination by cold-vapor atomic absorption spectrometry to the analysis of soils, sediments and sludges. Analytica Chimica Acta, 298, 363–374.
Lobel, P. B., Bajdik, C. D., Belkhode, S. P., Jackson, S. E., & Longerich, H. P. (1991). Improved protocol for collecting mussel watch specimens taking into account sex, size, condition, shell shape and chronological age. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 21, 409–414.
Long, E. R., Mac Donald, D. D., Smith, S. L., & Calder, F. D. (1995). Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environmental Management, 19, 81–97.
MacDonald, D. D., Carr, R. S., Calder, F. D., Long, E. R., & Ingersoll, C. G. (1996). Development and evaluation of sediment quality guidelines for Florida coastal waters. Ecotoxicology, 5, 253–278.
Moukhchan, F., March, J. G., & Cerdá, V. (2012). Distribution of trace metals in marine sediments of the Bay of Palma de Mallorca (Mallorca Island, Spain). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. doi:10.1007/s10661-012-2585-1.
Mzoughi, N., & Chouba, L. (2012). Heavy metals and PAH assessment based on mussel caging in the North coast of Tunisia (Mediterranean Sea). International Journal of Environmental Research, 6, 109–118.
Przytarska, J. E., Sokołowski, E., Wołowicz, M., Hummel, H., & Jansen, J. (2010). Comparison of trace metal bioavailabilities in European coastal waters using mussels from Mytilus edulis complex as biomonitors. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 166, 461–476.
Rainbow, P. S. (1995). Biomonitoring of heavy metal availability in the marine environment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 31, 183–192.
Rainbow, P. S., Wolowicz, M., Fialkowski, W., Smith, B. D., & Sokolowski, A. (2000). Biomonitoring of trace metals in the Gulf of Gdansk, using mussels (Mytilus trossulus) and barnacles (Balanus improvisus). Water Research, 34, 1823–1829.
Salomons, W., & Foerstner, U. (1984). Metals in the hydrocycle. Berlin: Springer.
Smith, P. A., & Cronan, D. S. (1975). Chemical composition of Aegean Sea sediments. Marine Geology, 18, 7–11.
Sprovieri, M., Feo, M. L., Prevedello, L., Manta, D. S., Sammartino, S., Tamburrino, S., et al. (2007). Heavy metals, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and polychlorinated biphenyls in surface sediments of the Naples harbour (southern Italy). Chemosphere, 67, 998–1009.
Stamatis, N., Ioannidou, D., Christoforidis, A., & Koutrakis, E. (2002). Sediment pollution by heavy metals in the Strymonikos and Ierissos Gulfs, North Aegean Sea, Greece. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 80, 33–49.
Szefer, P., Szefer, K., Glasby, G. P., Pempkowiak, J., & Kaliszan, R. (1996). Heavy metal pollution in surficial sediments from the Southern Baltic Sea off Poland. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part A-Toxic/Hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering, 31, 2723–2754.
Tsangaris, C., Strogyloudi, E., & Papathanassiou, E. (2004). Measurement of biochemical markers of pollution in mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis from coastal areas of the Saronicos Gulf (Greece). Mediterranean Marine Science, 5, 175–186.
Tsangaris, C., Papathanasiou, E., & Cotou, E. (2007). Assessment of the impact of heavy metal pollution from a ferro-nickel smelting plant using biomarkers. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 66, 232–243.
Tsangaris, C., Hatzianestis, I., Catsiki, V. A., Kormas, K. A., Strogyloudi, E., Neofitou, C., et al. (2011). Active biomonitoring in Greek coastal waters: application of the integrated biomarker response index in relation to contaminant levels in caged mussels. Science of the Total Environment, 412–413, 359–365.
UNEP. (1984). Determination of total Cd, Zn, Pd and Cu in selected marine organisms by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Reference Methods for Marine Pollution Studies, No 11, Rev 1
Violintzis, C., Arditsoglou, A., & Voutsa, D. (2009). Elemental composition of suspended particulate matter and sediments in the coastal environment of Thermaikos Bay, Greece: delineating the impact of inland waters and wastewaters. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 166, 1250–1260.
Voutsinou-Taliadouri, F., & Georgakopoulou-Grigoriadou, E. (1989). Heavy metal concentrations in surface sediments from Pagassitikos Gulf, Greece. Toxicological & Environmental Chemistry, 20–21, 53–58.
Voutsinou-Taliadouri, F., & Satsmadjis, J. (1982). Trace metals in the Pagassitikos Gulf, Greece. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 15, 221–228.
Voutsinou-Taliadouri, F., & Varnavas, S. P. (1993). Geochemical study of sediments from northern Euboekos Bay, Greece, with regard to the presence of submarine mineral deposits. Marine Geology, 110, 93–114.
Voutsinou-Taliadouri, F., Kaberi, H., Krassakopoulou, E., Zeri, C., & Kioroglou, S. (2007). Study of the origin of certain metals in surface sediments of Pagassitikos Gulf, Aegean Sea. Rapp. Comm. Int. Mer Medit., 38.
Walker, C. H., Hopkin, S. P., Sibly, R. M., & Peakal, D. B. (2006). Principles of ecotoxicology (3rd ed.). Boca Raton: CRC, Taylor & Francis Group.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsangaris, C., Kaberi, H. & Catsiki, VA. Metal levels in sediments and transplanted mussels in Pagassitikos Gulf (Aegean Sea, Eastern Mediterranean). Environ Monit Assess 185, 6077–6087 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-3008-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-3008-z