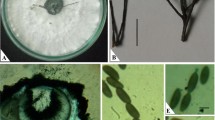
Abstract
The causal agent of red root rot disease of common vetch (Vicia sativa) on the far North Coast of New South Wales, Australia, has been identified as Atractiella rhizophila. This basidiomycete infected root tissues directly without specialized appressoria, and developed as a necrotroph in the cortex external to the stele. It has been recorded previously as a non-pathogenic endophyte of Populus spp. and Pinus spp. roots, and a symbiont on Quercus rubra, but this is the first report of A. rhizophila as a plant pathogen.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Difco:
-
a product name of Becton, Dickinson and Company, 7 Loveton Circle, Sparks, Maryland 21,152, USA
- DNA:
-
deoxyribonucleic acid
- GenBank:
-
USA National Centre for Biotechnology Information Nucleotide Database
- ITS:
-
internal transcribed spacer
- LSU:
-
large sub-unit
- M:
-
molar; mol dm-3
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- PDA:
-
half-strength Difco potato dextrose agar; 19.5 g l-1 Difco PDA plus 7.5 g l-1 Difco agar
- USA:
-
United States of America
- WA:
-
15 g l-1 Difco agar
References
Allen, R. N. (1967). The root and stem rot disease of vetch. M.Sc.Agric. Dissertation, University of Sydney, 135 pp.
Allen, R. N. (1972). Diseases of Golden Tares in the Richmond Valley of New South Wales. Agricultural Gazette of New South Wales, 81, 244–246.
Baker, K. F. (1957). The UC system for producing healthy container grown plants. Berkeley, USA: University of California Press.
Barnard, C. (1970). Register of Australian herbage plant cultivars, 2nd edition. Canberra, Australia: CSIRO Publishing.
Bonito, G., Hameed, K., Toome-Heller, M., Healy, R., Reid, C., Liao, H.-L., Aime, M. C., Schadt, C. & Vilgalys, R. (2017). Atractiella rhizophila sp. nov., an endorrhizal fungus isolated from the Populus root microbiome. Mycologia, 109, 18–26.
Date, R. A. & Vincent, J. M. (1962). Determination of the number of root nodule bacteria in the presence of other organisms. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture and Animal Husbandry, 2, 5–7.
Gardes, M. & Bruns, T. D. (1993). ITS primers with enhanced specificity for basidiomycetes - application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Molecular Ecology, 2, 113–118.
Holder, J. M., Swain, F. G. & Colman, R. L. (1963). The use of sod-sown vetch (Vicia sativa) as a supplement by dairy cows on the far north coast of New South Wales. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture and Animal Husbandry, 3, 153–160.
Koch, H. H. R. (1882). Die Aetiologie der Tuberculose. Berliner Klinische Wochenschrift, 19, 221–230.
Muyolo, N. G., Lipps, P. E. & Schmitthenner, A. F. (1993). Anastomosis grouping and variation in virulence among isolates of Rhizoctonia solani associated with dry bean and soybean in Ohio and Zaire. Phytopathology, 83, 438-444.
Vilgalys, R. & Hester, M. (1990). Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. Journal of Bacteriology, 172, 4238–4246.
White, T. J., Bruns, T., Lee, S. & Taylor, J. W. (1990). Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. (In M.A. Innis, D.H. Getfand, J.J. Sninsky & T.J. White (Eds.), PCR Protocols: A guide to methods and applications. (pp. 315–322)). (New York, USA: Academic Press).
Acknowledgements
We thank R. L. Dodman and R. J. Vilgalys for commenting on the text, and D. J. Firth and G. P. Kennedy for technical assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by Biosecurity Queensland, a division of the Queensland Government, Department of Agriculture and Fisheries. Some of the work was conducted while the senior author was employed by the New South Wales Government, Department of Agriculture. The research was not externally funded and the authors derived no commercial benefit from any aspect of the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All three authors contributed to the work, and the senior author prepared the first draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Human studies and participants
There was no involvement of human participants and/or animals in the present study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allen, R.N., Bransgrove, K. & Shivas, R.G. Red root rot of Vicia sativa caused by Atractiella rhizophila. Eur J Plant Pathol 157, 293–297 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-020-01985-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-020-01985-z