Abstract
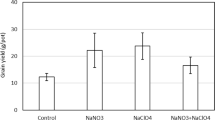
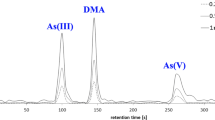
The effects of arsenic (As) species, such as As(III), As(V) and dimethylarsinic acid (DMA), on the accumulation of As in cucumber (Cucumis sativus), as well as on its growth in a soil mesocosm were evaluated. When Cucumis sativus was cultivated in soils contaminated with 20 and 50 mg/kg of As(III), As(V) or DMA for 40 days, the growth was markedly inhibited by the inorganic As (As(III) and As(V)) rather than the organic As (DMA). Irrespective of the As species, the As concentrations accumulated in Cucumis sativus increased with increasing As concentration in the soil. The As bioaccumulation factors from soil into the tissue of Cucumis sativus were 17.5–35.4, 29.3–42.7 and 17.6–25.7 for As(III), As(V) and DMA, respectively. In addition, the As translocation factors from the roots to shoots were 0.025–0.031, 0.018–0.032 and 0.014–0.026 for As(III), As(V) and DMA, respectively. In conclusion, Cucumis sativus mainly accumulated As in its roots rather than its shoots and easily accumulated inorganic rather than organic As from the soil into its tissue.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrea, L. H., Malcolm, R. S., Damien, J., Klerk, W., Bastone, E. B., Gerostamoulos, J., et al. (2004). Exposure to inorganic arsenic in soil increases urinary inorganic arsenic concentrations of residents living in old mining areas. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 26, 27–36.
Carbonell-Barrachina, A. A., Burló, F., Valero, D., López, E., Martínez-Romero, D., & Martínez-Sánchez, F. (1999). Arsenic toxicity and accumulation in turnip as affected by arsenical chemical speciation. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 47, 2288–2294.
Cheng, S. (2003). Heavy metal pollution in China: origin, pattern and control. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 10, 192–198.
Cullen, W. R., & Reimer, K. J. (1989). Arsenic speciation in the environment. Chemical Reviews, 89, 713–764.
Fitz, W. J., & Wenzel, W. W. (2002). Arsenic transformations in the soil-rhizosphere-plant system: fundamentals and potential application to phytoremediation. Journal of Biotechnology, 99, 259–278.
Francesconi, K., Visoottiviseth, P., Sridokchan, W., & Goessler, W. (2002). Arsenic species in an arsenic hyperaccumulating fern, Pityrogramma calomelanos, a potential phytoremediator of arsenic-contaminated soils. Science of the Total Environment, 284, 27–35.
Helgesen, H., & Larsen, E. H. (1998). Bioavailability and speciation of arsenic in carrots grown in contaminated soil. The Analyst, 123, 791–796.
Hong, S. H., Choi, S. A., Yoon, H., Cho, K. S. (2010). Screening of Cucumis sativus as a new arsenic-accumulating plant and its arsenic accumulation in hydroponic culture. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. doi:10.1007/s10653-010-9350-6
Jiang, Q. Q., & Singh, B. R. (1994). Effect of different forms and sources of arsenic on crop yield and arsenic concentration. Water, Air, and Soil pollution, 74, 321–343.
Koch, I., Feldmann, J., Wang, L., Andrewes, P., Reimer, K. J., & Cullen, W. R. (1999). Arsenic in the Meager Creek hot springs environment, British Columbia, Canada. Science of the Total Environment, 236, 101–117.
Liang, H. M., Lin, T. H., Chiou, J. M., & Yeh, K. C. (2009). Model evaluation of the phytoextraction potential of heavy metal hyperaccumulators and non-hyperaccumulators. Environmental Pollution, 157, 1945–1952.
Mandal, B. K., Chowdhury, T. R., Samanta, G., Basu, G. K., Chowdhury, P. P., Chanda, C. R., et al. (1996). Arsenic in groundwater in seven districts of West Bengal, India-the biggest arsenic calamity in the world. Current Science, 70, 976–986.
Mandal, B. K., & Suzuki, K. T. (2002). Arsenic round the world: A review. Talanta, 58, 201–235.
Marin, A. R., Masscheleyn, P. H., & Patrick, W. H. (1992). The influence of chemical form and concentration of arsenic on rice growth and tissue arsenic concentration. Plant and Soil, 139, 175–183.
Masscheleyn, P. H., Delaune, R. D., & Patrick, W. H., Jr. (1991). Effect of redox potential and pH on arsenic speciation and solubility in a contaminated soil. Environmental Science and Technology, 25, 1414–1419.
McGrath, S. P., Chaudri, A. M., & Giller, K. E. (1995). Long-term effects of metals in sewage sludge on soils, microorganisms and plants. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 14, 94–104.
Meharg, A. A., & Hartley-Whitaker, J. (2002). Arsenic uptake and metabolism in arsenic resistant and nonresistant plant species. New Phytologist, 154, 29–43.
Meharg, A. A., & Macnair, M. R. (1992). Suppression of the high-affinity phosphate uptake system: A mechanism of arsenate tolerance in Holcus lanatus L. Journal of Experimental Botany, 43, 519–524.
Melo, E. E. C., Costa, E. T. S., Guilhermea, L. R. G., Faquina, V., & Nascimentob, C. W. A. (2009). Accumulation of arsenic and nutrients by castor bean plants grown on an As-enriched nutrient solution. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 168, 479–483.
Memon, A. R., & Schröder, P. (2009). Implications of metal accumulation mechanisms to phytoremediation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 16, 162–175.
Patel, K. S., Shrivas, K., Brandt, R. N., Jakubowski, W. C., & Hoffmann, P. (2005). Arsenic contamination in water, soil, sediment and rice of central India. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 27, 131–145.
Pyles, R. A., & Woolson, E. A. (1982). Quantitation and characterization of arsenic compounds in vegetables grown in arsenic acid treated soil. Journals of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 30, 866–870.
Ruby, M. V., Davis, A., Schoof, R., Eberle, S., & Sellstone, C. M. (1996). Estimation of lead and arsenic bioavailability using a physiologically based extraction test. Environmental Science and Technology, 30, 422–430.
Schmöger, M. E. V., Oven, M., & Grill, E. (2000). Detoxification of arsenic by phytochelatins in plants. Plant Physiology, 122, 793–801.
Singh, N., & Ma, L. Q. (2006). Arsenic speciation, and arsenic and phosphate distribution in arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata L. and non-hyperaccumulator Pteris ensiformis L. Environmental Pollution, 141, 238–246.
Smith, E., Naidu, R., & Alston, A. M. (1998). Arsenic in the soil environment: a review. Advances in Agronomy, 64, 149–195.
Tamaki, S., & Frankenberger, W. T., Jr. (1992). Environmental biochemistry of arsenic. In G. W. Ware (Ed.), Reviews of environmental contamination and toxiciology (pp. 79–110). New York: Springer-Verlag.
Tlustoš, P., Goessler, W., Száková, J., & Balík, J. (2002). Arsenic compounds in leaves and roots of radish grown in soil treated by arsenite, arsenate and dimethylarsinic acid. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 16, 216–220.
Tu, C., Ma, L. Q., & Luongo, T. (2004). Root exudates and arsenic accumulation in arsenic hyperaccumulating Pteris vittata and non-hyperaccumulating Nephrolepis exaltata. Plant and Soil, 258, 9–19.
Tu, C., Ma, L. Q., Zhang, W., Cai, Y., & Harris, W. G. (2003). Arsenic species and leach ability in the fronds of the hyperaccumulator Chinese brake (Pteris vittata L.). Environmental Pollution, 124, 223–230.
Wei, C. Y., Wang, C., & Sun, X. (2007). Arsenic accumulation by ferns: A fild survey in southern china. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 29, 169–177.
Yang, L. S., Peterson, P. J., Williams, W. P., Wang, W. Y., Hou, S. F., & Tan, J. A. (2002). The relationship between exposure to arsenic concentrations in drinking water and the development of skin lesions in farmers from Inner Mongolia, China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 24, 293–303.
Zabłudowska, E., Kowalska, J., Jedynak, L., Wojas, S., Skłodowska, A., & Antosiewicz, D. M. (2009). Search for a plant for phytoremediation-what can we learn from field and hydroponic studies? Chemosphere, 77, 301–307.
Zhao, F. J., & McGrath, S. P. (2009). Biofortification and phytoremediation. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 12, 373–380.
Zhu, Y. G., & Rosen, B. P. (2009). Perspectives for genetic engineering for the phytoremediation of arsenic-contaminated environments: from imagination to reality? Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 20, 220–224.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MEST) (KRF-2008-C00388). Sun Ah Choi was financially supported by the NRL program (R0A-2008-000-20044-0) of the NRF, MEST.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, S.H., Choi, S.A., Lee, MH. et al. Effect of arsenic species on the growth and arsenic accumulation in Cucumis sativus . Environ Geochem Health 33 (Suppl 1), 41–47 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-010-9351-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-010-9351-5