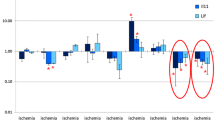
Abstract
Consisting of a fragment of ACTH(4–7) and C-terminal PGP tripeptide, the polypeptide Semax is successfully used for acute stroke therapy. Previous experiments showed rapid induction of Bdnf, Ngf, and TrkB expression in intact rat hippocampus following Semax treatment. To investigate the mRNA expression of neurotrophins and their receptors after treatment with either Semax or PGP, the rat brains were analyzed at three time points following a permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion (pMCAO). We have shown for the first time that both Semax and PGP activate the transcription of neurotrophins and their receptors in the cortex of rats subjected to pMCAO. The profiles of transcription alteration under PGP and Semax treatment were partially overlapped. Semax enhanced the transcription of Bdnf, TrkC, and TrkA 3 h after occlusion, Nt-3 and Ngf 24 h after occlusion, and Ngf 72 h after occlusion. PGP enhanced the transcription of Bdnf and TrkC 3 h after pMCAO and Ngf, TrkB, TrkC, and TrkA 24 h after pMCAO. The analysis of the transcription alterations under PGP and Semax treatment in the cortex of rats without surgery, sham-operated rats and rats subjected to pMCAO revealed that Semax selectively affected the transcription of neurotrophins and their receptors in the ischemic rat cortex, whereas the influence of PGP was mainly unspecific.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACTH:
-
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
- pMCAO:
-
Permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion
- Bdnf:
-
Brain-derived neurotropic factor
- Ngf:
-
Nerve growth factor
- Gapdh:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
References
Agapova TY, Agniullin YV, Shadrina MI, Shram SI, Slominsky PA, Lymborska SA, Myasoedov NF (2007) Neurotrophin gene expression in rat brain under the action of Semax, an analogue of ACTH 4–10. Neurosci Lett 417(2):201–205
Ashmarin IP, Nezavibat’ko VN, Levitskaya NG, Koshelev VB, Kamensky AA (1995) Design and investigation of ACTH(4–10) analog deprived of D-aminoacids and hydrophobic radicals. Neurosci Res Commun 16:105–112
Ashmarin IP, Nezavibat’ko VN, Miasoedov NF, Kamenskii AA, Grivennikov IA, Ponomareva-Stepnaia MA, Andreeva LA, Kaplan AYa, Koshelev VB, Riasina TV (1997) A nootropic adrenocorticotropin analog 4–10-semax: 15 years experience in its design and study. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova 47(2):420–430
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Cui JK, Hsu CY, Liu PK (1999) Suppression of postischemic hippocampal nerve growth factor expression by a c-fos antisense oligodeoxynucleotide. J Neurosci 19(4):1335–1344
De Wied D (1977) Behavioral effects of pituitary peptides. Acta Physiol Pol 28(15):77–91
De Wied D (1999) Behavioral pharmacology of neuropeptides related to melanocortins and the neurohypophyseal hormones. Eur J Pharmacol 375(1–3):1–11
Dmitrieva VG, Torshina EV, Yuzhakov VV, Povarova OV, Skvortsova VI, Limborska SA, Dergunova LV (2008a) Expression of sphingomyelin synthase 1 gene in rat brain focal ischemia. Brain Res 1188:222–227
Dmitrieva VG, Dergunova LV, Povarova OV, Skvortsova VI, Limborskaya SA, Myasoedov NF (2008b) The effect of Semax and the C-terminal peptide PGP on expression of growth factor genes and receptors in rats under conditions of experimental cerebral ischemia. Dokl Akad Nauk 422(2):402–405
Dolotov OV, Zolotarev IuA, Dorokhova EM, Andreeva LA, Alfeeva LIu, Grivennikov IA, Miasoedov NF (2004) The binding of Semax, ACTH 4–10 heptapeptide, to plasma membranes of the rat for a brain basal nuclei and biodegradation. Biorg Khim 30(3):241–246
Dolotov OV, Karpenko EA, Inozemtseva LS, Seredenina TS, Levitskaya NG, Rozyczka J, Dubynina EV, Novosadova EV, Andreeva LA, Alfeeva LY, Kamensky AA, Grivennikov IA, Myasoedov NF, Engele J (2006) Semax, an analog of ACTH(4–10) with cognitive effects, regulates BDNF and trkB expression in the rat hippocampus. Brain Res 1117(1):54–60
Ferrer I, Krupinski J, Goutan E, Marty E, Ambrosio S, Arenas E (2001) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor reduces cortical cell death by ischemia after middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. Acta Neuropathol 101:229–238
Gusev EI, Skvortsova VI (2002). Neuroprotectors in complex therapy of ischemic insult. Ther Neurol Dis 3(8)
Kaplan AYa, Kochetova AG, Nezavibat`ko VN, Rjasina TV, Ashmarin IP (1996) Synthetic ACTH analogue semax displays nootropic-like activity in humans. Neurosci Res Commun 19:115–123
Kim M-W, Bang M-S, Han T-R, Ko Y-J, Yoon B-W (2005) Exercise increased bdnf and trkB in contralateral hemisphere of the ischemic rat brain. Brain Res 1052:16–21
Kokaia Z, Zhao Q, Kokaia M, Elmer E, Metsis M, Smith ML, Siesjo BK, Lindvall O (1995) Regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene expression after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion with and without brain damage. Exp Neurol 136:73–88
Lee TH, Kato H, Chen ST, Kogure K, Itoyama Y (1998) Expression of nerve growth factor and trkA after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 29(8):1687–1696
Lindvall O, Ernfors P, Bengzon J, Kokaia Z, Smith ML, Siesjo BK, Persson H (1992) Differential regulation of mRNAs for nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and neurotrophin 3 in the adult rat brain following cerebral ischemia and hypoglycemic coma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89(2):648–652
Lipton P (1999) Ischemic cell death in brain neurons. Physiol Rev 79(4):1431–1568
Lu A, Tang Y, Ran R, Clark JF, Aronow BJ, Sharp FR (2003) Genomics of the periinfarction cortex after focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23(7):786–810
Lyapina LA, Pastorova VE, Samonina GE, Ashmarin IP (2000) The effect of prolyl-glycyl-proline (PGP) peptide and PGP-rich substances on haemostatic parameters of rat blood. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 11(5):409–414
Majda BT, Meloni BP, Rixon N, Knuckey NW (2001) Suppression subtraction hybridization and northern analysis reveal upregulation of heat shock, trkB, and sodium calcium exchanger genes following global cerebral ischemia in the rat. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 93(2):173–179
Pera J, Malgorzata Z, Kaminska B, Szczudlik A (2005) Neurotrophic factor expression after focal brain ischemia preceded by different preconditioning strategies. Cerebrovasc Dis 19:247–252
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW, Dempfle L (2002) Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 30(9):e36
Potaman VN, Antonova LV, Dubynin VA, Zaitsev DA, Kamensky AA, Myasoedov NF, Nezavibatko VN (1991) Entry of the synthetic ACTH(4–10) analogue into the rat brain following intravenous injection. Neurosci Lett 127(1):133–136
Potaman VN, Alfeeva LY, Kamensky AA, Nezavibatko VN (1993) Degradation of ACTH/MSH(4–10) and its synthetic analog semax by rat serum enzymes: an inhibitor study. Peptides 14(3):491–495
Romanova GA, Silachev DN, Shakova FM, Kvashennikova YN, Viktorov IV, Shram SI, Myasoedov NF (2006) Neuroprotective and antiamnesic effects of Semax during experimental ischemic infarction of the cerebral cortex. Bull Exp Biol Med 142(6):663–666
Samonina GE, Kopylova GN, Sergeev VI, Zhuikova SE, Bakaeva ZV (2001) Correction of the stomach blood flow as a mechanism of anti-ulcer effects of short proline-containing peptides. Ross Fiziol Zh Im I M Sechenova 87(11):1488–1492
Schabitz WR, Schwab S, Spranger M, Hacke W (1997) Intraventricular brain-derived neurotrophic factor reduces infarct size after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 17(5):500–506
Shadrina MI, Dolotov OV, Grivennikov IA, Slominsky PA, Andreeva LA, Inozemtseva LS, Limborska SA, Myasoedov NF (2001) Rapid induction of neurotrophin mRNAs in rat glial cell cultures by Semax, an adrenocorticotropic hormone analog. Neurosci Lett 308(2):115–118
Shevchenko KV, Nagaev IIu, Alfeeva LIu, Andreeva LA, Kamenskiĭ AA, Levitskaia NG, Shevchenko VP, Grivennikov IA, Miasoedov NF (2006) Kinetics of Semax penetration into the brain and blood of rats after its intranasal administration. Bioorg Khim 32(1):64–70
Storozhevykh TP, Tukhbatova GR, Senilova YE, Pinelis VG, Andreeva LA, Myasoyedov NF (2007) Effects of semax and its Pro-Gly-Pro fragment on calcium homeostasis of neurons and their survival under conditions of glutamate toxicity. Bull Exp Biol Med 143(5):601–604
Vladychenskaya IP, Dergunova LV, Dmitrieva VG, Limborska SA (2004) Human gene MOB: structure specification and aspects of transcriptional activity. Gene 338(2):257–265
Wu D (2005) Neuroprotection in experimental stroke with targeted neurotrophins. NeuroRx 2(1):120–128
Yakovleva EV, Kuzenkov VS, Fedorov VN, Skvortsova VI, Koshelev VB, Gusev EI, Ashmarin IP (1999) Study of the efficacy of semax in global cerebral ischemia in vivo. Biull Eksp Biol Med 127(8):172–174
Zhang Y, Pardridge WM (2001) Neuroprotection in transient focal brain ischemia after delayed intravenous administration of brain-derived neurotrophic factor conjugated to a blood-brain barrier drug targeting system. Stroke 32(6):1378–1384
Zhang ZH, Wang RZ, Wang RZ, Li GL, Wei JJ, Li ZJ, Feng M, Kang J, Du WC, Ma WB, Li YN, Yang Y, Kong YG (2008) Transplantation of neural stem cells modified by human neurotrophin-3 promotes functional recovery after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Neurosci Lett 444(3):227–230
Zhuikova SE, Badmaeva KE, Samonina GE, Plesskaia LG (2003) Semax and some glyproline peptides accelerate the healing of acetic ulcers in rats. Eksp Klin Gastroenterol 4:88–92
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project no. 08-04-01279), Molecular and Cell Biology program of the Russian Academy of Sciences, and the Federal Support of Leading Schools of the Russian Ministry of Science and Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dmitrieva, V.G., Povarova, O.V., Skvortsova, V.I. et al. Semax and Pro-Gly-Pro Activate the Transcription of Neurotrophins and Their Receptor Genes after Cerebral Ischemia. Cell Mol Neurobiol 30, 71–79 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-009-9432-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-009-9432-0