Abstract
Background
Mental health problems are gaining attention among court-involved youth with emphasis on the role of childhood adversity, but assessment lags.
Objective
The present study uses a commonly delivered assessment tool to examine mental health problems (current mental health problem, mental health interfered with probation goals, and suicide ideation) as a function of an expanded set of adverse childhood experiences (ACEs; childhood maltreatment, family dysfunction, and social disadvantage). Adaptive coping resources–impulse control, aspirations, and social support–were tested as both direct contributors and moderators of the influence of ACEs on mental health.
Methods
Using a diverse sample of youth on probation (N = 5378), this study utilized logistic regression models to test contributions of the three domains of childhood adversity–childhood maltreatment, family dysfunction, and social disadvantage. These models also examined the moderating roles of coping resources.
Results
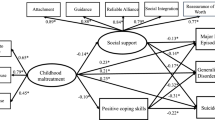
Childhood maltreatment emerged as the strongest contributor to mental health problems, with significant moderation from social support. Youth aspirations were inversely related to mental health problems and moderated the relation with ACEs and mental health problems that interfered with probation.
Conclusions
Assessment and mitigation of the detrimental effects of childhood maltreatment are important considerations in the intervention programs that target mental health outcomes of court-involved youth. Intervention programs to prevent recidivism and improve mental health should improve impulse control and aspirations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abram, K. M., Choe, J. Y., Washburn, J. J., Teplin, L. A., King, D. C., & Dulcan, M. K. (2008). Suicidal ideation and behaviors among youths in juvenile detention. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 47(3), 291–300. doi:10.1097/CHI.0b013e318160b3ce.
Agnew, R. (2001). Building on the foundation of general strain theory: Specifying the types of strain most likely to lead to crime and delinquency. Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency, 38(4), 319–361. doi:10.1177/0022427801038004001.
Arata, C. M., Langhinrichsen-Rohling, J., Bowers, D., & O’Brien, N. (2007). Differential correlates of multi-type maltreatment among urban youth. Child Abuse and Neglect, 31(4), 393–415.
Arnow, B. A. (2003). Relationships between childhood maltreatment, adult health and psychiatric outcomes, and medical utilization. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 65, 10–15.
Baglivio, M. T., & Epps, N. (2015). The interrelatedness of adverse childhood experiences among high-risk juvenile offenders. Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice. doi:10.1177/1541204014566286.
Baglivio, M. T., Epps, N., Swartz, K., Sayedul Huq, M., Sheer, A., & Hardt, N. S. (2014). The prevalence of adverse childhood experiences (ACE) in the lives of juvenile offenders. Journal of Juvenile Justice, 3(2), 1–23.
Baglivio, M. T., & Jackowski, K. (2013). Examining the validity of a juvenile offending risk assessment instrument across gender and race/ethnicity. Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice, 11(1), 26–43.
Baglivio, M. T., Wolff, K. T., Piquero, A. R., & Epps, N. (2015). The relationship between adverse childhood experiences (ACE) and juvenile offending trajectories in a juvenile offender sample. Journal of Criminal Justice, 43(3), 229–241.
Barnoski, R. (2004a). Assessing risk for re-offense: Validating the Washington State Juvenile Court assessment appendices. Olympia, WA: Washington State Institute for Public Policy.
Barnoski, R. (2004b). Washington State juvenile court assessment manual, version 2.1. Olympia: Washington State Institute for Public Policy.
Barrett, D. E., Katsiyannis, A., Zhang, D., & Zhang, D. (2014). Delinquency and recidivism: A multicohort, matched-control study of the role of early adverse experiences, mental health problems, and disabilities. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 22(1), 3–15. doi:10.1177/1063426612470514.
Burke, N. J., Hellman, J. L., Scott, B. G., Weems, C. F., & Carrion, V. G. (2011). The impact of adverse childhood experiences on an urban pediatric population. Child Abuse and Neglect, 35(6), 408–413. doi:10.1016/j.chiabu.2011.02.006.
Cauffman, E., Lexcen, F. J., Goldweber, A., Shulman, E. P., & Grisso, T. (2007). Gender differences in mental health symptoms among delinquent and community youth. Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice, 5(3), 287–307. doi:10.1177/1541204007301292.
Chapman, D. P., Whitfield, C. L., Felitti, V. J., Dube, S. R., Edwards, V. J., & Anda, R. F. (2004). Adverse childhood experiences and the risk of depressive disorders in adulthood. Journal of Affective Disorders, 82(2), 217–225.
Choi, H. (2011). Parents’ health and adult children’s subsequent working status: A perspective of intergenerational transfer and time allocation. Journal of Family and Economic Issues, 32(3), 493–507.
Chu, P. S., Saucier, D. A., & Hafner, E. (2010). Meta-analysis of the relationships between social support and well-being in children and adolescents. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 29(6), 624–645.
Craig, J. M., Baglivio, M. T., Wolff, K. T., Piquero, A. R., & Epps, N. (2017). Do social bonds buffer the impact of adverse childhood experiences on reoffending? Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice, 15(1), 3–20. doi:10.1177/1541204016630033.
Cronholm, P. F., Forke, C. M., Wade, R., Bair-Merritt, M. H., Davis, M., Harkins-Schwarz, M., et al. (2015). Adverse childhood experiences: Expanding the concept of adversity. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 49(3), 354–361.
Danese, A., & McEwen, B. S. (2012). Adverse childhood experiences, allostasis, allostatic load, and age-related disease. Physiology & Behavior, 106(1), 29–39. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.08.019.
Dawson, J. F. (n.d.). Interpreting interaction effects. Retrieved January 17, from http://www.jeremydawson.com/slopes.htm.
Desai, R. A., Goulet, J. L., Robbins, J., Chapman, J. F., Migdole, S. J., & Hoge, M. A. (2006). Mental health care in juvenile detention facilities: A review. Journal of the American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law Online, 34(2), 204–214.
Dierkhising, C. B., Ko, S. J., Woods-Jaeger, B., Briggs, E. C., Lee, R., & Pynoos, R. S. (2013). Trauma histories among justice-involved youth: Findings from the National Child Traumatic Stress Network. European Journal of Psychotraumatology. doi:10.3402/ejpt.v4i0.20274.
Downey, J., Gudmunson, C. G., Pang, Y. C., & Lee, K. (2017). Adverse childhood experiences affect health risk behaviors and chronic health of Iowans. Journal of Family Violence. doi:10.1007/s10896-017-9909-4. (First Online: 08 February 2017).
Dube, S. R., Felitti, V. J., Dong, M., Chapman, D. P., Giles, W. H., & Anda, R. F. (2003). Childhood abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction and the risk of illicit drug use: The adverse childhood experiences study. Pediatrics, 111(3), 564–572.
Duke, N. N., Pettingell, S. L., McMorris, B. J., & Borowsky, I. W. (2010). Adolescent violence perpetration: Associations with multiple types of adverse childhood experiences. Pediatrics, 125(4), e778–e786. doi:10.1542/peds.2009-0597.
Edwards, V. J., Holden, G. W., Felitti, V. J., & Anda, R. F. (2003). Relationship between multiple forms of childhood maltreatment and adult mental health in community respondents: Results from the adverse childhood experiences study. American Journal of Psychiatry, 160(8), 1453–1460.
Evans, G. W. (2003). A multimethodological analysis of cumulative risk and allostatic load among rural children. Developmental Psychology, 39(5), 924.
Evans, G. W., & Kim, P. (2013). Childhood poverty, chronic stress, self-regulation, and coping. Child Development Perspectives, 7(1), 43–48.
Evans, G. W., Li, D., & Whipple, S. S. (2013). Cumulative risk and child development. Psychological Bulletin, 139(6), 1342.
Fagan, A. A., Wright, E. M., & Pinchevsky, G. M. (2013). The protective effects of neighborhood collective efficacy on adolescent substance use and violence following exposure to violence. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 43(9), 1498–1512. doi:10.1007/s10964-013-0049-8.
Fang, X., & Corso, P. S. (2007). Child maltreatment, youth violence, and intimate partner violence. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 33(4), 281–290. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2007.06.003.
Fazel, S., Doll, H., & Långström, N. (2008). Mental disorders among adolescents in juvenile detention and correctional facilities: A systematic review and metaregression analysis of 25 surveys. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 47(9), 1010–1019. doi:10.1097/CHI.ObO13e31817eecf3.
Felitti, F., Vincent, J., Anda, M., Robert, F., Nordenberg, D., Williamson, P., et al. (1998). Relationship of childhood abuse and household dysfunction to many of the leading causes of death in adults: The adverse childhood experiences (ACE) study. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 14(4), 245–258. doi:10.1016/S0749-3797(98)00017-8.
Finkelhor, D., Ormrod, R. K., & Turner, H. A. (2007). Poly-victimization: A neglected component in child victimization. Child Abuse and Neglect, 31(1), 7–26.
Flouri, E., & Tzavidis, N. (2008). Psychopathology and prosocial behavior in adolescents from socio-economically disadvantaged families: The role of proximal and distal adverse life events. European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 17(8), 498–506.
Fox, B. H., Perez, N., Cass, E., Baglivio, M. T., & Epps, N. (2015). Trauma changes everything: Examining the relationship between adverse childhood experiences and serious, violent and chronic juvenile offenders. Child Abuse and Neglect, 46, 163–173. doi:10.1016/j.chiabu.2015.01.011.
Gallagher, M. W., & Lopez, S. J. (2009). Positive expectancies and mental health: Identifying the unique contributions of hope and optimism. Journal of Positive Psychology, 4(6), 548–556. doi:10.1080/17439760903157166.
Garland, A. F., Lau, A. S., Yeh, M., McCabe, K. M., Hough, R. L., & Landsverk, J. A. (2005). Racial and ethnic differences in utilization of mental health services among high-risk youths. American Journal of Psychiatry, 162(7), 1336–1343.
Hardt, J., Vellaisamy, P., & Schoon, I. (2010). Sequelae of prospective versus retrospective reports of adverse childhood experiences. Psychological Reports, 107(2), 425–440.
Hayes, A. F. (n.d.). The PROCESS macro for SPSS and SAS. Retrieved from http://www.processmacro.org/index.html.
Hayes, A. F. (2013). Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: A regression-based approach. New York: Guilford Press.
Hayes, A. F., & Matthes, J. (2009). Computational procedures for probing interactions in OLS and logistic regression: SPSS and SAS implementations. Behavior Research Methods, 41, 924–936.
Herts, K. L., McLaughlin, K. A., & Hatzenbuehler, M. L. (2012). Emotion dysregulation as a mechanism linking stress exposure to adolescent aggressive behavior. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 40(7), 1111–1122.
Hill, T. D., Kaplan, L. M., French, M. T., & Johnson, R. J. (2010). Victimization in early life and mental health in adulthood: An examination of the mediating and moderating influences of psychosocial resources. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 51(1), 48–63.
Hirschfield, P., Maschi, T., White, H. R., Traub, L. G., & Loeber, R. (2006). Mental health and juvenile arrests: Criminality, criminalization, or compassion? Criminology, 44(3), 593–630. doi:10.1111/j.1745-9125.2006.00058.x.
Hollist, D. R., Hughes, L. A., & Schaible, L. M. (2009). Adolescent maltreatment, negative emotion, and delinquency: An assessment of general strain theory and family-based strain. Journal of Criminal Justice, 37(4), 379–387. doi:10.1016/j.jcrimjus.2009.06.005.
Hostinar, C. E., Stellern, S. A., Schaefer, C., Carlson, S. M., & Gunnar, M. R. (2012). Associations between early life adversity and executive function in children adopted internationally from orphanages. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109(Supplement 2), 17208–17212. doi:10.1073/pnas.1121246109.
Jarjoura, G. R., Triplett, R. A., & Brinker, G. P. (2002). Growing up poor: Examining the link between persistent childhood poverty and delinquency. Journal of Quantitative Criminology, 18(2), 159–187.
Jonson-Reid, M., & Barth, R. P. (2000). From placement to prison: The path to adolescent incarceration from child welfare supervised foster or group care. Children and Youth Services Review, 22(7), 493–516.
Joshi, P. D., & Fast, N. J. (2013). Power and reduced temporal discounting. Psychological Science, 24(4), 432–438. doi:10.1177/0956797612457950.
Kataoka, S. H., Zhang, L., & Wells, K. B. (2002). Unmet need for mental health care among US children: Variation by ethnicity and insurance status. American Journal of Psychiatry, 159(9), 1548–1555.
Kim, C. Y., Losen, D. J., & Hewitt, D. T. (2010). The school-to-prison pipeline: Structuring legal reform. New York: NYU Press.
Kinner, S. A., Degenhardt, L., Coffey, C., Sawyer, S., Hearps, S., & Patton, G. (2014). Complex health needs in the youth justice system: A survey of community-based and custodial offenders. Journal of Adolescent Health, 54(5), 521–526. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2013.10.003.
Kort-Butler, L. A. (2010). Experienced and vicarious victimization: Do social support and self-esteem prevent delinquent responses? Journal of Criminal Justice, 38(4), 496–505.
Lengua, L. J., Kiff, C., Moran, L., Zalewski, M., Thompson, S., Cortes, R., et al. (2014). Parenting mediates the effects of income and cumulative risk on the development of effortful control. Social Development, 23(3), 631–649.
Logan-Greene, P., Kim, B. E., & Nurius, P. S. (2016). Childhood adversity among court-involved youth: Heterogeneous needs for prevention and treatment. Journal of Juvenile Justice, 5(2), 68–84.
Lovallo, W. R., Farag, N. H., Sorocco, K. H., Acheson, A., Cohoon, A. J., & Vincent, A. S. (2013). Early life adversity contributes to impaired cognition and impulsive behavior: Studies from the Oklahoma Family Health Patterns Project. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 37(4), 616–623.
Martinez, D. J., & Abrams, L. S. (2013). Informal social support among returning young offenders: A metasynthesis of the literature. International Journal of Offender Therapy and Comparative Criminology, 57(2), 169–190.
Masten, A. S., & Cicchetti, D. (2010). Developmental cascades. Development and Psychopathology, 22(special issue 03), 491–495. doi:10.1017/S0954579410000222.
McBride Murry, V., Berkel, C., Gaylord-Harden, N. K., Copeland-Linder, N., & Nation, M. (2011). Neighborhood poverty and adolescent development. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 21(1), 114–128.
McElroy, S., & Hevey, D. (2014). Relationship between adverse early experiences, stressors, psychosocial resources and wellbeing. Child Abuse & Neglect, 38(1), 65–75.
McLaughlin, K. A. (2016). Future directions in childhood adversity and youth psychopathology. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 45(3), 361–382. doi:10.1080/15374416.2015.1110823.
Nurius, P. S., Green, S., Logan-Greene, P., & Borja, S. (2015). Life course pathways of adverse childhood experiences toward adult psychological well-being: A stress process analysis. Child Abuse and Neglect, 45, 143–153.
Perez, N. M., Jennings, W. G., Piquero, A. R., & Baglivio, M. T. (2016). Adverse childhood experiences and suicide attempts: The mediating influence of personality development and problem behaviors. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 45(8), 1527–1545. doi:10.1007/s10964-016-0519-x.
Piquero, A. R., Jennings, W. G., Farrington, D. P., Diamond, B., & Gonzalez, J. M. R. (2016). A meta-analysis update on the effectiveness of early self-control improvement programs to improve self-control and reduce delinquency. Journal of Experimental Criminology, 12(2), 249–264.
Purewal, S. K., Bucci, M., Gutiérrez Wang, L., Koita, K., Silvério Marques, S., Oh, D., et al. (2016). Screening for adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) in an integrated pediatric care model. Zero to Three, 37(1), 10–17.
Putnam-Hornstein, E., Needell, B., & Rhodes, A. E. (2013). Understanding risk and protective factors for child maltreatment: The value of integrated, population-based data. Child Abuse and Neglect, 37(2), 116–119.
Ramiro, L. S., Madrid, B. J., & Brown, D. W. (2010). Adverse childhood experiences (ACE) and health-risk behaviors among adults in a developing country setting. Child Abuse and Neglect, 34(11), 842–855. doi:10.1016/j.chiabu.2010.02.012.
Rebbe, R., Nurius, P. S., Ahrens, K., & Courtney, M. (2017). Adverse childhood experiences among youth aging out of foster care: A latent class analysis. Children and Youth Services Review, 74, 108–116.
Rebellon, C. J., Manasse, M. E., Van Gundy, K. T., & Cohn, E. S. (2012). Perceived injustice and delinquency: A test of general strain theory. Journal of Criminal Justice, 40(3), 230–237. doi:10.1016/j.jcrimjus.2012.02.001.
Riva, M., Bambra, C., Easton, S., & Curtis, S. (2011). Hard times or good times? Inequalities in the health effects of economic change. International Journal of Public Health, 56(1), 3–5.
Sacks, V. (2014). Adverse childhood experiences: National and state-level prevalence. Retrieved from https://calio.dspacedirect.org/handle/11212/1663.
Schilling, E. A., Aseltine, R. H., & Gore, S. (2007). Adverse childhood experiences and mental health in young adults: A longitudinal survey. BMC Public Health, 7, 30. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-7-30.
Scott, B. G., Burke, N. J., Weems, C. F., Hellman, J. L., & Carrión, V. G. (2013). The interrelation of adverse childhood experiences within an at-risk pediatric sample. Journal of Child & Adolescent Trauma, 6(3), 217–229. doi:10.1080/19361521.2013.811459.
Shonkoff, J. P., Garner, A. S., Siegel, B. S., Dobbins, M. I., Earls, M. F., Garner, A. S., et al. (2012). The lifelong effects of early childhood adversity and toxic stress. Pediatrics, 129(1), e232–e246. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-2663.
Shufelt, J. L., & Cocozza, J. J. (2006). Youth with mental health disorders in the juvenile justice system: Results from a multi-state prevalence study. Delmar, NY: National Center for Mental Health and Juvenile Justice.
Sickmund, M., & Puzzanchera, C. (2014). Juvenile offenders and victims: 2014 National report. Pittsburgh, PA: National Center for Juvenile Justice.
Skowyra, K. R., & Cocozza, J. J. (2007). Blueprint for change: A comprehensive model for the identification and treatment of youth with mental health needs in contact with the juvenile justice system. Delmar: Policy Research Associates, Inc.
Smith, C., & Thornberry, T. P. (1995). The relationship between childhood maltreatment and adolescent involvement in delinquency. Criminology, 33(4), 451–481. doi:10.1111/j.1745-9125.1995.tb01186.x.
Sprague, J., Verona, E., Kalkhoff, W., & Kilmer, A. (2011). Moderators and mediators of the stress–aggression relationship: Executive function and state anger. Emotion, 11(1), 61–73. doi:10.1037/a0021788.
Taylor, S. E., Way, B. M., & Seeman, T. E. (2011). Early adversity and adult health outcomes. Development and Psychopathology, 23(special issue 03), 939–954. doi:10.1017/S0954579411000411.
Tedeschi, R. G., & Calhoun, L. G. (2004). Posttraumatic growth: Conceptual foundations and empirical evidence. Psychological Inquiry, 15(1), 1–18. doi:10.1207/s15327965pli1501_01.
Teplin, L. A., Abram, K. M., McClelland, G. M., Dulcan, M. K., & Mericle, A. A. (2002). Psychiatric disorders in youth in juvenile detention. Archives of General Psychiatry, 59(12), 1133–1143. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.59.12.1133.
Teplin, L. A., McClelland, G. M., Abram, K. M., & Mileusnic, D. (2005). Early violent death among delinquent youth: A prospective longitudinal study. Pediatrics, 115(6), 1586–1593. doi:10.1542/peds.2004-1459.
Turner, R. J., Thomas, C. S., & Brown, T. H. (2016). Childhood adversity and adult health: Evaluating intervening mechanisms. Social Science and Medicine, 156, 114–124.
Underwood, L. A., & Washington, A. (2016). Mental illness and juvenile offenders. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 13(2), 228. doi:10.3390/ijerph13020228.
Wade, R., Shea, J. A., Rubin, D., & Wood, J. (2014). Adverse childhood experiences of low-income urban youth. Pediatrics, 134(1), e13–e20.
Wang, M.-T., & Eccles, J. S. (2012). Social support matters: Longitudinal effects of social support on three dimensions of school engagement from middle to high school. Child Development, 83(3), 877–895.
Yancura, L. A., & Aldwin, C. M. (2009). Stability and change in retrospective reports of childhood experiences over a 5-year period: Findings from the Davis Longitudinal Study. Psychology and Aging, 24(3), 715–721.
Acknowledgements
We thank TJ Bohl and Shelly Maluo from the Pierce County Juvenile Justice System for their support and contribution to this research. We also thank Isaias Hernandez for his contributions to data cleaning. This research was supported in part by a grant from the National Institute on Mental Health Grant 5 T32 MH20010 “Mental Health Prevention Research Training Program”, the National Center For Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number TL1TR000422, and a Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development research infrastructure Grant, R24 HD042828, to the Center for Studies in Demography and Ecology at the University of Washington. The authors thank Dr. Eugene Maguin for his statistical support in the final preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The local Institutional Review Board approved all procedures. The first author takes responsibility for the data integrity and analysis procedures.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Logan-Greene, P., Tennyson, R.L., Nurius, P.S. et al. Adverse Childhood Experiences, Coping Resources, and Mental Health Problems among Court-Involved Youth. Child Youth Care Forum 46, 923–946 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10566-017-9413-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10566-017-9413-2