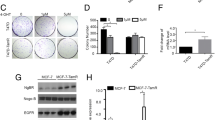
Abstract
Purpose
Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC), an aggressive subtype of breast cancer, lacks the three major receptors for predicting outcome or targeting therapy. Hence, our aim was to evaluate the potential of estrogen receptor beta (ERβ) as a possible endocrine therapy target in TNBC.
Methods
The expression and prognostic effect of ERβ isoforms were analyzed using TCGA breast tumor data, and the expression of ERβ isoform mRNA and protein in TNBC cell lines was assayed. Endogenous ERβ2 and ERβ5 were knocked down with siRNA, and ERβ2, ERβ5, and ERβ1 were upregulated using a doxycycline-inducible lentiviral system. Cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and specific gene expressions were evaluated.
Results
ERβ2 and ERβ5 were the predominant endogenous forms of ERβ in TNBC tumors and cell lines. High ERβ2 predicted worse clinical outcome. Knockdown of endogenous ERβ2/ERβ5 in cell lines suppressed proliferation, migration and invasion, and downregulated proto-oncogene survivin expression. ERβ2/ERβ5 upregulation did the reverse, increasing survivin and these cell activities. ERβ1 was barely detectable in TNBC cell lines, but its upregulation reduced survivin, increased tumor suppressor expression (E-cadherin and cystatins), and suppressed proliferation, migration and invasion in both ligand-independent and dependent manners, suggesting the possible translational benefit of ERβ ligands.
Conclusions
ERβ2/ERβ5 and ERβ1 exhibit sharply contrasting activities in TNBC cells. Our findings imply that delineating the absolute amounts and relative ratios of the different ERβ isoforms might have prognostic and therapeutic relevance, and could enable better selection of optimal approaches for treatment of this often aggressive form of breast cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waks AG, Winer EP (2019) Breast Cancer Treatment: A Review. JAMA 321(3):288–300. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2018.19323
Hudis CA, Gianni L (2011) Triple-negative breast cancer: an unmet medical need. Oncologist 16(Suppl 1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2011-S1-01
Pan D, Kocherginsky M, Conzen SD (2011) Activation of the glucocorticoid receptor is associated with poor prognosis in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res 71(20):6360–6370. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0362
Chia K, O'Brien M, Brown M, Lim E (2015) Targeting the androgen receptor in breast cancer. Curr Oncol Rep 17(2):4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-014-0427-8
Bialesova L, Xu L, Gustafsson JA, Haldosen LA, Zhao C, Dahlman-Wright K (2017) Estrogen receptor beta2 induces proliferation and invasiveness of triple negative breast cancer cells: association with regulation of PHD3 and HIF-1alpha. Oncotarget 8(44):76622–76633. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20635
Huang B, Omoto Y, Iwase H, Yamashita H, Toyama T, Coombes RC, Filipovic A, Warner M, Gustafsson JA (2014) Differential expression of estrogen receptor alpha, beta1, and beta2 in lobular and ductal breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(5):1933–1938. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1323719111
Mosselman S, Polman J, Dijkema R (1996) ER beta: identification and characterization of a novel human estrogen receptor. FEBS Lett 392(1):49–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(96)00782-x
Kuiper GG, Enmark E, Pelto-Huikko M, Nilsson S, Gustafsson JA (1996) Cloning of a novel receptor expressed in rat prostate and ovary. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(12):5925–5930. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.93.12.5925
Katzenellenbogen BS, Korach KS (1997) A new actor in the estrogen receptor drama–enter ER-beta. Endocrinology 138(3):861–862. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.138.3.5080
Choi I, Ko C, Park-Sarge OK, Nie R, Hess RA, Graves C, Katzenellenbogen BS (2001) Human estrogen receptor beta-specific monoclonal antibodies: characterization and use in studies of estrogen receptor beta protein expression in reproductive tissues. Mol Cell Endocrinol 181(1–2):139–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0303-7207(01)00492-0
Huang B, Warner M, Gustafsson JA (2015) Estrogen receptors in breast carcinogenesis and endocrine therapy. Mol Cell Endocrinol 418(Pt 3):240–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2014.11.015
Nelson AW, Groen AJ, Miller JL, Warren AY, Holmes KA, Tarulli GA, Tilley WD, Katzenellenbogen BS, Hawse JR, Gnanapragasam VJ, Carroll JS (2017) Comprehensive assessment of estrogen receptor beta antibodies in cancer cell line models and tissue reveals critical limitations in reagent specificity. Mol Cell Endocrinol 440:138–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2016.11.016
Andersson S, Sundberg M, Pristovsek N, Ibrahim A, Jonsson P, Katona B, Clausson CM, Zieba A, Ramstrom M, Soderberg O, Williams C, Asplund A (2017) Insufficient antibody validation challenges oestrogen receptor beta research. Nat Commun 8:15840. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15840
Hawse JR, Carter JM, Aspros KGM, Bruinsma ES, Koepplin JW, Negron V, Subramaniam M, Ingle JN, Rech KL, Goetz MP (2020) Optimized immunohistochemical detection of estrogen receptor beta using two validated monoclonal antibodies confirms its expression in normal and malignant breast tissues. Breast Cancer Res Treat 179(1):241–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-019-05441-3
Madak-Erdogan Z, Charn TH, Jiang Y, Liu ET, Katzenellenbogen JA, Katzenellenbogen BS (2013) Integrative genomics of gene and metabolic regulation by estrogen receptors alpha and beta, and their coregulators. Mol Syst Biol 9:676. https://doi.org/10.1038/msb.2013.28
Chang EC, Frasor J, Komm B, Katzenellenbogen BS (2006) Impact of estrogen receptor beta on gene networks regulated by estrogen receptor alpha in breast cancer cells. Endocrinology 147(10):4831–4842. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2006-0563
Jiang Y, Gong P, Madak-Erdogan Z, Martin T, Jeyakumar M, Carlson K, Khan I, Smillie TJ, Chittiboyina AG, Rotte SC, Helferich WG, Katzenellenbogen JA, Katzenellenbogen BS (2013) Mechanisms enforcing the estrogen receptor beta selectivity of botanical estrogens. FASEB J 27(11):4406–4418. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.13-234617
Reese JM, Bruinsma ES, Nelson AW, Chernukhin I, Carroll JS, Li Y, Subramaniam M, Suman VJ, Negron V, Monroe DG, Ingle JN, Goetz MP, Hawse JR (2018) ERbeta-mediated induction of cystatins results in suppression of TGFbeta signaling and inhibition of triple-negative breast cancer metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115(41):E9580–e9589. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1807751115
Ziegler Y, Laws MJ, Sanabria Guillen V, Kim SH, Dey P, Smith BP, Gong P, Bindman N, Zhao Y, Carlson K, Yasuda MA, Singh D, Li Z, El-Ashry D, Madak-Erdogan Z, Katzenellenbogen JA, Katzenellenbogen BS (2019) Suppression of FOXM1 activities and breast cancer growth in vitro and in vivo by a new class of compounds. NPJ breast cancer 5:45. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41523-019-0141-7
Drews-Elger K, Brinkman JA, Miller P, Shah SH, Harrell JC, da Silva TG, Ao Z, Schlater A, Azzam DJ, Diehl K, Thomas D, Slingerland JM, Perou CM, Lippman ME, El-Ashry D (2014) Primary breast tumor-derived cellular models: characterization of tumorigenic, metastatic, and cancer-associated fibroblasts in dissociated tumor (DT) cultures. Breast Cancer Res Treat 144(3):503–517. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-014-2887-9
De Angelis M, Stossi F, Carlson KA, Katzenellenbogen BS, Katzenellenbogen JA (2005) Indazole estrogens: highly selective ligands for the estrogen receptor beta. J Med Chem 48(4):1132–1144. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm049223g
Bergamaschi A, Madak-Erdogan Z, Kim YJ, Choi YL, Lu H, Katzenellenbogen BS (2014) The forkhead transcription factor FOXM1 promotes endocrine resistance and invasiveness in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer by expansion of stem-like cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res 16(5):436. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-014-0436-4
Li B, Dewey CN (2011) RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics 12:323. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-12-323
Sun W, Duan T, Ye P, Chen K, Zhang G, Lai M, Zhang H (2018) TSVdb: a web-tool for TCGA splicing variants analysis. BMC Genomics 19(1):405. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-4775-x
Gustafsson JA, Strom A, Warner M (2019) Update on ERbeta. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 191:105312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.02.007
Sellitto A, D'Agostino Y, Alexandrova E, Lamberti J, Pecoraro G, Memoli D, Rocco D, Coviello E, Giurato G, Nassa G, Tarallo R, Weisz A, Rizzo F (2020) Insights into the Role of Estrogen Receptor beta in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061477
Wang Z, Jensen MA, Zenklusen JC (2016) A Practical Guide to The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). Methods Mol Biol 1418:111–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3578-9_6
Paterni I, Granchi C, Katzenellenbogen JA, Minutolo F (2014) Estrogen receptors alpha (ERalpha) and beta (ERbeta): subtype-selective ligands and clinical potential. Steroids 90:13–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2014.06.012
Sun J, Meyers MJ, Fink BE, Rajendran R, Katzenellenbogen JA, Katzenellenbogen BS (1999) Novel ligands that function as selective estrogens or antiestrogens for estrogen receptor-alpha or estrogen receptor-beta. Endocrinology 140(2):800–804. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.140.2.6480
Norman BH, Dodge JA, Richardson TI, Borromeo PS, Lugar CW, Jones SA, Chen K, Wang Y, Durst GL, Barr RJ, Montrose-Rafizadeh C, Osborne HE, Amos RM, Guo S, Boodhoo A, Krishnan V (2006) Benzopyrans are selective estrogen receptor beta agonists with novel activity in models of benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Med Chem 49(21):6155–6157. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm060491j
Zhao Y, Gong P, Chen Y, Nwachukwu JC, Srinivasan S, Ko C, Bagchi MK, Taylor RN, Korach KS, Nettles KW, Katzenellenbogen JA, Katzenellenbogen BS (2015) Dual suppression of estrogenic and inflammatory activities for targeting of endometriosis. Sci Transl Med 7(271):271–279. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3010626
Cox JL (2017) Cystatins as regulators of cancer. Medical Research Archives 5(7):1–11
Cox JL (2009) Cystatins and cancer Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 14:463–474. https://doi.org/10.2741/3255
Johnstone CN, Pattison AD, Gorringe KL, Harrison PF, Powell DR, Lock P, Baloyan D, Ernst M, Stewart AG, Beilharz TH, Anderson RL (2018) Functional and genomic characterisation of a xenograft model system for the study of metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer. Dis Model Mech 11(5):032250. https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.032250
Mendonsa AM, Na TY, Gumbiner BM (2018) E-cadherin in contact inhibition and cancer. Oncogene 37(35):4769–4780. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0304-2
Asnaghi L, Vass WC, Quadri R, Day PM, Qian X, Braverman R, Papageorge AG, Lowy DR (2010) E-cadherin negatively regulates neoplastic growth in non-small cell lung cancer: role of Rho GTPases. Oncogene 29(19):2760–2771. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.39
Na TY, Schecterson L, Mendonsa AM, Gumbiner BM (2020) The functional activity of E-cadherin controls tumor cell metastasis at multiple steps. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117(11):5931–5937. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1918167117
Polyak K, Weinberg RA (2009) Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states: acquisition of malignant and stem cell traits. Nat Rev Cancer 9(4):265–273. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2620
Chen X, Duan N, Zhang C, Zhang W (2016) Survivin and Tumorigenesis: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies. Journal of Cancer 7(3):314–323. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.13332
Leung YK, Mak P, Hassan S, Ho SM (2006) Estrogen receptor (ER)-beta isoforms: a key to understanding ER-beta signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(35):13162–13167. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0605676103
Ogawa S, Inoue S, Watanabe T, Orimo A, Hosoi T, Ouchi Y, Muramatsu M (1998) Molecular cloning and characterization of human estrogen receptor betacx: a potential inhibitor ofestrogen action in human. Nucleic Acids Res 26(15):3505–3512. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/26.15.3505
Poola I, Abraham J, Baldwin K, Saunders A, Bhatnagar R (2005) Estrogen receptors beta4 and beta5 are full length functionally distinct ERbeta isoforms: cloning from human ovary and functional characterization. Endocrine 27(3):227–238. https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:27:3:227
Liu J, Sareddy GR, Zhou M, Viswanadhapalli S, Li X, Lai Z, Tekmal RR, Brenner A, Vadlamudi RK (2018) Differential Effects of Estrogen Receptor beta Isoforms on Glioblastoma Progression. Cancer Res 78(12):3176–3189. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-3470
Christenson JL, Butterfield KT, Spoelstra NS, Norris JD, Josan JS, Pollock JA, McDonnell DP, Katzenellenbogen BS, Katzenellenbogen JA, Richer JK (2017) MMTV-PyMT and Derived Met-1 mouse mammary tumor cells as models for studying the role of the androgen receptor in triple-negative breast cancer progression. Horm Cancer 8(2):69–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12672-017-0285-6
Gerratana L, Basile D, Buono G, De Placido S, Giuliano M, Minichillo S, Coinu A, Martorana F, De Santo I, Del Mastro L, De Laurentiis M, Puglisi F, Arpino G (2018) Androgen receptor in triple negative breast cancer: A potential target for the targetless subtype. Cancer Treat Rev 68:102–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2018.06.005
Reese JM, Suman VJ, Subramaniam M, Wu X, Negron V, Gingery A, Pitel KS, Shah SS, Cunliffe HE, McCullough AE, Pockaj BA, Couch FJ, Olson JE, Reynolds C, Lingle WL, Spelsberg TC, Goetz MP, Ingle JN, Hawse JR (2014) ERbeta1: characterization, prognosis, and evaluation of treatment strategies in ERalpha-positive and -negative breast cancer. BMC cancer 14:749. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-14-749
Alexandrova E, Giurato G, Saggese P, Pecoraro G, Lamberti J, Ravo M, Rizzo F, Rocco D, Tarallo R, Nyman TA, Collina F, Cantile M, Di Bonito M, Botti G, Nassa G, Weisz A (2020) Interaction Proteomics Identifies ERbeta Association with Chromatin Repressive Complexes to Inhibit Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Exert An Oncosuppressive Role in Triple-negative Breast Cancer. Mol Cell Proteomics 19(2):245–260. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.RA119.001817
Zhao L, Huang S, Mei S, Yang Z, Xu L, Zhou N, Yang Q, Shen Q, Wang W, Le X, Lau WB, Lau B, Wang X, Yi T, Zhao X, Wei Y, Warner M, Gustafsson JA, Zhou S (2018) Pharmacological activation of estrogen receptor beta augments innate immunity to suppress cancer metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115(16):E3673–E3681. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1803291115
Karim H, Kim SH, Lauderdale K, Lapato AS, Atkinson K, Yasui N, Yamate-Morgan H, Sekyi M, Katzenellenbogen JA, Tiwari-Woodruff SK (2019) Analogues of ERbeta ligand chloroindazole exert immunomodulatory and remyelinating effects in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Sci Rep 9(1):503. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-37420-x
Moore SM, Khalaj AJ, Kumar S, Winchester Z, Yoon J, Yoo T, Martinez-Torres L, Yasui N, Katzenellenbogen JA, Tiwari-Woodruff SK (2014) Multiple functional therapeutic effects of the estrogen receptor beta agonist indazole-Cl in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(50):18061–18066. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1411294111
Saijo K, Collier JG, Li AC, Katzenellenbogen JA, Glass CK (2011) An ADIOL-ERbeta-CtBP transrepression pathway negatively regulates microglia-mediated inflammation. Cell 145(4):584–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.03.050
Bianchini G, Balko JM, Mayer IA, Sanders ME, Gianni L (2016) Triple-negative breast cancer: challenges and opportunities of a heterogeneous disease. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 13(11):674–690. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.66
Lehmann BD, Pietenpol JA (2015) Clinical implications of molecular heterogeneity in triple negative breast cancer. Breast 24(Suppl 2):S36–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.breast.2015.07.009
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grants from the Breast Cancer Research Foundation (BCRF-084 to JAK and BSK and BCRF-083 to BSK) and the NIH/NCI (1R01 CA220284 to BSK and JAK). SY was a Visiting Scholar supported in part by 345 Talent Project from Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University. XJ was a Visiting Scholar supported in part by a fellowship from Shenyang Chest Hospital, Shenyang, China. We thank Dr. Dorraya El-Ashry of the University of Minnesota for kindly providing DT28 cells.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
JAK is a stockholder of Radius Health, Inc. BSK and JAK have ownership interest in Celcuity, Inc. The other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or involving animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, S., Dey, P., Ziegler, Y. et al. Contrasting activities of estrogen receptor beta isoforms in triple negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 185, 281–292 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-020-05948-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-020-05948-0