Abstract
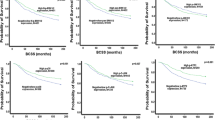
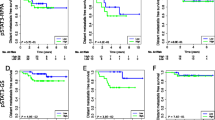
Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) transcription factors family are involved in diverse cellular biological functions. Reports regarding the prognostic impact of STAT3 expression in breast cancer (BC) are variable whether being a factor of poor or good prognosis. Immunohistochemical expression of phospho-STAT3 (pSTAT3) was studied in large series of invasive BC (n = 1270). pSTAT3 and STAT3 were quantified using reverse phase protein array (RPPA) on proteins extracted from macro-dissected FFPE tissues (n = 49 cases). STAT3 gene expression in the METABRIC cohort was also investigated. STAT3 gene expression prognostic impact was externally validated using the online BC gene expression data (n = 26 datasets, 4.177 patients). pSTAT3 was expressed in the nuclei and cytoplasm of invasive BC cells. Nuclear pSTAT3 overexpression was positively associated with smaller tumour size, lower grade, good NPI, negative lymphovascular invasion (LVI), ER+, PgR+, p53−, HER2−, and low Ki67LI and an improved breast cancer-specific survival (BCSS), independently of other factors. On RPPA, the mean pSTAT3 and STAT3 expressions were higher in ER+, PgR+, and smaller size tumours. Higher STAT3 transcripts in the METABRIC cohort were observed in cases with favourable prognostic criteria and as well as improved BCSS within the whole cohort, ER+ cohort with and without hormonal therapy, and ER− cohort including those who did not receive adjuvant chemotherapy. Pooled STAT3 gene expression data in the external validation cohort showed an association with improved patients’ outcome (P < 0.001, HR = 0.84, 95 % CI 0.79–0.90). Results of this study suggest nuclear localisation of pSTAT3 as favourable prognostic marker in invasive BC, results re-enforced by analysis of STAT3 gene expression data. This good prognostic advantage was maintained in patients who received and who did not receive adjuvant therapy. Therefore, STAT3 could have context-dependent molecular roles of in BC, results which warrant further prospective verification in clinical trials.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levy DE, Darnell JE Jr (2002) Stats: transcriptional control and biological impact. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3(9):651–662
Aggarwal BB, Kunnumakkara AB, Harikumar KB, Gupta SR, Tharakan ST, Koca C, Dey S, Sung B (2009) Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3, inflammation, and cancer: how intimate is the relationship? Ann N Y Acad Sci 1171:59–76
Watson CJ, Neoh K (2008) The Stat family of transcription factors have diverse roles in mammary gland development. Semin Cell Dev Biol 19(4):401–406
Inghirami G, Chiarle R, Simmons WJ, Piva R, Schlessinger K, Levy DE (2005) New and old functions of STAT3: a pivotal target for individualized treatment of cancer. Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex), 4(9):1131–1133
Johnston PA, Grandis JR (2011) STAT3 signaling: anticancer strategies and challenges. Mol Interv 11(1):18–26
Pectasides E, Egloff AM, Sasaki C, Kountourakis P, Burtness B, Fountzilas G, Dafni U, Zaramboukas T, Rampias T, Rimm D et al (2010) Nuclear localization of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is associated with a better prognosis. Clin Cancer Res 16(8):2427–2434
Chen Y, Wang J, Wang X, Liu X, Li H, Lv Q, Zhu J, Wei B, Tang Y (2013) STAT3, a poor survival predicator, is associated with lymph node metastasis from breast cancer. J Breast Cancer 16(1):40–49
Sonnenblick A, Shriki A, Galun E, Axelrod JH, Daum H, Rottenberg Y, Hamburger T, Mali B, Peretz T (2012) Tissue microarray-based study of patients with lymph node-positive breast cancer shows tyrosine phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (tyrosine705-STAT3) is a marker of good prognosis. Clin Transl Oncol 14(3):232–236
Dolled-Filhart M, Camp RL, Kowalski DP, Smith BL, Rimm DL (2003) Tissue microarray analysis of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 (Stat3) and phospho-Stat3 (Tyr705) in node-negative breast cancer shows nuclear localization is associated with a better prognosis. Clin Cancer Res 9(2):594–600
Abd El-Rehim DM, Ball G, Pinder SE, Rakha E, Paish C, Robertson JF, Macmillan D, Blamey RW, Ellis IO (2005) High-throughput protein expression analysis using tissue microarray technology of a large well-characterised series identifies biologically distinct classes of breast cancer confirming recent cDNA expression analyses. Int J Cancer J Int du Cancer 116(3):340–350
Rakha EA, Elsheikh SE, Aleskandarany MA, Habashi HO, Green AR, Powe DG, El-Sayed ME, Benhasouna A, Brunet JS, Akslen LA et al (2009) Triple-negative breast cancer: distinguishing between basal and nonbasal subtypes. Clin Cancer Res 15(7):2302–2310
Blamey RW, Ellis IO, Pinder SE, Lee AH, Macmillan RD, Morgan DA, Robertson JF, Mitchell MJ, Ball GR, Haybittle JL et al (2007) Survival of invasive breast cancer according to the Nottingham Prognostic Index in cases diagnosed in 1990–1999. Eur J Cancer (Oxford, England: 1990), 43(10):1548–1555
McCarty KS Jr, McCarty KS Sr (1984) Histochemical approaches to steroid receptor analyses. Semin Diagn Pathol 1(4):297–308
Aleskandarany MA, Negm OH, Rakha EA, Ahmed MA, Nolan CC, Ball GR, Caldas C, Green AR, Tighe PJ, Ellis IO (2012) TOMM34 expression in early invasive breast cancer: a biomarker associated with poor outcome. Breast Cancer Res Treat 136(2):419–427
Curtis C, Shah SP, Chin S-F, Turashvili G, Rueda OM, Dunning MJ, Speed D, Lynch AG, Samarajiwa S, Yuan Y et al (2012) The genomic and transcriptomic architecture of 2000 breast tumours reveals novel subgroups. Nature 486(7403):346–352
Jezequel P, Campone M, Gouraud W, Guerin-Charbonnel C, Leux C, Ricolleau G, Campion L (2012) bc-GenExMiner: an easy-to-use online platform for gene prognostic analyses in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 131(3):765–775
Santos CI, Costa-Pereira AP (1816) Signal transducers and activators of transcription-from cytokine signalling to cancer biology. Biochim Biophys Acta 1:38–49
Alvarez JV, Frank DA (2004) Genome-wide analysis of STAT target genes: elucidating the mechanism of STAT-mediated oncogenesis. Cancer Biol Ther 3(11):1045–1050
Hodge DR, Hurt EM, Farrar WL (2005) The role of IL-6 and STAT3 in inflammation and cancer. Eur J Cancer 41(16):2502–2512
Clevenger CV (2004) Roles and regulation of stat family transcription factors in human breast cancer. Am J Pathol 165(5):1449–1460
Aleskandarany MA, Soria D, Green AR, Nolan C, Diez-Rodriguez M, Ellis IO, Rakha EA (2015) Markers of progression in early-stage invasive breast cancer: a predictive immunohistochemical panel algorithm for distant recurrence risk stratification. Breast Cancer Res Treat 151(2):325–333
Sonnenblick A, Uziely B, Nechushtan H, Kadouri L, Galun E, Axelrod JH, Katz D, Daum H, Hamburger T, Maly B et al (2013) Tumor STAT3 tyrosine phosphorylation status, as a predictor of benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 138(2):407–413
Mao Y, Qu Q, Zhang YZ, Liu JJ, Wang G, Liang Y, Shen KW (2014) The prognosis of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 expression on breast cancer survival: a meta-analysis and retrospective study. Ann Oncol 25(suppl 1):i14
de la Iglesia N, Konopka G, Puram SV, Chan JA, Bachoo RM, You MJ, Levy DE, DePinho RA, Bonni A (2008) Identification of a PTEN-regulated STAT3 brain tumor suppressor pathway. Genes Dev 22(4):449–462
Gordziel C, Bratsch J, Moriggl R, Knosel T, Friedrich K (2013) Both STAT1 and STAT3 are favourable prognostic determinants in colorectal carcinoma. Br J Cancer 109(1):138–146
Li MX, Bi XY, Huang Z, Zhao JJ, Han Y, Li ZY, Zhang YF, Li Y, Chen X, Hu XH et al (2015) Prognostic role of phospho-STAT3 in patients with cancers of the digestive system: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Plos One 10(5):e0127356
Sosonkina N, Starenki D, Park J-I (2014) The role of STAT3 in thyroid cancer. Cancers 6(1):526–544
Xiong H, Du W, Wang JL, Wang YC, Tang JT, Hong J, Fang JY (2012) Constitutive activation of STAT3 is predictive of poor prognosis in human gastric cancer. J Mol Med (Berlin, Germany), 90(9):1037–1046
Huang X, Meng B, Iqbal J, Ding BB, Perry AM, Cao W, Smith LM, Bi C, Jiang C, Greiner TC et al (2013) Activation of the STAT3 signaling pathway is associated with poor survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. J Clin Oncol 31(36):4520–4528
Kusaba T, Nakayama T, Yamazumi K, Yakata Y, Yoshizaki A, Inoue K, Nagayasu T, Sekine I (2006) Activation of STAT3 is a marker of poor prognosis in human colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep 15(6):1445–1451
Seethala RR, Gooding WE, Handler PN, Collins B, Zhang Q, Siegfried JM, Grandis JR (2008) Immunohistochemical analysis of phosphotyrosine signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and epidermal growth factor receptor autocrine signaling pathways in head and neck cancers and metastatic lymph nodes. Clin Cancer Res 14(5):1303–1309
de la Iglesia N, Konopka G, Lim KL, Nutt CL, Bromberg JF, Frank DA, Mischel PS, Louis DN, Bonni A (2008) Deregulation of a STAT3-interleukin 8 signaling pathway promotes human glioblastoma cell proliferation and invasiveness. J Neurosci 28(23):5870–5878
Li H, Xiao W, Ma J, Zhang Y, Li R, Ye J, Wang X, Zhong X, Wang S (2014) Dual high expression of STAT3 and cyclinD1 is associated with poor prognosis after curative resection of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7(11):7989–7998
Kong H, Zhang Q, Zeng Y, Wang H, Wu M, Zheng T, Zeng Y, Shi H (2015) Prognostic significance of STAT3/phosphorylated-STAT3 in tumor: a meta-analysis of literatures. (1940–5901 (Electronic))
Ecker A, Simma O, Hoelbl A, Kenner L, Beug H, Moriggl R, Sexl V (2009) The dark and the bright side of Stat3: proto-oncogene and tumor-suppressor. Front Biosci 14:2944–2958
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aleskandarany, M.A., Agarwal, D., Negm, O.H. et al. The prognostic significance of STAT3 in invasive breast cancer: analysis of protein and mRNA expressions in large cohorts. Breast Cancer Res Treat 156, 9–20 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-016-3709-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-016-3709-z