Abstract
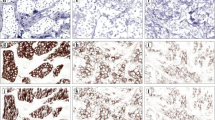
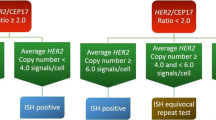
The purpose of this study was to develop and validate a new software, HER2-CONNECTTM, for digital image analysis of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) in breast cancer specimens. The software assesses immunohistochemical (IHC) staining reactions of HER2 based on an algorithm evaluating the cell membrane connectivity. The HER2-CONNECTTM algorithm was aligned to match digital image scorings of HER2 performed by 5 experienced assessors in a training set and confirmed in a separate validation set. The training set consisted of 167 breast carcinoma tissue core images in which the assessors individually and blinded outlined regions of interest and gave their HER2 score 0/1+/2+/3+ to the specific tumor region. The validation set consisted of 86 core images where the result of the automated image analysis software was correlated to the scores provided by the 5 assessors. HER2 fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was performed on all cores and used as a reference standard. The overall agreement between the image analysis software and the digital scorings of the 5 assessors was 92.1% (Cohen’s Kappa: 0.859) in the training set and 92.3% (Cohen’s Kappa: 0.864) in the validation set. The image analysis sensitivity was 99.2% and specificity 100% when correlated to FISH. In conclusion, the Visiopharm HER2 IHC algorithm HER2-CONNECTTM can discriminate between amplified and non-amplified cases with high accuracy and diminish the equivocal category and thereby provides a promising supplementary diagnostic tool to increase consistency in HER2 assessment.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HER2:
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemical/immunohistochemistry
- IA:
-
Image analysis
- DR:
-
Digital reading
- ROI:
-
Regions of interest
- FISH:
-
Fluorescence in situ hybridization
References
Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL (1987) Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science 235:177–182
Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, Fuchs H, Paton V, Bajamonde A et al (2001) Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med 344:783–792
Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Schwartz JN, Hagerty KL, Allred DC, Cote RJ et al (2007) American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 25:118–145
http://www.ukneqasicc.ucl.ac.uk/Vol6_No3_run_76.pdf Archived at http://webcitation.org/5vL50wxVL. Accessed 29 Dec 2010
http://www.nordiqc.org/Run-30-B10/Assessment/assessment-B10-HER2.htm Archived at http://webcitation.org/5vL4oteol. Accessed 29 Dec 2010
Di Palma S, Collins N, Faulkes C, Ping B, Ferns G, Haagsma B et al (2007) Chromogenic in situ hybridisation (CISH) should be an accepted method in the routine diagnostic evaluation of HER2 status in breast cancer. J Clin Pathol 60:1067–1068
Skaland I, Ovestad I, Janssen EA, Klos J, Kjellevold KH, Helliesen T et al (2008) Comparing subjective and digital image analysis HER2/neu expression scores with conventional and modified FISH scores in breast cancer. J Clin Pathol 61:68–71
Skaland I, Ovestad I, Janssen EA, Klos J, Kjellevold KH, Helliesen T et al (2008) Digital image analysis improves the quality of subjective HER-2 expression scoring in breast cancer. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 16:185–190
Ciampa A, Xu B, Ayata G, Baiyee D, Wallace J, Wertheimer M et al (2006) HER-2 status in breast cancer: correlation of gene amplification by FISH with immunohistochemistry expression using advanced cellular imaging system. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 14:132–137
Ellis CM, Dyson MJ, Stephenson TJ, Maltby EL (2005) HER2 amplification status in breast cancer: a comparison between immunohistochemical staining and fluorescence in situ hybridisation using manual and automated quantitative image analysis scoring techniques. J Clin Pathol 58:710–714
Gokhale S, Rosen D, Sneige N, Diaz LK, Resetkova E, Sahin A et al (2007) Assessment of two automated imaging systems in evaluating estrogen receptor status in breast carcinoma. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 15:451–455
Hanley KZ, Siddiqui MT, Lawson D, Cohen C, Nassar A (2009) Evaluation of new monoclonal antibodies in detection of estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and Her2 protein expression in breast carcinoma cell block sections using conventional microscopy and quantitative image analysis. Diagn Cytopathol 37:251–257
Minot DM, Kipp BR, Root RM, Meyer RG, Reynolds CA, Nassar A et al (2009) Automated cellular imaging system III for assessing HER2 status in breast cancer specimens: development of a standardized scoring method that correlates with FISH. Am J Clin Pathol 132:133–138
Mulrane L, Rexhepaj E, Penney S, Callanan JJ, Gallagher WM (2008) Automated image analysis in histopathology: a valuable tool in medical diagnostics. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 8:707–725
Tawfik OW, Kimler BF, Davis M, Donahue JK, Persons DL, Fan F et al (2006) Comparison of immunohistochemistry by automated cellular imaging system (ACIS) versus fluorescence in situ hybridization in the evaluation of HER-2/neu expression in primary breast carcinoma. Histopathology 48:258–267
Dobson L, Conway C, Hanley A, Johnson A, Costello S, O’Grady A et al (2010) Image analysis as an adjunct to manual HER-2 immunohistochemical review: a diagnostic tool to standardize interpretation. Histopathology 57:27–38
Haines GK III, Wiley E, Susnik B, Apple SK, Frkovic-Grazio S, Reyes C et al (2008) HER2 in well differentiated breast cancer: is testing necessary? Breast Cancer Res Treat 112:551–556
Kononen J, Bubendorf L, Kallioniemi A, Barlund M, Schraml P, Leighton S et al (1998) Tissue microarrays for high-throughput molecular profiling of tumor specimens. Nat Med 4:844–847
Kumar B, De SM, Venter DJ, Armes JE (2004) Tissue microarrays: a practical guide. Pathology 36:295–300
Breiman L, Friedman F, Stone CJ, Olshen RA (1984) Classification and regression trees. Chapman and Hall, Boca Raton, FL
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Lacroix-Triki M, Mathoulin-Pelissier S, Ghnassia JP, Macgrogan G, Vincent-Salomon A, Brouste V et al (2006) High inter-observer agreement in immunohistochemical evaluation of HER-2/neu expression in breast cancer: a multicentre GEFPICS study. Eur J Cancer 42:2946–2953
Press MF, Sauter G, Bernstein L, Villalobos IE, Mirlacher M, Zhou JY et al (2005) Diagnostic evaluation of HER-2 as a molecular target: an assessment of accuracy and reproducibility of laboratory testing in large, prospective, randomized clinical trials. Clin Cancer Res 11:6598–6607
Bilous M, Ades C, Armes J, Bishop J, Brown R, Cooke B et al (2003) Predicting the HER2 status of breast cancer from basic histopathology data: an analysis of 1500 breast cancers as part of the HER2000 International Study. Breast 12:92–98
Jung SY, Jeong J, Shin SH, Kwon Y, Kim EA, Ko KL et al (2010) The invasive lobular carcinoma as a prototype luminal A breast cancer: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Cancer 10:664
Yu J, Bhargava R, Dabbs DJ (2010) Invasive lobular carcinoma with extracellular mucin production and HER-2 overexpression: a case report and further case studies. Diagn Pathol 5:36
Conflict of interest
Michael Grunkin, Johan D. Hansen and Niels T. Foged are employees of Visiopharm, Denmark.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brügmann, A., Eld, M., Lelkaitis, G. et al. Digital image analysis of membrane connectivity is a robust measure of HER2 immunostains. Breast Cancer Res Treat 132, 41–49 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-011-1514-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-011-1514-2