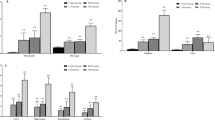
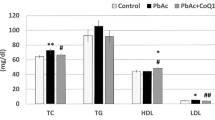
Abstract
Human lead (Pb) exposure induces many adverse health effects, including some related to lead accumulation in organs. Although lead bio-distribution in the body has been described, the molecular mechanism underlying distribution and excretion is not well understood. The transport of essential and toxic metals is principally mediated by proteins. How lead affects the expression of metal transporter proteins in the principal metal excretory organs, i.e., the liver and kidney, is unknown. Considering that co-administration of melatonin and lead reduces the toxic effects of lead and lead levels in the blood in vivo, we examined how lead and co-administration of lead and melatonin affect the gene and protein expression of metal transporter proteins (ZIP8, ZIP14, CTR1 and DMT1) in these organs. Rats were exposed intraperitoneally to lead or lead-melatonin. Our results show that Pb exposure induces changes in the protein and gene expression of ZIP8, ZIP14 and CTR1. Alterations in the copper/zinc ratio found in the blood, liver and kidney were likely related to these changes. With DMT1 expression (gene and protein), a positive correlation was found with lead levels in the kidney. Co-administration of melatonin and lead reduced lead-induced DMT1 expression through an unknown mechanism. This effect of melatonin relates to reduced lead levels in the blood and kidney. The metal transport protein function and our results suggest that DMT1 likely contributes to lead accumulation in organs. These data further elucidate the effects of lead on Cu and Zn and the molecular mechanism underlying lead bio-distribution in animals.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Dmt1 :
-
Divalent metal transporter 1
- Zip14 :
-
Zinc transporter protein 14
- Zip8 :
-
Zinc transporter protein 8
- Ctr1 :
-
Copper transporter 1
- Pb:
-
Lead
References
An DZ, Ai JT, Fang HJ, Sun RB, Shi Y, Wang LL, Wang Q (2015) Influence of iron supplementation on DMT1 (IRE)-induced transport of lead by brain barrier systems in vivo. Biomed Environ Sci 28:651–659. https://doi.org/10.3967/bes2015.091
Bannon DI, Portnoy ME, Olivi L, Lees PS, Culotta VC, Bressler JP (2002) Uptake of lead and iron by divalent metal transporter 1 in yeast and mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 295:978–984
Canonne-Hergaux F, Gros P (2002) Expression of the iron transporter DMT1 in kidney from normal and anemic mk mice. Kidney Int 62:147–156. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.2002.00405.x
Chen J et al (2014) Melatonin attenuates inflammatory response-induced brain edema in early brain injury following a subarachnoid hemorrhage: a possible role for the regulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines. J Pineal Res 57:340–347. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12173
Conrad ME, Barton JC (1978) Factors affecting the absorption and excretion of lead in the rat. Gastroenterology 74:731–740
Fujishiro H, Yano Y, Takada Y, Tanihara M, Himeno S (2012) Roles of ZIP8, ZIP14, and DMT1 in transport of cadmium and manganese in mouse kidney proximal tubule cells. Metallomics 4:700–708. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2mt20024d
Galvez-Peralta M, Wang Z, Bao S, Knoell DL, Nebert DW (2014) Tissue-specific induction of mouse ZIP8 and ZIP14 divalent cation/bicarbonate symporters by, and cytokine response to inflammatory signals. Int J Toxicol 33:246–258. https://doi.org/10.1177/1091581814529310
Garrick MD et al (2006) DMT1: which metals does it transport? Biol Res 39:79–85
Gidlow DA (2004) Lead toxicity. Occup Med (Lond) 54:76–81
Gottesfeld P, Were FH, Adogame L, Gharbi S, San D, Nota MM, Kuepouo G (2018) Soil contamination from lead battery manufacturing and recycling in seven African countries. Environ Res 161:609–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2017.11.055
Grosse C, Herzberg M, Schuttau M, Wiesemann N, Hause G, Nies DH (2016) Characterization of the Delta7 mutant of Cupriavidus metallidurans with deletions of seven secondary metal uptake systems. mSystems. https://doi.org/10.1128/msystems.00004-16
Guney M, Zagury GJ (2011) Toxic chemicals in toys and children’s products. Environ Sci Technol 45:3819. https://doi.org/10.1021/es200810s
Gunshin H et al (1997) Cloning and characterization of a mammalian proton-coupled metal-ion transporter. Nature 388:482–488. https://doi.org/10.1038/41343
Hernandez-Plata E et al (2015) Melatonin reduces lead levels in blood, brain and bone and increases lead excretion in rats subjected to subacute lead treatment. Toxicol Lett 233:78–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2015.01.009
Jang SS, Kim WD, Park WY (2009) Melatonin exerts differential actions on X-ray radiation-induced apoptosis in normal mice splenocytes and Jurkat leukemia cells. J Pineal Res 47:147–155. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2009.00694.x
Ji YL et al (2012) Melatonin alleviates cadmium-induced cellular stress and germ cell apoptosis in testes. J Pineal Res 52:71–79. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00921.x
Lee IC et al (2012) Melatonin attenuates gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity and oxidative stress in rats. Arch Toxicol 86:1527–1536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-012-0849-8
Li N et al (2015) The effects of early life lead exposure on the expression of interleukin (IL) 1beta, IL-6, and glial fibrillary acidic protein in the hippocampus of mouse pups. Hum Exp Toxicol 34:357–363. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327114529451
Lichten LA, Liuzzi JP, Cousins RJ (2009) Interleukin-1beta contributes via nitric oxide to the upregulation and functional activity of the zinc transporter Zip14 (Slc39a14) in murine hepatocytes. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 296:G860–G867. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.90676.2008
Liu Z et al (2008) Cd2+ versus Zn2+ uptake by the ZIP8 HCO3-dependent symporter: kinetics, electrogenicity and trafficking. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 365:814–820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.11.067
Malavolta M, Piacenza F, Basso A, Giacconi R, Costarelli L, Mocchegiani E (2015) Serum copper to zinc ratio: relationship with aging and health status. Mech Ageing Dev 151:93–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2015.01.004
Martinez-Alfaro M, Hernandez-Cortes D, Wrobel K, Cruz-Jimenez G, Rivera-Leyva JC, Pina-Zentella RM, Carabez Trejo A (2012) Effect of melatonin administration on DNA damage and repair responses in lymphocytes of rats subchronically exposed to lead. Mutat Res 742:37–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2011.11.011
Martinez-Alfaro M, Ramirez-Garcia G, Gutierrez-Granados S, Alcaraz-Contreras Y, Gallegos-Corona MA, de Larrea GZ, Carabez-Trejo A (2013) Melatonin attenuates the effects of sub-acute administration of lead on kidneys in rats without altering the lead-induced reduction in nitric oxide. J Trace Elem Med Biol 27:364–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2013.05.003
Rodriguez C, Mayo JC, Sainz RM, Antolin I, Herrera F, Martin V, Reiter RJ (2004) Regulation of antioxidant enzymes: a significant role for melatonin. J Pineal Res 36:1–9
van den Berghe PV, Klomp LW (2010) Posttranslational regulation of copper transporters. J Biol Inorg Chem 15:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00775-009-0592-7
Vilar A et al (2014) Melatonin suppresses nitric oxide production in glial cultures by pro-inflammatory cytokines through p38 MAPK inhibition. Free Radic Res 48:119–128. https://doi.org/10.3109/10715762.2013.845295
Wang X, Garrick MD, Yang F, Dailey LA, Piantadosi CA, Ghio AJ (2005) TNF, IFN-gamma, and endotoxin increase expression of DMT1 in bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 289:L24–L33. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00428.2003
Wang X, Li GJ, Zheng W (2006) Upregulation of DMT1 expression in choroidal epithelia of the blood–CSF barrier following manganese exposure in vitro. Brain Res 1097:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2006.04.046
Wang H, Li S, Teng X (2016) The antagonistic effect of selenium on lead-induced inflammatory factors and heat shock proteins mRNA expression in chicken livers. Biol Trace Elem Res 171:437–444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0532-z
Zheng G et al (2014) Involvement of CTR1 and ATP7A in lead (Pb)-induced copper (Cu) accumulation in choroidal epithelial cells. Toxicol Lett 225:110–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2013.11.034
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Juan Pedro Galván, Dr. Martín Garcia, and Evelyn Flores for technical assistance. This work was partially supported by CONACYT (Grant CB-2011/0168474) and the Universidad de Guanajuato (Grant 2015-21 Excellency DAIP Funding).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soto-Arredondo, K.J., Robles, J., Díaz-Cervantes, E. et al. Effects of lead and lead–melatonin exposure on protein and gene expression of metal transporters, proteins and the copper/zinc ratio in rats. Biometals 31, 859–871 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-018-0127-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-018-0127-1