Abstract
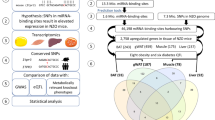
The present work is aimed at finding variants associated with Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) that reside in functionally validated miRNAs binding sites and that can have a functional role in determining diabetes and related pathologies. Using bioinformatics analyses we obtained a database of validated polymorphic miRNA binding sites which has been intersected with genes related to DM or to variants associated and/or in linkage disequilibrium (LD) with it and is reported in genome-wide association studies (GWAS). The workflow we followed allowed us to find variants associated with DM that also reside in functional miRNA binding sites. These data have been demonstrated to have a functional role by impairing the functions of genes implicated in biological processes linked to DM. In conclusion, our work emphasized the importance of SNPs located in miRNA binding sites. The results discussed in this work may constitute the basis of further works aimed at finding functional candidates and variants affecting protein structure and function, transcription factor binding sites, and non-coding epigenetic variants, contributing to widen the knowledge about the pathogenesis of this important disease.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431:350–355
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Baxter AG, Jordan MA (2011) From markers to molecular mechanisms: type 1 diabetes in the post-GWAS era. Rev Diabet Stud 9:201–223
Bhattacharya A, Ziebarth JD, Cui Y (2014) PolymiRTS Database 3.0: linking polymorphisms in microRNAs and their target sites with human diseases and biological pathways. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D86–D91
Bulik-Sullivan B, Selitsky S, Sethupathy P (2013) Prioritization of genetic variants in the microRNA regulome as functional candidates in genome-wide association studies. Hum Mutat 34:1049–1056
Bushati N, Cohen SM (2007) MicroRNA functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 23:175–205
Calin GA, Croce CM (2006) MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer 6:857–866
Chen K, Song F, Calin GA, Wei Q, Hao X, Zhang W (2008) Polymorphisms in microRNA targets: a gold mine for molecular epidemiology. Carcinogenesis 29:1306–1311
Ciccacci C et al (2013) MicroRNA genetic variations: association with type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol 50:867–872
Consortium GP (2012) An integrated map of genetic variation from 1092 human genomes. Nature 491:56–65
Cui Y (2014) In silico mapping of polymorphic miRNA-mRNA interactions in autoimmune thyroid diseases. Autoimmunity 47(5):327–333
Edwards SL, Beesley J, French JD, Dunning AM (2013) Beyond GWASs: illuminating the dark road from association to function. Am J Hum Genet 93:779–797
Ficarra E (2012) One decade of development and evolution of microRNA target prediction algorithms. Genom Proteom Bioinform 10:254–263
Guay C, Regazzi R (2013) Circulating microRNAs as novel biomarkers for diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol 9:513–521
Guay C, Roggli E, Nesca V, Jacovetti C, Regazzi R (2011) Diabetes mellitus, a microRNA-related disease? Transl Res 157:253–264
Hafner M et al (2010) Transcriptome-wide identification of RNA-binding protein and microRNA target sites by PAR-CLIP. Cell 141:129–141
Helwak A, Kudla G, Dudnakova T, Tollervey D (2013) Mapping the human miRNA interactome by CLASH reveals frequent noncanonical binding. Cell 153:654–665
Herrera B et al (2010) Global microRNA expression profiles in insulin target tissues in a spontaneous rat model of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 53:1099–1109
Hindorff LA, Sethupathy P, Junkins HA, Ramos EM, Mehta JP, Collins FS, Manolio TA (2009) Potential etiologic and functional implications of genome-wide association loci for human diseases and traits. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:9362–9367
Kanehisa M, Goto S (2000) KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 28:27–30
Kloosterman WP, Plasterk RH (2006) The diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease. Dev Cell 11:441–450
Li J, Zhang Z (2013) miRNA regulatory variation in human evolution. Trends Genet 29:116–124
Li R, Zhang P, Barker LE, Chowdhury FM, Zhang X (2010) Cost-effectiveness of interventions to prevent and control diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Diabetes care 33:1872–1894
Lovis P et al (2008) Alterations in microRNA expression contribute to fatty acid–induced pancreatic β-cell dysfunction. Diabetes 57:2728–2736
Lu J, Clark AG (2012) Impact of microRNA regulation on variation in human gene expression. Genome Res 22:1243–1254
Madhyastha R, Madhyastha H, Nakajima Y, Omura S, Maruyama M (2012) MicroRNA signature in diabetic wound healing: promotive role of miR-21 in fibroblast migration. Int Wound J 9:355–361
Meola N, Gennarino VA, Banfi S (2009) microRNAs and genetic diseases. Pathogenetics 2:7
Nesca V et al (2013) Identification of particular groups of microRNAs that positively or negatively impact on beta cell function in obese models of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 56:2203–2212
Nielsen LB et al (2012) Circulating levels of microRNA from children with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes and healthy controls: evidence that miR-25 associates to residual beta-cell function and glycaemic control during disease progression. Exp Diabetes Res 2012:896362
Osipova J et al (2014) Diabetes-associated microRNAs in pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional cohort study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 99:E1661–E1665
Pasquinelli AE (2012) MicroRNAs and their targets: recognition, regulation and an emerging reciprocal relationship. Nat Rev Genet 13:271–282
Poy MN et al (2004) A pancreatic islet-specific microRNA regulates insulin secretion. Nature 432:226–230
Poy MN et al (2009) miR-375 maintains normal pancreatic α-and β-cell mass. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:5813–5818
Prentki M, Nolan CJ (2006) Islet β cell failure in type 2 diabetes. J Clin Investig 116:1802–1812
Roggli E, Gattesco S, Caille D, Briet C, Boitard C, Meda P, Regazzi R (2012) Changes in microRNA expression contribute to pancreatic β-cell dysfunction in prediabetic NOD mice. Diabetes 61:1742–1751
Ryan BM, Robles AI, Harris CC (2010) Genetic variation in microRNA networks: the implications for cancer research. Nat Rev Cancer 10:389–402
Salas-Pérez F, Codner E, Valencia E, Pizarro C, Carrasco E, Pérez-Bravo F (2013) MicroRNAs miR-21a and miR-93 are down regulated in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from patients with type 1 diabetes. Immunobiology 218:733–737
Sayed D, Abdellatif M (2011) MicroRNAs in development and disease. Physiol Rev 91:827–887
Sebastiani G, Grieco FA, Spagnuolo I, Galleri L, Cataldo D, Dotta F (2011) Increased expression of microRNA miR-326 in type 1 diabetic patients with ongoing islet autoimmunity. Diabetes/Metab Res Rev 27:862–866
Sesti G, Federici M, Hribal ML, Lauro D, Sbraccia P, Lauro R (2001) Defects of the insulin receptor substrate (IRS) system in human metabolic disorders. FASEB J 15:2099–2111
Shantikumar S, Caporali A, Emanueli C (2012) Role of microRNAs in diabetes and its cardiovascular complications. Cardiovasc Res 93:583–593
Taylor J, Schenck I, Blankenberg D, Nekrutenko A (2007) Using galaxy to perform large-scale interactive data analyses. Curr Protoc Bioinform. 10:10.5. doi:10.1002/0471250953.bi1005s19
Trajkovski M et al (2011) MicroRNAs 103 and 107 regulate insulin sensitivity. Nature 474:649–653
Wang Y, Liu J, Liu C, Naji A, Stoffers DA (2013) MicroRNA-7 regulates the mTOR pathway and proliferation in adult pancreatic β-cells. Diabetes 62:887–895
Ward LD, Kellis M (2012) HaploReg: a resource for exploring chromatin states, conservation, and regulatory motif alterations within sets of genetically linked variants. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D930–D934
Welter D et al (2014) The NHGRI GWAS Catalog, a curated resource of SNP-trait associations. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D1001–D1006
Whiting DR, Guariguata L, Weil C, Shaw J (2011) IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 94:311–321
Yang J-H, Li J-H, Shao P, Zhou H, Chen Y-Q, Qu L-H (2011) starBase: a database for exploring microRNA–mRNA interaction maps from Argonaute CLIP-Seq and Degradome-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res 39:D202–D209
Zampetaki A et al (2010) Plasma microRNA profiling reveals loss of endothelial miR-126 and other microRNAs in type 2 diabetes. Circ Res 107:810–817
Acknowledgments
We thank Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences for providing the fund of this work (Fund Number: 1393-1-91-13285). Also this work was supported partly by Italian Ministry of Health by providing financial support to Andrea Masotti (Ricerca Corrente 2014 and 2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghaedi, H., Bastami, M., Jahani, M.M. et al. A Bioinformatics Approach to the Identification of Variants Associated with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus that Reside in Functionally Validated miRNAs Binding Sites. Biochem Genet 54, 211–221 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-016-9713-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-016-9713-5