Abstract
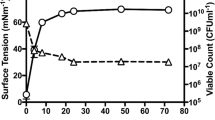
Planctomycetes are a unique and important phylum containing mostly aquatic bacteria, which are often associated with phototrophic surfaces. A complex lifestyle, their potential for the production of bioactive small molecules, their unusual cell biology and a large number of giant and hypothetical genes in their genomes make these microorganisms a fascinating topic for further research. Here, we characterise three novel planctomycetal strains isolated from polystyrene and polyethylene particles that were submerged in the German part of the Baltic Sea and the estuary of the river Warnow. All three strains showed typical planctomycetal traits such as division by polar budding and formation of rosettes. The isolated strains were mesophilic and neutrophilic chemoheterotrophs and reached generation times of 10–25 h during laboratory-scale cultivation. Taxonomically, the three strains belong to the genus Rubripirellula. Based on our analyses all three strains represent novel species, for which we propose the names Rubripirellula amarantea sp. nov., Rubripirellula tenax sp. nov. and Rubripirellula reticaptiva sp. nov. The here characterised strains Pla22T (DSM 102267T = LMG 29691T), Poly51T (DSM 103356T = VKM B-3438T) and Poly59T (DSM 103767T = LMG 29696T) are the respective type strains of these novel species. We also emend the description of the genus Rubripirellula.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acehan D, Santarella-Mellwig R, Devos DP (2013) A bacterial tubulovesicular network. J Cell Sci 127:277–280
Bengtsson MM, Øvreås L (2010) Planctomycetes dominate biofilms on surfaces of the kelp Laminaria hyperborea. BMC Microbiol 10:261
Bengtsson MM, Sjøtun K, Lanzén A, Øvreås L (2012) Bacterial diversity in relation to secondary production and succession on surfaces of the kelp Laminaria hyperborea. ISME J 6:2188–2198
Boedeker C, Schuler M, Reintjes G, Jeske O, van Teeseling MC, Jogler M, Rast P, Borchert D, Devos DP, Kucklick M, Schaffer M, Kolter R, van Niftrik L, Engelmann S, Amann R, Rohde M, Engelhardt H, Jogler C (2017) Determining the bacterial cell biology of Planctomycetes. Nat Commun 8:14853
Bondoso J, Harder J, Lage OM (2013) rpoB gene as a novel molecular marker to infer phylogeny in Planctomycetales. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 104:477–488
Bondoso J, Balague V, Gasol JM, Lage OM (2014) Community composition of the Planctomycetes associated with different macroalgae. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 88:445–456
Bondoso J, Albuquerque L, Nobre MF, Lobo-da-Cunha A, da Costa MS, Lage OM (2015) Roseimaritima ulvae gen. nov., sp. nov. and Rubripirellula obstinata gen. nov., sp. nov. two novel planctomycetes isolated from the epiphytic community of macroalgae. Syst Appl Microbiol 38:8–15
Bondoso J, Godoy-Vitorino F, Balague V, Gasol JM, Harder J, Lage OM (2017) Epiphytic Planctomycetes communities associated with three main groups of macroalgae. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 93(3):fiw255
Cayrou C, Raoult D, Drancourt M (2010) Broad-spectrum antibiotic resistance of Planctomycetes organisms determined by Etest. J Antimicrob Chemother 65:2119–2122
Devos DP (2014) PVC bacteria: variation of, but not exception to, the Gram-negative cell plan. Trends Microbiol 22:14–20
Devos DP, Reynaud EG (2010) Evolution. Intermediate steps. Science 330:1187–1188
Devos DP, Jogler C, Fuerst JA (2013) The 1st EMBO workshop on PVC bacteria-Planctomycetes-Verrucomicrobia-Chlamydiae superphylum: exceptions to the bacterial definition? Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 104:443–449
Frank O, Michael V, Pauker O, Boedeker C, Jogler C, Rohde M, Petersen J (2014) Plasmid curing and the loss of grip—the 65-kb replicon of Phaeobacter inhibens DSM 17395 is required for biofilm formation, motility and the colonization of marine algae. Syst Appl Microbiol 38:120–127
Fuerst JA, Sagulenko E (2011) Beyond the bacterium: planctomycetes challenge our concepts of microbial structure and function. Nat Rev Microbiol 9:403–413
Godinho O, Calisto R, Ovreas L, Quinteira S, Lage OM (2019) Antibiotic susceptibility of marine Planctomycetes. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 112:1273–1280
Graca AP, Calisto R, Lage OM (2016) Planctomycetes as novel source of bioactive molecules. Front Microbiol 7:1241
Jeske O, Jogler M, Petersen J, Sikorski J, Jogler C (2013) From genome mining to phenotypic microarrays: planctomycetes as source for novel bioactive molecules. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 104:551–567
Jeske O, Schüler M, Schumann P, Schneider A, Boedeker C, Jogler M, Bollschweiler D, Rohde M, Mayer C, Engelhardt H, Spring S, Jogler C (2015) Planctomycetes do possess a peptidoglycan cell wall. Nat Commun 6:7116
Jeske O, Surup F, Ketteniß M, Rast P, Förster B, Jogler M, Wink J, Jogler C (2016) Developing techniques for the utilization of Planctomycetes as producers of bioactive molecules. Front Microbiol 7:1242
Jogler C, Glöckner FO, Kolter R (2011) Characterization of Planctomyces limnophilus and development of genetic tools for its manipulation establish it as a model species for the phylum Planctomycetes. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:5826–5829
Jogler C, Waldmann J, Huang X, Jogler M, Glöckner FO, Mascher T, Kolter R (2012) Identification of proteins likely to be involved in morphogenesis, cell division, and signal transduction in Planctomycetes by comparative genomics. J Bacteriol 194:6419–6430
Kallscheuer N, Jogler M, Wiegand S, Peeters S, Heuer A, Boedeker C, Jetten M, Rohde M, Jogler C (2019) Rubinisphaera italica sp. nov. isolated from a hydrothermal area in the Tyrrhenian Sea close to the volcanic island Panarea. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-019-01329-w
Kim M, Oh HS, Park SC, Chun J (2014) Towards a taxonomic coherence between average nucleotide identity and 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity for species demarcation of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:346–351
Kohn T, Heuer A, Jogler M, Vollmers J, Boedeker C, Bunk B, Rast P, Borchert D, Glöckner I, Freese HM, Klenk HP, Overmann J, Kaster AK, Wiegand S, Rohde M, Jogler C (2016) Fuerstia marisgermanicae gen. nov., sp. nov., an unusual member of the phylum Planctomycetes from the German Wadden Sea. Front Microbiol 7:2079
Kohn T, Wiegand S, Boedeker C, Rast P, Heuer A, Jetten MSM, Schüler M, Becker S, Rohde C, Müller R-W, Brümmer F, Rohde M, Engelhardt H, Jogler M, Jogler C (2019) Planctopirus ephydatiae, a novel Planctomycete isolated from a freshwater sponge. Syst Appl Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2019.126022
König E, Schlesner H, Hirsch P (1984) Cell wall studies on budding bacteria of the Planctomyces/Pasteuria group and on a Prosthecomicrobium sp. Arch Microbiol 138:200–205
Lachnit T, Fischer M, Kunzel S, Baines JF, Harder T (2013) Compounds associated with algal surfaces mediate epiphytic colonization of the marine macroalga Fucus vesiculosus. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 84:411–420
Lage OM, Bondoso J (2014) Planctomycetes and macroalgae, a striking association. Front Microbiol 5:267
Lage OM, Bondoso J, Lobo-da-Cunha A (2013) Insights into the ultrastructural morphology of novel Planctomycetes. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 104:467–476
Lee I, Ouk Kim Y, Park SC, Chun J (2016) OrthoANI: an improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:1100–1103
Lindsay MR, Webb RI, Fuerst JA (1997) Pirellulosomes: a new type of membrane-bounded cell compartment in planctomycete bacteria of the genus Pirellula. Microbiology 143:739–748
Luo C, Rodriguez RL, Konstantinidis KT (2014) MyTaxa: an advanced taxonomic classifier for genomic and metagenomic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 42:e73
Oberbeckmann S, Kreikemeyer B, Labrenz M (2018) Environmental factors support the formation of specific bacterial assemblages on microplastics. Front Microbiol 8:2709
Pilhofer M, Rappl K, Eckl C, Bauer AP, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH, Petroni G (2008) Characterization and evolution of cell division and cell wall synthesis genes in the bacterial phyla Verrucomicrobia, Lentisphaerae, Chlamydiae, and Planctomycetes and phylogenetic comparison with rRNA genes. J Bacteriol 190:3192–3202
Pruesse E, Peplies J, Glöckner FO (2012) SINA: accurate high-throughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes. Bioinformatics 28:1823–1829
Qin Q-L, Xie B-B, Zhang X-Y, Chen X-L, Zhou B-C, Zhou J, Oren A, Zhang Y-Z (2014) A proposed genus boundary for the prokaryotes based on genomic insights. J Bacteriol 196:2210–2215
Rast P, Glöckner I, Boedeker C, Jeske O, Wiegand S, Reinhardt R, Schumann P, Rohde M, Spring S, Glöckner FO (2017) Three novel species with peptidoglycan cell walls form the new genus Lacunisphaera gen. nov. in the family Opitutaceae of the verrucomicrobial subdivision 4. Front Microbiol 8:202
Rodriguez-R LM, Konstantinidis KT (2016) The enveomics collection: a toolbox for specialized analyses of microbial genomes and metagenomes. PeerJ Preprints, 1900v1
Santarella-Mellwig R, Pruggnaller S, Roos N, Mattaj IW, Devos DP (2013) Three-dimensional reconstruction of bacteria with a complex endomembrane system. PLoS Biol 11:e1001565
Sievers F, Wilm A, Dineen D, Gibson TJ, Karplus K, Li W, Lopez R, McWilliam H, Remmert M, Söding J (2011) Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol Syst Biol 7:539
Spring S, Bunk B, Sproer C, Schumann P, Rohde M, Tindall BJ, Klenk HP (2016) Characterization of the first cultured representative of Verrucomicrobia subdivision 5 indicates the proposal of a novel phylum. ISME J 10:2801–2816
Stackebrandt E, Ebers J (2006) Taxonomic parameter revisited: tarnished gold standards. Microbiol Today 33:152–155
Staley JT, Fuerst JA, Giovannoni S, Schlesner H (1992) The order Planctomycetales and the genera Planctomyces, Pirellula, Gemmata, and Isosphaera. In: Balows A, Trüper HG, Dworkin M, Harder W, Schleifer K-H (eds) The Prokaryotes. Springer, New York, pp 3710–3731
Stamatakis A (2014) RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30:1312–1313
van Teeseling MC, Mesman RJ, Kuru E, Espaillat A, Cava F, Brun YV, Van Nieuwenhze MS, Kartal B, van Niftrik L (2015) Anammo× Planctomycetes have a peptidoglycan cell wall. Nat Commun 6:6878
Vollmers J, Frentrup M, Rast P, Jogler C, Kaster AK (2017) untangling genomes of novel Planctomycetal and Verrucomicrobial species from monterey bay kelp forest metagenomes by refined binning. Front Microbiol 8:472
Wagner M, Horn M (2006) The Planctomycetes, Verrucomicrobia, Chlamydiae and sister phyla comprise a superphylum with biotechnological and medical relevance. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:241–249
Wiegand S, Jogler M, Jogler C (2018) On the maverick Planctomycetes. FEMS Microbiol Rev 42:739–776
Wiegand S, Jogler M, Boedeker C, Pinto D, Vollmers J, Rivas-Marín E, Kohn T, Peeters SH, Heuer A, Rast P, Oberbeckmann S, Bunk B, Jeske O, Meyerdierks A, Storesund JE, Kallscheuer N, Lücker S, Lage OM, Pohl T, Merkel BJ, Hornburger P, Müller R-W, Brümmer F, Labrenz M, Spormann AM, Op den Camp HJM, Overmann J, Amann R, Jetten MSM, Mascher T, Medema MH, Devos DP, Kaster A-K, Øvreås L, Rohde M, Galperin MY, Jogler C (2019) Cultivation and functional characterization of 79 planctomycetes uncovers their unique biology. Nat Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-019-0588-1
Will SE, Henke P, Boedeker C, Huang S, Brinkmann H, Rohde M, Jarek M, Friedl T, Seufert S, Schumacher M (2018) Day and night: metabolic profiles and evolutionary relationships of six axenic non-marine cyanobacteria. Gen Biol Evol 11:270–294
Yarza P, Yilmaz P, Pruesse E, Glöckner FO, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH, Whitman WB, Euzeby J, Amann R, Rossello-Mora R (2014) Uniting the classification of cultured and uncultured bacteria and archaea using 16S rRNA gene sequences. Nat Rev Microbiol 12:635–645
Acknowledgements
Part of this research was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) Grants No. KA 4967/1-1 and JO 893/4-1, Grant ALWOP.308 of the Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek (NWO), SIAM (Soehngen Institute for Anaerobic Microbiology) Grant No. 024002002 and the Radboud Excellence fellowship. We thank Ina Schleicher for skillful technical assistance and our collaborators Sonja Oberbeckmann and Matthias Labrenz (IOW Warnemünde, Germany) for sampling support. We would also like to thank Brian Tindall and Regine Fähnrich as well as the BCCM/LMG Bacteria collection for on-going support during strain deposition.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NK wrote the manuscript, analyzed the data and prepared the figures; SW and MJ performed the genomic and phylogenetic analysis; AH isolated the strains and performed the initial cultivation and strain deposition; SHP and CB performed the light microscopic analysis; MSMJ contributed to text preparation and revised the manuscript; MR performed the electron microscopic analysis; CJ and MJ took the samples in the Baltic Sea and the river Warnow and CJ supervised the study. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethicals statement
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kallscheuer, N., Jogler, M., Wiegand, S. et al. Three novel Rubripirellula species isolated from plastic particles submerged in the Baltic Sea and the estuary of the river Warnow in northern Germany. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 113, 1767–1778 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-019-01368-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-019-01368-3