Abstract
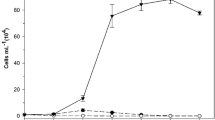
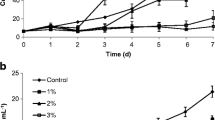
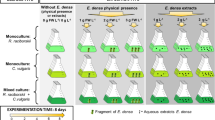
Morphological responses of green algae to submerged macrophytes were rarely studied, and the potential active substances played roles in the interaction were little known previously. In the current work, according to acetone extract experiments, it was demonstrated that submerged macrophytes (Ceratophyllum demersum L.) could allelopathically inhibit the growth of Chlorella vulgaris Beij. and induce its colony formation, the effects of which were concentration dependent. Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis revealed eight kinds of active substances from the C. demersum extracts, namely hexanoic acid, phthalic acid, octanedioic acid, butenoic acid, azelaic acid, palmitic acid, alpha linolenic acid and pentanedioic acid. Standard compound addition test indicated that palmitic acid and alpha linolenic acid might play important roles in the induction of colony formation and growth inhibition of C. vulgaris. This study provided some more new insights into the photosynthetic organism interaction between submerged macrophytes and green algae, in terms of not only growth but also morphological responses.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson DM, Cembella AD, Hallegraeff GM (2012) Progress in understanding harmful algal blooms: paradigm shifts and new technologies for research, monitoring, and management. Annu Rev Mar Sci 4:143–176
Anthoni U, Christophersen C, Wium-Anderson S, Jacobsen N (1980) Biological active sulphur compounds from the green algae Chara globularis. Phytochemistry 19(6):1228–1229
Boraas ME, Seale DB, Boxhorn JE (1998) Phagotrophy by a flagellate selects for colonial prey: a possible origin of multicellularity. Evol Ecol 12(2):153–164
Dong J, Lu JJ, Li GB, Song LR (2013) Influences of a submerged macrophyte on colony formation and growth of a green alga. Aquat Biol 19(5):265–274
Dong J, Chang MY, Li CL, Li JC, Shang XY (2018a) Morphological and growth responses of two green algal strains to toxic Microcystis are dependent on the cultivation growth phase of filtrate and target strain. Ann Limnol Int J Limnol 54(8):70–76
Dong J, Gao YN, Chang MY, Ma HH, Han K, Tao X, Li Y (2018b) Colony formation by the green alga Chlorella vulgaris in response to the competitor Ceratophyllum demersum. Hydrobiologia 805(1):177–187
Fisher RM, Bel T, West SA (2016) Multicellular group formation in response to predators in the algae Chlorella vulgaris. J Evol Biol 29:551–559
Gao YN, Liu BY, Xu D, Zhou QH, Hu CY, Ge FJ, Zhang LP, Wu ZB (2011a) Phenolic compounds exuded from two submerged freshwater macrophytes and their allelopathic effects on Microcystis aeruginosa. Pol J Environ Stud 20(5):1153–1159
Gao YN, Liu BY, Ge FJ, Xu D, Zhang LP, Wu ZB (2011b) Isolation and identification of allelopathic fatty acids exuded from three submerged hydrocharitaceae species. Acta Hydrobiol Sin 35(1):170–174 (in Chinese)
Gao YN, Ge FJ, Zhang LP, He Y, Lu ZY, Zhang YY, Liu BY, Zhou QH, Wu ZB (2017) Enhanced toxicity to the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa by low-dosage repeated exposure to the allelochemical N-phenyl-1-naphthylamine. Chemosphere 174:732–738
Gross EM, Erhard D, Enikö I (2003) Allelopathic activity of Ceratophyllum demersum L. and Najas marina spp. Intermedia (Wolfgang) Casper. Hydrobiologia 506-509(1-3): 583-589
Hilt S, Gross EM (2008) Can allelopathically active submerged macrophytes stabilise clear-water states in shallow lakes. Basic Appl Ecol 9:422–432
Hong Y, Hu HY (2007) Effects of the aquatic extracts of Arundo donax L. on the growth of freshwater algae. Allelopath J 20(2):315–326
Huang Y, Nan HH, Zhu XX, Li BP, Zhang Z, Yang Z (2016) Waterborne copper impairs grazer-induced colony formation and photosynthetic efficiency in Scenedesmus obliquus. Limnol Oceanogr 61:625–634
Huang Y, Cui GL, Li BP, Zhu XX, Yang Z (2018) Elevated atmospheric CO2 enhances grazer-induced morphological defense in the freshwater green alga Scenedesmus obliquus. Limnol Oceanogr 63:1004–1014
Iacarella JC, Barrow JL, Giani A, Beisner BE, Gregory-Eaves I (2018) Shifts in algal dominance in freshwater experimental ponds across differing levels of macrophytes and nutrients. Ecosphere 9(1):1–15
Jiang H, Zhao DH, Zhao H, Cai Y, Xu DL, Zhou CF, Leng X, Xie D (2015) Density-dependent interactions between Hydrilla verticillata (L.F.) Royle and phytoplankton: a mesocosm experiment. CLEAN Soil Air Water 43(12):1623–1632
Jin PF, Wang HN, Huang WK, Liu WB, Fan YM, Miao WG (2018) The allelopathic effect and safety evaluation of 3,4-dihydroxybenzalacetone on Microcystis aeruginosa. Pestic Biochem Phys 147:145–152
Kozak A, Gołdyn R (2016) Macrophyte response to the protection and restoration measures of four water bodies. Int Rev Hydrobiol 101:160–172
Kurashov EA, Mitrukova GG, Krylova JV (2018) Interannual variability of low-molecular metabolite composition in Ceratophyllum demersum (Ceratophyllaceae) from a floodplain lake with a changeable tropical status. Contemp Probl Ecol 11(2):179–194
Leflaive J, Lacroix G, Nicaise Y, Ten-Hage L (2008) Colony induction and growth inhibition in Desmodesmus quadrispina (Chlorococcales) by allelochemicals released from the filamentous alga Uronema confervicolum (Ulotrichales). Environ Microb 10(6):1536–1546
Li M, Nkrumah PN, Peng Q (2015) Different tolerances to chemical contaminants between unicellular and colonial morph of Microcystis aeruginosa: excluding the differences among different strains. J Hazard Mater 285:245–249
Lichtenthaler HK, Buschmann C (2001) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: measurement and characterization by UV–VIS spectroscopy. In: Wrolstad RE, Acree TE, An H, Decker EA, Penner MH, Reid DS, Schwartz SJ, Shoemaker CF, Sporns P (eds) Current protocols in food analytical chemistry. Wiley, London, pp F4.3.1–F4.3.8
Liu Y, Wang W, Zhang M, Xing P, Yang Z (2010) PSII-efficiency, polysaccharide production, and phenotypic plasticity of Scenedesmus obliquus in response to changes in metabolic carbon flux. Biochem Syst Ecol 38:292–299
Liu LZ, Huang Q, Qin BQ, Zhu G, Wu WuY (2016) Characterizing cell surface of blooming Microcystis in Lake Taihu, China. Water Sci Technol 73(11):2731–2738
Liu PP, Wang L, Xia X, Zeng L, Zhou QH, Liu BY, He F, Wu ZB (2019) Microzooplankton grazing and phytoplankton growth in a Chinese lake. Pol J Environ Stud 28(1):225–235
Lürling M, Beekman W (2006) Palmelloides formation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: defence against rotifer predator? Int J Limnol 42(2):65–72
Lürling M, Van Geest G, Scheffer M (2006) Importance of nutrient competition and allelopathic effects in suppression of the green alga Scenedesmus obliquus by the macrophytes Chara, Elodea and Myriophyllum. Hydrobiologia 556:209–220
Mello MME, Soares MCS, Roland F, Lürling M (2012) Growth of inhibition and colony formation in the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa induced by the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. J Plankton Res 34(11):987–994
Mulderij G, Mooij WM, Van Donk E (2005) Allelopathic growth inhibition and colony formation of the green alga Scenedesmus obliquus by the aquatic macrophyte Stratiotes aloides. Aquat Ecol 39:11–21
Nakai S, Asaoka S, Okuda T, Nishijima W (2014) Growth inhibition of Microcystis aeruginosa by allelopathic compounds originally isolated from Myriophyllum spicatum: temperature and light effects and evidence of possible major mechanisms. J Chem Eng Jpn 47(6):488–493
O’Donnell DR, Fey SB, Cottingham KL (2013) Nutrient availability influences kairomone-induced defenses in Scenedesmus acutus (Chlorophyceae). J Plankton Res 35(1):191–200
O’Neil JM, Davis TW, Burford MA, Gobler CJ (2012) The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: the potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 14:313–334
Paerl HW, Husiman J (2008) Blooms like it hot. Science 320:57–58
Pan Y, Liu C, Li F, Zhou CQ, Yan SW, Dong JY, Li TR, Duan CQ (2017) Norfloxacin disrupts Daphnia magna-induced colony formation in Scenedesmus quadricauda and facilitates grazing. Ecol Eng 10:255–261
Pełechata A, Pełechaty M (2010) The in situ influence of Ceratophyllum demersum on a phytoplankton assemblage. Oceanol Hydrobiol Stud 39:95–101
Song L, Chen W, Peng L, Wan N, Gan N, Zhang X (2007) Distribution and bioaccumulation of microcystins in water columns: a systematic investigation into the environmental fate and the risks associated with microcystins in Meiliang Bay, Lake Taihu. Water Res 41:2853–2864
Švanys A, Paškauskas R, Hilt S (2014) Effects of the allelopathically active macrophyte Myriophyllum spicatum on a natural phytoplankton community: a mesocosm study. Hydrobiologia 737:57–66
Van Donk E, Ianora A, Vos M (2011) Induced defences in marine and freshwater phytoplankton: a review. Hydrobiologia 668(1):3–19
Vanderstukken M, Declerck SAJ, Decaestecker E, Muylaert K (2014) Long-term allelopathic control of phytoplankton by the submerged macrophyte Elodea nuttallii. Freshw Biol 59:930–941
Wang HQ, Zhu HJ, Zhang LY, Xue WJ, Yuan B (2014) Identification of antialgal compounds from the aquatic plant Elodea nuttallii. Allelopath J 34(2):207–213
Wang R, Xue QN, Wang JT, Tan LJ, Zhang QC, Zhao Y, Anderson DM (2017) Effects of an allelochemical in Phaeodactylum tricornutum filtrate on Heterosigma akashiwo: morphological, physiological and growth effects. Chemosphere 186:527–534
Wu XY, Zhang J, Qin BL, Cui GL, Yang Z (2013) Grazer density-dependent response of induced colony formation of Scenedesmus obliquus to grazing-associated infochemicals. Biochem Syst Ecol 50:286–292
Xian QM, Chen HD, Zou HX, Yin DQ (2004) Analysis of organic acids in aqueous leachates of three submerged macrophytes. J Plant Resour Environ 13(3):57–58 (in Chinese)
Xiao M, Li M, Reynolds CS (2018) Colony formation in the cyanobacterium Microcystis. Biol Rev 93(3):1399–1420
Yasumoto M, Ooi T, Takenori K, Kasai F (2000) Characterization of Daphnia kairomone inducing morphological change of green alga Actinastrum sp. Tennen Yuki Kagobutsu Toronkai Keon Yoshishu 42:385–390
Zhang TT, Zheng CY, Hu WW, Xu W, Wang HF (2010) The allelopathy and allelopathic mechanism of phenolic acids on toxic Microcystis aeruginosa. J Appl Phycol 22:71–77
Zhao LF, Lu L, Li M, Xu ZR, Zhu W (2011) Effects of Ca and Mg levels on colony formation and EPS content of cultured M. aeruginosa. Procedia Environ Sci 10:1452–1458
Zhao JG, He FF, Chen ZH, Li HJ, Hu JM, Liu FP (2012) Effect of culture and extract solutions of macrophytes on the growth of three common algae. J Freshw Ecol 27:367–379
Zheng GL, Xu RB, Chang XX, Hilt S, Wu C (2013) Cyanobacteria can allelopathically inhibit submerged macrophytes: effects of Microcystis aeruginosa extracts and exudates on Potamogeton malaianus. Aquat Bot 109:1–7
Zhu JY, Liu BY, Wang J, Gao YN, Wu ZB (2010) Study on the mechanism of allelopathic influence on cyanobacteria and chlorophytes by submerged macrophyte (Myriophyllum spicatum) and its secretion. Aquat Toxicol 98:196–203
Zhu W, Dai XX, Li M (2014) Relationship between extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) content and colony size of Microcystis is colonial morphology dependent. Biochem Syst Ecol 55:346–350
Zhu XX, Nan HH, Chen QW, Wu ZQ, Wu XY, Huang Y, Yang Z (2015) Potential grazing intensity directly determines the extent of grazer-induced colony formation in Scenedesmus obliquus. Biochem Syst Ecol 61:271–277
Zuo SP, Wan K, Ma SM, Ye LT (2014) Combined allelopathic potential of aquatic plants species to control algae. Allelopath J 2:315–323
Zuo SP, Fang ZS, Yang SY, Wan K, Han YJ (2015) Effect of allelopathic potential from selected aquatic macrophytes on algal interaction in the polluted water. Biochem Syst Ecol 61:133–138
Zuo SP, Zhou SB, Ye LT, Ding Y, Jiang XF (2016a) Antialgal effects of five individual allelochemicals and their mixtures in low level pollution conditions. Environ Sci Poll Res 23:15703–15711
Zuo SP, Zhou SB, Ye LT, Ma SM (2016b) Synergistic and antagonistic interactions among five allelochemicals with antialgal effects on bloom-forming Microcystis aeruginosa. Ecol Eng 97:486–492
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation Project of China (Nos. 31500380 & 31700405). Besides, we really thank the editors and anonymous reviewers’ suggestions on improving the whole manuscript. We are also grateful to our co-author Dr. Yunni Gao for her assistance in the experimentation and manuscript revision.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Handling Editor: Bastiaan Willem Ibelings.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, J., Chang, M., Li, C. et al. Allelopathic effects and potential active substances of Ceratophyllum demersum L. on Chlorella vulgaris Beij.. Aquat Ecol 53, 651–663 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-019-09715-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-019-09715-2