Abstract
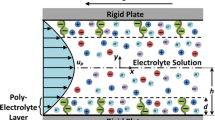
In this paper, we compute the electrokinetic transport in soft nanochannels grafted with poly-zwitterionic (PZI) brushes. The transport is induced by an external pressure gradient, which drives the ionic cloud (in the form of an electric double layer or EDL) at the brush surfaces to induce an electric field that drives an induced electroosmotic transport. We characterize the overall transport by quantifying this electric field, overall flow velocity, and the energy conversion associated with the development of the electric field and a streaming current. We specially focus on how the ability of the PZI to ionize and demonstrate a significant charge at both large and small pH can be efficiently maneuvered to develop a liquid transport, an electric field, and an electrokinetically induced power across a wide range of pH values.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander S (1977) Polymer adsorption on small spheres. A scaling approach. J Phys 38:977
Ali M, Schiedt B, Healy K, Neumann R, Ensinger W (2008) Modifying the surface charge of single track-etched conical nanopores in polyimide. Nanotechnology 19:085713
Ali M, Yameen B, Neumann R, Ensinger W, Knoll W, Azzaroni O (2008) Biosensing and supramolecular bioconjugation in single conical polymer nanochannels. Facile incorporation of biorecognition elements into nanoconfined geometries. J Am Chem Soc 130:16351
Ali M, Ramirez P, Mafe S, Neumann R, Ensinger W (2009) A pH-tunable nanofluidic diode with a broad range of rectifying properties. ACS Nano 3:603
Ali M, Schiedt B, Neumann R, Ensinger W (2010a) Biosensing with functionalized single asymmetric polymer nanochannels. Macromol Biosci 10:28
Ali M, Yameen B, Cervera J, Ramirez P, Neumann R, Ensinger W, Knoll W, Azzaroni O (2010b) Layer-by-layer assembly of polyelectrolytes into ionic current rectifying solid-state nanopores: insights from theory and experiment. J Am Chem Soc 132:8338
Azzaroni O, Brown AA, Huck WTS (2006) UCST wetting transitions of polyzwitterionic brushes driven by self-association. Angew Chem Int Ed 118:1802
Baldessari F, Santiago JG (2008) Electrokinetics in nanochannels: part I. Electric double layer overlap and channel-to-well equilibrium. J Colloid Interface Sci 325:526
Behrens SH, Grier DG (2001) The charge of glass and silica surfaces. J Chem Phys 115:6716
Benson L, Yeh L-H, Chou T-H, Qian S (2013) Field effect regulation of donnan potential and electrokinetic flow in a functionalized soft nanochannel. Soft Matter 9:9767
Cao Q, You H (2016) Electroosmotic flow in mixed polymer brush-grafted nanochannels. Polymers 8:438
Chanda S, Sinha S, Das S (2014) Streaming potential and electroviscous effects in soft nanochannels: towards designing more efficient nanofluidic electrochemomechanical energy converters. Soft Matter 10:7558
Chen G, Das S (2015a) Scaling laws and ionic current inversion in polyelectrolyte-grafted nanochannels. J Phys Chem B 119:12714
Chen G, Das S (2015b) Electroosmotic transport in polyelectrolyte-grafted nanochannels with pH-dependent charge density. J Appl Phys 117:185304
Chen G, Das S (2015c) Electrostatics of soft charged interfaces with pH-dependent charge density: effect of consideration of appropriate hydrogen ion concentration distribution. RSC Adv 5:4493
Chen G, Das S (2015d) Streaming potential and electroviscous effects in soft nanochannels beyond Debye–Hckel linearization. J Colloid Interface Sci 445:357
Chen G, Das S (2017a) Thermodynamics, electrostatics, and ionic current in nanochannels grafted with pH-responsive end-charged polyelectrolyte brushes. Electrophoresis 38:720
Chen G, Das S (2017b) Massively enhanced electroosmotic transport in nanochannels grafted with end-charged polyelectrolyte brushes. J Phys Chem B 121:3130
Chen M, Briscoe WH, Armes SP, Klein J (2009) Lubrication at physiological pressures by polyzwitterionic brushes. Science 323:1698
Chen M, Briscoe WH, Armes SP, Cohen H, Klein J (2011) Polyzwitterionic brushes: extreme lubrication by design. Eur Polym J 47:511
Chen G, Sachar HS, Das S (2018) Efficient electrochemomechanical energy conversion in nanochannels grafted with end-charged polyelectrolyte brushes at medium and high salt concentration. Soft Matter 14:5246
Cheng N, Brown AA, Azzaroni O, Huck WTS (2008) Thickness-dependent properties of polyzwitterionic brushes. Macromolecules 41:6317
Daiguji H, Yang P, Szeri AJ, Majumdar A (2004) Electrochemomechanical energy conversion in nanofluidic channels. Nano Lett 4:2315
Das S, Guha A, Mitra SK (2013) Exploring new scaling regimes for streaming potential and electroviscous effects in a nanocapillary with overlapping electric double layers. Anal Chim Acta 804:159
Das S, Chanda S, Eijkel JCT, Tas NR, Chakraborty S, Mitra SK (2014) Filling of charged cylindrical capillaries. Phys Rev E 90:043011
Das S, Banik M, Chen G, Sinha S, Mukherjee R (2015) Polyelectrolyte brushes: theory, modelling, synthesis and applications. Soft Matter 11:8550
de Gennes P-G (1976) Scaling theory of polymer adsorption. J Phys 37:1443
de Gennes P-G (1980) Conformations of polymers attached to an interface. Macromolecules 13:1069
de Groot GW, Santonicola MG, Sugihara K, Zambelli T, Reimhult E, Vrös J, Vancso GJ (2013) Switching transport through nanopores with pH-responsive polymer brushes for controlled ion permeability. ACS Appl Mater Interface 5:1400
Fidale LC, Nikolajski M, Rudolph T, Dutz S, Schacher FH, Heinze T (2013) Hybrid Fe\(_3\)O\(_4\)@ amino cellulose nanoparticles in organic mediaheterogeneous ligands for atom transfer radical polymerizations. J Colloid Interface Sci 390:25
Gilles FM, Tagliazucchi M, Azzaroni O, Szleifer I (2016) Ionic conductance of polyelectrolyte-modified nanochannels: nanoconfinement effects on the coupled protonation equilibria of polyprotic brushes. J Phys Chem C 120:4789
Guo X, Ballauff M (2000) Spatial dimensions of colloidal polyelectrolyte brushes as determined by dynamic light scattering. Langmuir 16:8719
Guo X, Ballauff M (2001) Spherical polyelectrolyte brushes: comparison between annealed and quenched brushes. Phys Rev E 64:051406
Higaki Y, Kobayashi M, Murakami D, Takahara A (2016) Anti-fouling behavior of polymer brush immobilized surfaces. Polym J 48:325
Hoffmann M, Jusufi A, Schneider C, Ballauff M (2009) Surface potential of spherical polyelectrolyte brushes in the presence of trivalent counterions. J Colloid Interface Sci 338(566):566
Ilcikova M, Tkac J, Kasak P (2015) Switchable materials containing polyzwitterion moieties. Polymers 7:2344
Knop K, Hoogenboom R, Fischer D, Schubert US (2010) Poly(ethylene glycol) in drug delivery: pros and cons as well as potential alternatives. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:6288
Kobayashi M, Takahara A (2013) Environmentally friendly repeatable adhesion using a sulfobetaine-type polyzwitterion brush. Polym Chem 4:4987
Li F, Jian Y, Chang L, Zhao G, Yang L (2016) Alternating current electroosmotic flow in polyelectrolyte-grafted nanochannel. Colloid Surf B 147:234
Li H, Chen G, Das S (2016) Electric double layer electrostatics of pH-responsive spherical polyelectrolyte brushes in the decoupled regime. Colloid Surf B 147:180
Li F, Jian Y, Xie Z, Liu Y, Liu Q (2017) Transient alternating current electroosmotic flow of a jeffrey fluid through a polyelectrolyte-grafted nanochannel. RSC Adv 7:782
Lin J-Y, Lin C-Y, Hsu J-P, Tseng S (2016) Ionic current rectification in a pH-tunable polyelectrolyte brushes functionalized conical nanopore: effect of salt gradient. Anal Chem 88:1176
Lowe AB, McCormick CL (2006) Polyelectrolytes and polyzwitterions: synthesis, properties, and applications. In: ACS Symposium Series, American Chemical Society
Ma Y, Yeh L-H, Lin C-Y, Mei L, Qian S (2015) pH-regulated ionic conductance in a nanochannel with overlapped electric double layers. Anal Chem 87:4508
Milne Z, Yeh LH, Chou TH, Qian S (2014) Tunable donnan potential and electrokinetic flow in a biomimetic gated nanochannel with ph-regulated polyelectrolyte brushes. J Phys Chem C 118:19806
Milner ST (1991) Polymer brushes. Science 251:905
Monteil C, Bar N, Bee A, Villemin D (2016) An efficient recyclable magnetic material for the selective removal of organic pollutants. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 7:1447
Moya S, Azzaroni O, Farhan T, Osborne VL, Huck WTS (2005) Locking and unlocking of polyelectrolyte brushes: toward the ffabrication of chemically controlled nanoactuators. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:4578
Netz RR, Andelman D (2003) Neutral and charged polymers at interfaces. Phys Rep 380:1
Nguyen T, Xie Y, de Vreede LJ, van den Berg A, Eijkel JCT (2013) Highly enhanced energy conversion from the streaming current by polymer addition. Lab Chip 13:3210
Patwary J, Chen G, Das S (2015) Efficient electrochemomechanical energy conversion in nanochannels grafted with polyelectrolyte layers with pH-dependent charge density. Microfluid Nanofluid 20:37
Poddar A, Maity D, Bandopadhyay A, Chakraborty S (2016) Electrokinetics in polyelectrolyte grafted nanofluidic channels modulated by the ion partitioning effect. Soft Matter 12:5968
Saleh TA, Rachman IB, Ali SA (2017) Tailoring hydrophobic branch in polyzwitterionic resin for simultaneous capturing of Hg(II) and methylene blue with response surface optimization. Sci Rep 7:4573
ShamsiJazeyi H, Miller CA, Wong MS, Tour JM, Verduzco R, ShamsiJazeyi Hadi (2014) Polymer coated nanoparticles for enhanced oil recovery. J Appl Polym Sci 131:40576
Suk JS, Xu Q, Kim N, Hanes J, Ensign LM (2015) PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j:addr.2015.09.012
Tagliazucchi M, Szleifer I (2012) Stimuli-responsive polymers grafted to nanopores and other nano-curved surfaces: structure, chemical equilibrium and transport. Soft Matt. 8:7292
Tagliazucchi M, Azzaroni O, Szleifer I (2010) Responsive polymers end-tethered in solid-state nanochannels: when nanoconfinement really matters. J Am Chem Soc 132:12404
Umehara S, Karhanek M, Davis RW, Pourmand N (2009) Label-free biosensing with functionalized nanopipette probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:4611
Urena-Benavides EE, Lin EL, Foster EL, Xue Z, Ortiz MR, Fei Y, Larsen ES, Kmetz AA, Lyon BA, Moaseri E, Bielawski CW, Pennell KD, Ellison CJ, Johnston KP (2016) Low adsorption of magnetite nanoparticles with uniform polyelectrolyte coatings in concentrated brine on model silica and sandstone. Ind Eng Chem Res 55:1522
van der Heyden FHJ, Stein D, Dekker C (2005) Streaming currents in a single nanofluidic channel. Phys Rev Lett 95:116104
van der Heyden FHJ, Bonthuis DJ, Stein D, Meyer C, Dekker C (2006a) Electrokinetic energy conversion efficiency in nanofluidic channels. Nano Lett 7:2232
van der Heyden FHJ, Stein D, Besteman K, Lemay SG, Dekker C (2006b) Charge inversion at high ionic strength studied by streaming currents. Phys Rev Lett 96:224502
van der Heyden FHJ, Bonthuis DJ, Stein D, Meyer C, Dekker C (2007) Power generation by pressure-driven transport of ions in nanofluidic channels. Nano Lett 7:1022
Vilozny B, Wollenberg AL, Actis P, Hwang D, Singaram B, Pourmand N (2013) Carbohydrate-actuated nanofluidic diode: switchable current rectification in a nanopipette. Nanoscale 5:9214
Wang X, Xu J, Li L, Wu S, Chen Q, Lu Y, Ballauff M, Guo X (2010) Synthesis of spherical polyelectrolyte brushes by thermocontrolled emulsion polymerization. Macromol Rapid Commun 31:1272
Xiao W, Lin J, Li M, Ma Y, Chen Y, Zhang C, Li D, Gu H (2012) Prolonged in vivo circulation time by zwitterionic modification of magnetite nanoparticles for blood pool contrast agents. Contrast Media Mol Imaging 7:320
Xue S, Yeh LH, Ma Y, Qian S (2014) Tunable streaming current in a pH-regulated nanochannel by a field effect transistor. J Phys Chem C 118:6090
Yameen B, Ali M, Neumann R, Ensinger W, Knoll W, Azzaroni O (2009) Single conical nanopores displaying ph-tunable rectifying characteristics. Manipulating ionic transport with zwitterionic polymer brushes. J Am Chem Soc 131:2070
Yameen B, Ali M, Neumann R, Ensinger W, Knoll W, Azzaroni O (2009) Synthetic proton-gated ion channels via single solid-state nanochannels modified with responsive polymer brushes. Nano Lett 9:2788
Yeh L-H, Zhang M, Hu N, Joo SW, Qian S, Hsu J-P (2012a) Controlling pH-regulated bionanoparticles translocation through nanopores with polyelectrolyte brushes. Anal Chem 84:9615
Yeh L-H, Zhang M, Hu N, Joo SW, Qian S, Hsu J-P (2012b) Electrokinetic ion and fluid transport in nanopores functionalized by polyelectrolyte brushes. Nanoscale 4:5169
Zeng Z, Yeh L-H, Zhang M, Qian S (2015) Ion transport and selectivity in biomimetic nanopores with pH-tunable zwitterionic polyelectrolyte brushes. Nanoscale 7:17020
Zhao Y, Chen Y, Xiong X, Sun X, Zhang Q, Gan Y, Zhang L, Zhang W (2017) Synthesis of magnetic zwitterionichydrophilic material for the selective enrichment of N-linked glycopeptides. J Chromatogr A 1482:23
Zhou C, Mei L, Su Y-S, Yeh L-H, Zhang X, Qian S (2016) Gated ion transport in a soft nanochannel with biomimetic polyelectrolyte brush layers. Sens Actuators B 229:305
Zhulina EB, Borisov OV (2011) Poisson–Boltzmann theory of pH-sensitive (annealing) polyelectrolyte brush. Langmuir 27:10615
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G., Patwary, J., Sachar, H.S. et al. Electrokinetics in nanochannels grafted with poly-zwitterionic brushes. Microfluid Nanofluid 22, 112 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-018-2133-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-018-2133-6