Abstract
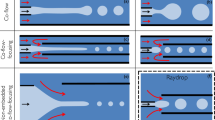
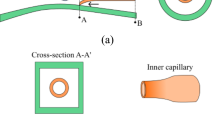
We report a parallelized capillary microfluidic device for enhanced production rate of monodisperse polymersomes. This device consists of four independent capillary microfluidic devices, operated in parallel; each device produces monodisperse water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) double-emulsion drops through a single-step emulsification. During generation of the double-emulsion drops, the innermost water drop is formed first and it triggers a breakup of the middle oil phase over wide range of flow rates; this enables robust and stable formation of the double-emulsion drops in all drop makers of the parallelized device. Double-emulsion drops are transformed to polymersomes through a dewetting of the amphiphile-laden middle oil phase on the surface of the innermost water drop, followed by the subsequent separation of the oil drop. Therefore, we can make polymersomes with a production rate enhanced by a factor given by the number of drop makers in the parallelized device.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anna SL, Bontoux N, Stone HA (2003) Formation of dispersions using “flow focusing” in microchannels. Appl Phys Lett 82(3):364–366
Choi SW, Zhang Y, Xia YN (2009) Fabrication of microbeads with a controllable hollow interior and porous wall using a capillary fluidic device. Adv Funct Mater 19(18):2943–2949
Dendukuri D, Tsoi K, Hatton TA, Doyle PS (2005) Controlled synthesis of nonspherical microparticles using microfluidics. Langmuir 21(6):2113–2116
Guillot P, Colin A, Utada AS, Ajdari A (2007) Stability of a jet in confined pressure-driven biphasic flows at low Reynolds numbers. Phys Rev Lett 99(10):104502
Hwang DK, Dendukuri D, Doyle PS (2008) Microfluidic-based synthesis of non-spherical magnetic hydrogel microparticles. Lab Chip 8(10):1640–1647
Kim SH, Weitz DA (2011) One-step emulsification of multiple concentric shells with capillary microfluidic devices. Angew Chem Int Ed 50(37):8731–8734
Kim JW, Utada AS, Fernandez-Nieves A, Hu ZB, Weitz DA (2007) Fabrication of monodisperse gel shells and functional microgels in microfluidic devices. Angew Chem Int Ed 46(11):1819–1822
Kim SH, Jeon SJ, Jeong WC, Park HS, Yang SM (2008a) Optofluidic synthesis of electroresponsive photonic Janus balls with isotropic structural colors. Adv Mater 20(21):4129–4134
Kim SH, Jeon SJ, Yang SM (2008b) Optofluidic encapsulation of crystalline colloidal arrays into spherical membrane. J Am Chem Soc 130(18):6040–6046
Kim SH, Sim JY, Lim JM, Yang SM (2010) Magnetoresponsive microparticles with nanoscopic surface structures for remote-controlled locomotion. Angew Chem Int Ed 49(22):3786–3790
Kim SH, Abbaspourrad A, Weitz DA (2011a) Amphiphilic crescent-moon-shaped microparticles formed by selective adsorption of colloids. J Am Chem Soc 133(14):5516–5524
Kim SH, Kim JW, Cho JC, Weitz DA (2011b) Double-emulsion drops with ultra-thin shells for capsule templates. Lab Chip 11(18):3162–3166
Kim SH, Shum HC, Kim JW, Cho JC, Weitz DA (2011c) Multiple polymersomes for programmed release of multiple components. J Am Chem Soc 133(38):15165–15171
Lee D, Weitz DA (2008) Double emulsion-templated nanoparticle colloidosomes with selective permeability. Adv Mater 20(18):3498–3503
Lorenceau E, Utada AS, Link DR, Cristobal G, Joanicot M, Weitz DA (2005) Generation of polymerosomes from double-emulsions. Langmuir 21(20):9183–9186
Nie ZH, Li W, Seo M, Xu SQ, Kumacheva E (2006) Janus and ternary particles generated by microfluidic synthesis: design, synthesis, and self-assembly. J Am Chem Soc 128(29):9408–9412
Nisisako T, Torii T (2007) Formation of biphasic Janus droplets in a microfabricated channel for the synthesis of shape-controlled polymer microparticles. Adv Mater 19(11):1489–1493
Nisisako T, Torii T (2008) Microfluidic large-scale integration on a chip for mass production of monodisperse droplets and particles. Lab Chip 8(2):287–293
Nisisako T, Torii T, Takahashi T, Takizawa Y (2006) Synthesis of monodisperse bicolored Janus particles with electrical anisotropy using a microfluidic co-flow system. Adv Mater 18(9):1152–1156
Okushima S, Nisisako T, Torii T, Higuchi T (2004) Controlled production of monodisperse double emulsions by two-step droplet breakup in microfluidic devices. Langmuir 20(23):9905–9908
Ota S, Yoshizawa S, Takeuchi S (2009) Microfluidic formation of monodisperse, cell-sized, and unilamellar vesicles. Angew Chem Int Ed 48(35):6533–6537
Romanowsky MB, Abate AR, Rotem A, Holtze C, Weitz DA (2012) High throughput production of single core double emulsions in a parallelized microfluidic device. Lab Chip 12:802–807
Shum HC, Kim JW, Weitz DA (2008) Microfluidic fabrication of monodisperse biocompatible and biodegradable polymersomes with controlled permeability. J Am Chem Soc 130(29):9543–9549
Shum HC, Santanach-Carreras E, Kim JW, Ehrlicher A, Bibette J, Weitz DA (2011) Dewetting-induced membrane formation by adhesion of amphiphile-laden interfaces. J Am Chem Soc 133(12):4420–4426
Thorsen T, Roberts RW, Arnold FH, Quake SR (2001) Dynamic pattern formation in a vesicle-generating microfluidic device. Phys Rev Lett 86(18):4163–4166
Umbanhowar PB, Prasad V, Weitz DA (2000) Monodisperse emulsion generation via drop break off in a coflowing stream. Langmuir 16(2):347–351
Utada AS, Lorenceau E, Link DR, Kaplan PD, Stone HA, Weitz DA (2005) Monodisperse double emulsions generated from a microcapillary device. Science 308(5721):537–541
Utada AS, Fernandez-Nieves A, Stone HA, Weitz DA (2007) Dripping to jetting transitions in coflowing liquid streams. Phys Rev Lett 99(9):094502
Xu S, Nie Z, Seo M, Lewis P, Kumacheva E, Stone HA, Garstecki P, Weibel DB, Gitlin I, Whitesides GM (2005) Generation of monodisperse particles by using microfluidics: control over size, shape, and composition. Angew Chem Int Ed 44(25):3799
Zhao YJ, Zhao XW, Sun C, Li J, Zhu R, Gu ZZ (2008) Encoded silica colloidal crystal beads as supports for potential multiplex immunoassay. Anal Chem 80(5):1598–1605
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Amore-Pacific, the National Science Foundation (DMR-1006546) and the Harvard Materials Research Science and Engineering Center (DMR-0820484).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SH., Kim, J.W., Kim, DH. et al. Enhanced-throughput production of polymersomes using a parallelized capillary microfluidic device. Microfluid Nanofluid 14, 509–514 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-012-1069-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-012-1069-5