Abstract
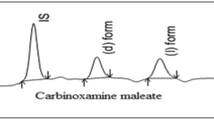
Simultaneous chiral and chemoseparation of R-(+)-rabeprazole and related (enantio)impurities was achieved on a cellulose tris-(3,5-dichlorophenylcarbamate) stationary phase chemically bonded to silica gel (Chiralpak IC). A gradient elution was applied in the reverse-phase separation mode. The mobile phase consisted of a mixture of acetonitrile and aqueous phosphate buffer at pH 7. The other operational parameters were flow rate of 1 mL min−1, column temperature of 35 °C and ultraviolet (UV) detection at 282 nm. Quantification limits for R-(+)-rabeprazole and the related impurities ranged in the interval of 0.02–0.03 %. Linear response intervals of 0.02–0.66 % were obtained with UV detection. Validation of the proposed method was achieved according to current regulations in force. For better understanding of the R-(+)-rabeprazole impurity profile, (+)-EMS/MS and MS/MS detection were also used.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Indian Pharmacopoeia (1996) Government of India, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, vol 3. Controller of Publications, Delhi, pp 25–27
Rao RN, Raju AN, Nagaraju D (2006) Enantiospecific resolution of rabeprazole by liquid chromatography on amylose-derived chiral stationary phase using photo diode array and polarimetric detectors in series. Talanta 70:805–810
Reddy GM, Bhaskar BV, Reddy PP, Sudhakar P, Babu JM, Vyas K, Reddy PR, Mukkanti K (2007) Identification and characterization of potential impurities of rabeprazole sodium. J Pharm Biomed Anal 43:1262–1269
Rao PS, Ray UK, Gupta PB, Srinivasa Rao DVN, Islam A, Rajput P, Mukkanti K (2010) Identification, isolation and characterization of new impurity in rabeprazole sodium. J Pharm Biomed Anal 52:620–624
Miura M, Tada H, Satoh S, Habuchi T, Suzuki T (2006) Determination of rabeprazole enantiomers and their metabolites by high-performance liquid chromatography with solid-phase extraction. J Pharm Biomed Anal 4:565–570
Karra UM, Yarkala S (2010) A simple and validated reverse phase HPLC method for the determination of rabeprazole in pharmaceutical dosage forms. J Chem 7:569–577
Kumar N, Sangeetha D (2013) Development and validation of a stability-indicating RP-HPLC method for the determination of process-related impurities and degradation products of rabeprazole sodium in pharmaceutical formulation. Sci Pharm 81:697–711
Belaz KRA, Coimbra M, Barreir JC, Montanari CA, Cass QB (2008) Multimilligram enantioresolution of sulfoxide proton pump inhibitors by liquid chromatography on polysaccharide-based chiral stationary phase. J Pharm Biomed Anal 47:81–87
Chennuru LN, Choppari T, Duvvuri S, Dubey PK (2013) Enantiomeric separation of proton pump inhibitors on new generation chiral columns using LC and supercritical fluid chromatography. J Sep Sci 36:3004–3010
Cirilli R, Ferretti R, Gallinella B, Zanitti L (2013) Retention behaviour of proton pump inhibitors using immobilized polysaccharide-derived chiral stationary phases with organic-aqueous mobile phases. J Chromatogr A 1304:147–153
Dixit S, Dubey R, Bhushan R (2014) Normal and polar organic phase high-performance liquid chromatographic enantioresolution of omeprazole, rabeprazole, lansoprazole and pantoprazole using monochloro-methylated cellulose-based chiral stationary phase and determination of dexrabeprazole. Biomed Chromatogr 28:112–119
Perara RWH, Lough WJ (2011) Assessment of chiral stationary phases for suitability for combined enantiomeric impurity/related substances assays. J Chromatogr A 1218:8655–8663
Cirilli R, Ferretti R, Gallinella B, Turchetto L, Zanitti L, Torre FL (2009) Development and validation of an enantioselective and chemoselective HPLC method using a Chiralpak IA column to simultaneously quantify (R)-(+)- and (S)-(−)-lansoprazole enantiomers and related impurities. J Pharm Biomed Anal 50:9–14
Zanitti L, Ferretti R, Gallinella B, Torre FL, Sanna ML, Mosca A, Cirilli R (2010) Direct HPLC enantioseparation of omeprazole and its chiral impurities: application to the determination of enantiomeric purity of esomeprazole magnesium trihydrate. J Pharm Biomed Anal 52:665–671
Wang T, Chen YW, Vailay A (2000) Enantiomeric separation of some pharmaceutical intermediates and reversal of elution orders by high-performance liquid chromatography using cellulose and amylose tris-(3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate) derivatives as stationary phases. J Chromatogr A 902:345–355
Wang T, Chen YW (1999) Application and comparison of derivatized cellulose and amylose chiral stationary phases for the separation of enantiomers of pharmaceutical compounds by HPLC. J Chromatogr A 855:411–421
Toribio L, Bernal JL, Del Nozal MJ, Jimenez JJ, Nieto EM (2001) Applications of the Chiralpak AD and Chiralcel OD chiral columns in the enantiomeric separation of several dioxolane compounds by supercritical fluid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 921:305–313
Okamoto Y, Kaida Y (1990) Polysaccharide derivatives as chiral stationary phases in HPLC. J High Resolut Chromatogr 13:708–712
Okamoto Y, Kaida Y (1994) Resolution by high-performance liquid chromatography using polysaccharide carbamates and benzoates as chiral stationary phases. J Chromatogr A 666:403–419
Oguni K, Oda H, Ichida A (1995) Development of chiral stationary phases consisting of polysaccharide derivatives. J Chromatogr A 694:91–100
Booth TD, Wainer IW (1996) Mechanistic investigation into the enantioselective separation of mexiletine and related compounds, chromatographed on an amylose tris-(3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate) chiral stationary phase. J Chromatogr A 741:205–211
Booth TD, Wainer IW (1996) Investigation of the enantioselective separations of α-alkylarylcarboxylic acids on an amylose tris-(3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate) chiral stationary phase using quantitative structure-enantioselective retention relationships identification of a conformationally driven chiral recognition mechanism. J Chromatogr A 737:157–169
Cavazzini A, Pasti L, Massi A, Marchetti N, Dondi F (2011) Recent applications in chiral high performance liquid chromatography: review. Anal Chim Acta 706:205–222
Zhang T, Kientzy C, Franco P, Ohnishi A, Kagamihara Y, Kurosawa H (2005) Solvent versatility of immobilized 3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate of amylose in enantiomeric separations by HPLC. J Chromatogr A 1075:65–75
Zhang T, Nguyen D, Franco P, Murakami T, Ohnishi A, Kurosawa H (2006) Cellulose 3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate immobilized on silica A new chiral stationary phase for the analysis of enantiomers. Anal Chim Acta 557:221–228
Zhang T, Nguyen D, Franco P, Isobe Y, Michishita T, Murakami T (2008) Cellulose tris-(3,5-dichlorophenylcarbamate) immobilised on silica: a novel chiral stationary phase for resolution of enantiomers. J Pharm Biomed Anal 46:882–891
Zhang T, Nguyen D, Franco P (2008) Enantiomer resolution screening strategy using multiple immobilised polysaccharide-based chiral stationary phases. J Chromatogr A 1191:214–222
Tachibana K, Ohnishi A (2001) Reversed-phase liquid chromatographic separation of enantiomers on polysaccharide type chiral stationary phases. J Chromatogr A 906:127–154
Khorassani MA, Taylor LT, Williams DG, Roston DA, Catalano TT (2001) Demonstrative validation study employing a packed column pressurized fluid chromatography method that provides assay, achiral impurities, chiral impurity, and IR identity testing for a drug substance. J Pharm Biomed Anal 26:725–738
Zhang T, Nguyen D, Franco P (2010) Reversed-phase screening strategies for liquid chromatography on polysaccharide-derived chiral stationary phases. J Chromatogr A 1217:1048–1055
Peng L, Jayapalan S, Chankvetadze B, Farkas T (2010) Reversed-phase chiral HPLC and LC/MS analysis with tris(chloromethylphenylcarbamate) derivatives of cellulose and amylose as chiral stationary phases. J Chromatogr A 1217:6942–6955
Franco P, Senso A, Oliveros L, Minguillon C (2001) Covalently bonded polysaccharide derivatives as chiral stationary phases in high-performance liquid chromatography: a review. J Chromatogr A 906:155–170
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the management of Cipla Ltd. for supporting this work. They extend their gratitude to Mr. P. L. Srinivas and other colleagues from R&D unit of Cipla Ltd., Bangalore, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balamurugan, P., Anver Basha, K., Jayachandran, J. et al. Simultaneous Chemo/Enantioseparation and Assay of R-(+)-Rabeprazole and Related Impurities in Pharmaceutical Formulations. Chromatographia 78, 1367–1375 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-015-2968-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-015-2968-x