Abstract
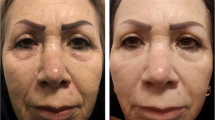
There are different modalities for hand rejuvenation. Fractional Er:YAG laser and long pulse Nd:YAG laser were introduced for treating hand wrinkles. We plan to compare fractional Er:YAG laser and long pulse Nd:YAG laser in a randomized controlled double-blind design with multiple sessions and larger sample size in comparison with previous studies. Thirty-three participants with hand wrinkles entered this study. They were randomly allocated to undergo three monthly laser treatments on each hand, one with a fractional Er:YAG laser and the other with a long pulse Nd:YAG laser. The evaluations included assessment of clinical improvement determined by two independent dermatologists not enrolled in the treatment along with measuring skin biomechanical property of hands using a sensitive biometrologic device with the assessment of cutaneous resonance running time (CRRT). Moreover, potential side effects and patients’ satisfaction have been documented at baseline, 1 month after each treatment, and 3 months after the final treatment session. Clinical evaluation revealed both modalities significantly reduce hand wrinkles (p value < 0.05), with no significant difference between two lasers. Mean CRRT values also decreased significantly after the laser treatment compared to those of the baseline in both laser groups. There was no serious persistent side effect after both laser treatments. Both fractional Er:YAG and long pulse Nd:YAG lasers show substantial clinical improvement of hand skin wrinkles with no serious side effects. However, combination treatment by these lasers along with the other modalities such as fat transfer could lead to better outcomes in hand rejuvenation. Trial registration: IRCT2016032020468N4




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jakubietz RG, Jakubietz MG, Kloss D, Gruenert JG (2005) Defining the basic aesthetics of the hand. Aesthet Plast Surg 29(6):546–551
Fabi SG, Goldman MP (2012) Hand rejuvenation: a review and our experience. Dermatol Surg 38(7 Pt 2):1112–1127
Riyaz FR, Ozog D (2015) Hand rejuvenation. Semin Cutan Med Surg 34(3):147–152
Verner I, Kutscher TD (2017) Clinical evaluation of the efficacy and safety of combined bipolar radiofrequency and optical energies vs. optical energy alone for the treatment of aging hands. Lasers Med Sci 32(6):1387–1392
Jih MH, Kimyai-Asadi A (2008) Fractional photothermolysis: a review and update. Semin Cutan Med Surg 27(1):63–71
Lee YB, Kang NH, Eun YS, Cheon MS, Kim KM, Cho BK, Park HJ (2012) Effects of long-pulsed 1,064-nm neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser on dermal collagen remodeling in hairless mice. Dermatol Surg 38(7 Pt 1):985–992
Schmults CD, Phelps R, Goldberg DJ (2004) Nonablative facial remodeling: erythema reduction and histologic evidence of new collagen formation using a 300-microsecond 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser. Arch Dermatol 140(11):1373–1376
Robati RM, Einollahi B, Einollahi H, Younespour S, Fadaifard S (2016) Skin biophysical characteristics in patients with keratoconus: a controlled study. Scientifica (Cairo) 2016:6789081
Campbell TM, Goldman MP (2010) Adverse events of fractionated carbon dioxide laser: review of 373 treatments. Dermatol Surg 36(11):1645–1650
Stebbins WG, Hanke CW (2011) Ablative fractional CO2 resurfacing for photoaging of the hands: pilot study of 10 patients. Dermatol Ther 24(1):62–70
Alshami MA (2013) New application of the long-pulsed Nd-YAG laser as an ablative resurfacing tool for skin rejuvenation: a 7-year study. J Cosmet Dermatol 12(3):170–178
Robati RM, Asadi E (2017) Efficacy and safety of fractional CO2 laser versus fractional Er:YAG laser in the treatment of facial skin wrinkles. Lasers Med Sci 32(2):283–289
Trelles MA, Alvarez X, Martín-Vázquez MJ, Trelles O, Velez M, Levy JL, Allones I (2005) Assessment of the efficacy of nonablative long-pulsed 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser treatment of wrinkles compared at 2, 4, and 6 months. Facial Plast Surg 21(2):145–153
Oktem A, Kocyigit P (2016) Comparison of effectiveness of 1,064-nm Nd:YAG laser and Nd:YAG laser-IPL combination treatments in hand skin rejuvenation. J Cosmet Laser Ther 18(5):270–274
Sadick N, Schecter AK (2004) Utilization of the 1320-nm Nd:YAG Laser for the reduction of photoaging of the hands. Dermatol Surg 30(8):1140–1144
Maruyama S (2016) Hand rejuvenation using standard intense pulsed light (IPL) in Asian patients. Laser Ther 25(1):43–54
Butterwick KSN (2016) Hand rejuvenation using a combination approach. Dermatol Surg 42(Suppl 2):S108–S118
Raziee M, Balighi K, Shabanzadeh-Dehkordi H, Robati RM (2008) Efficacy and safety of cryotherapy vs. trichloroacetic acid in the treatment of solar lentigo. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 22(3):316–319
Xin S, Man W, Fluhr JW, Song S, Elias PM, Man MQ (2010) Cutaneous resonance running time varies with age, body site and gender in a normal Chinese population. Skin Res Technol 16(4):413–421
Seirafi H, Farsinejad K, Firooz A, Davoudi SM, Robati RM, Hoseini MS, Ehsani AH, Sadr B (2009) Biophysical characteristics of skin in diabetes: a controlled study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 23(2):146–149
Role of funding source
This study has been funded by Skin Research Center, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences with grant number of 94/141.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Ethical Committee of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences with number of Ir.sbmu.ram.rec.1394.414. This project was performed according to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. The protocol was approved by the Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials (IRCT ID2016032020468N4).
Informed consent
All of the subjects signed a written informed consent after explanation of the procedure.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robati, R.M., Asadi, E., Shafiee, A. et al. Efficacy of long pulse Nd:YAG laser versus fractional Er:YAG laser in the treatment of hand wrinkles. Lasers Med Sci 33, 461–467 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-017-2351-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-017-2351-2