Abstract
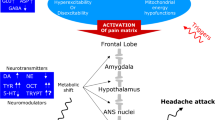
The aim of this study was to explore the possible role of tryptamine in the pathogenesis of chronic cluster headache along with that of adrenaline and noradrenaline (α-agonists) together with arginine metabolism in the origin of cluster bouts. Plasma levels of tyramine, tryptamine, serotonin, 5-hydroxyindolacetic acid, noradrenalin, adrenalin and the markers of arginine metabolism such as arginine, homoarginine, citrulline, ADMA and NMMA, were measured in 23 chronic cluster headache patients (10 chronic cluster ab initio and 13 transformed from episodic cluster) and 28 control subjects. The plasma levels of tyramine, tryptamine, noradrenalin and adrenalin were found several times higher in chronic cluster headache patients compared to controls, whereas the plasma levels of arginine, homoarginine and citrulline were significantly lower. No differences were found in the plasma levels of serotonin, 5-hydroxyindolacetic, ADMA and NMMA between chronic cluster headache patients and control subjects. These results provide support for a role of tryptamine in the pathogenesis of chronic cluster headache and, in particular, in the duration of the cluster bouts. In addition, the low levels of the nitric oxide substrates together with the high levels of noradrenalin and adrenalin suggest an activation of endothelial TAAR1 receptors followed by the release of nitric oxide in the circulation that may constitute the final step of the physiopathology of cluster crisis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altiokka O, Mutluay B, Koksal A, Ciftci-Kavaklioglu B, Ozturk M, Altunkaynak Y, Baybas S, Soysal A (2016) Evaluation of interictal autonomic function during attack and remission in cluster headache. Cephalalgia 36(1):37–43
Mitsikostas DD, Edvinson L, Jensen HR, Katsarava Z, Lampl C, Negro A, Osipova V, Paemeleire K, Siva A, Valade D, Martelletti P (2014) Refractory chronic cluster headache: a consensus statement on clinical definition from the European Headache Federation. J Headache Pain 15:79
Wollman H, Nilson E, Antonin KH, Reiderer P (1985) Tryptamine kinetics in human volunteers. In: Bolton AA, Maite L, Beick PR (eds) Neuropsychopharmacology of trace amines. Humana Press, Clifton, pp 361–378
Borowsky B, Adham N, Jones KA et al (2001) Traces amines: identification of a family of mammalian G protein-coupled receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:8966–8971
Curran DA, Lance JW (1964) Clinical trials of methysergide and other preparations in the management of migraine. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 27:463–469
Albert PR, Le Francois B, Millar AM (2011) Transcriptional dysregulation of 5-HT1A autoreceptors in mental illness. Mol Brain 4:21
Huo FQ, Qu CL, Li YQ, Tang JS, Jia (2008) Gabaergic modulation is involved in ventrolateral orbital cortex 5-HT1 receptor activation-induced antinociception in the rat. Pain 139(2):398–405
D’Andrea G, Nordera GP, Pizzolato G et al (2010) Trace amine metabolism in Parkinson’s disease: low circulating levels of octopamine in early disease stage. Neurosci Lett 469:348–351
Revel FG, Moreau JL, Gainetdinov RR, Bradaia A, Sotnikova TD et al (2011) TAAR1 activation modulates monoaminergic neurotransmission, preventing hyperdopaminergic and hypoglutamatergic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(20):8485–8490
Anwar MA, Ford WR, Broadley KJ, Herbert AA (2012) Vasoconstrictor and vasodilator responses to tryptamine of rat-isolated perfused mesentery: comparison with tyramine and β-phenylethylamine. Br J Pharmacol 165(7):2191–2202
D’Andrea G, D’Arrigo A, Dalle Carbonare M, Leon A (2012) Pathogenesis of migraine: the role of the neuromodulators. Headache 52(7):1155–1163
D’Andrea G, Granella F, Cadaladini M (2003) Platelet aggregation profiles in cluster headache Headache 43(3):272–275
The international classification of headache disorders: 3-beta edition (2013) Cephalalgia 33(9):629–808
D’Andrea G, D’Amico D, Bussone G et al (2013) The role of tyrosine metabolism in the pathogenesis of chronic migraine. Cephalalgia 33(11):932–937
D’Andrea G, D’Amico D, Bussone G et al (2014) Tryptamine levels are low in plasma of chronic migraine and chronic tension-type headache. Neurol Sci 35:1941–1945
Di Gangi IM, Chiandetti L, Gucciardi A et al (2010) Simultaneous quantitative determination of N(G),N(G)-dimethyl-l-arginine or asymmetric dimethylarginine and related pathway’s metabolites in biological fluids by ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 677(2):140–148
D’Andrea G, Granella F, Alecci M et al (1998) Serotonin metabolism in cluster headache. Cephalalgia 18(2):94–96
Viguer E, Michot B, Hamon M et al (2013) Multiple roles of serotonin in pain mechanism-implications of 5-HT7 and other receptor types. Eur J Pharmacol 716(1–3):8–16
Qu GL, Huo FQ, Huang FS (2008) The role of 5-HT receptors in medial prefrontal cortex of 5-HT induced antinociception in the rat. Neuroscience 152:487–494
Huo FQ, Qu GL, Ly YQ et al (2008) GABAergic modulation is involved in the ventrolateral orbital cortex 5-HT1A recept activation-induced antinociception in the rat. Pain 139(2):398–405
Pockros AL, Pentkowski NS, Swinford SE et al (2011) Blockade of 5-HT2A in medial prefrontal cortex attenuates reinstatement of cue-elicited cocaine-seeking behaviour in rats. Psycopharmacology (Berl) 213(2–3):307–320
Huo FQ, Huang FS, Lu BC et al (2010) Activation of serotonin 1A receptors in ventrolateral orbital cortex depresses persistent nociception: a presynaptic inhibition mechanism. Neurochem Int 57(7):749–755
Anwar MA, Ford WR, Herbert AA et al (2013) Signal transduction and modulating pathways in tryptamine-evoked responses of the rat isolated mesenteric bed. Vascul Pharmacol 58(1–2):140–149
Broadley PB (2010) The vascular effects of trace amines and amphetamines. Pharmacol Ther 125:363–375
Tsikas D, Guoyao W (2015) Homoarginine, arginine and relatives: analysis, metabolism, transport, physiology and pathology. Amino Acids 47:1697–1702
Böger RH, Bode-Böger SM (2001) The clinical pharmacology of l-arginine. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 41:79–99
Flam BR, Eichler DC, Solomonson LP (2007) Endothelial nitric oxide production is tightly coupled to the citrulline-NO cycle. Nitric Oxide 17(3–4):115–122
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest with the publication of this article.
Funding
The authors disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship and/or publication of the article. The research was partially funded by the F.I.CEF Charity (Italian Headache Foundation).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
D’Andrea, G., Bussone, G., Di Fiore, P. et al. Pathogenesis of chronic cluster headache and bouts: role of tryptamine, arginine metabolism and α1-agonists. Neurol Sci 38 (Suppl 1), 37–43 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-017-2862-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-017-2862-4