Abstract
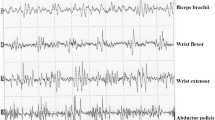
Axial myoclonus (AM) is characterized by sudden muscle jerks involving axial and proximal muscles. It includes propriospinal myoclonus (PSM) which consists of trunk flexion or extension jerking with activity arising in axial muscles and spreading to caudal and rostral muscles at low velocity along propriospinal pathways. We report on two patients displaying flexion AM jerks in the absence of structural lesion of the central nervous system or electrophysiological evidence of organic origin. A conversion disorder was diagnosed. The jerks disappeared after psychoeducation with the patients remaining symptom free in 6-year long follow-up. The diagnoses of psychogenic axial (propriospinal-like) myoclonus were established. The literature on psychogenic axial (propriospinal-like myoclonus) is limited to a case report. Our cases demonstrate a good response to psychotropic medication and psychoeducation and fulfill the psychogenic movement disorder criteria. The phenomenology of psychogenic abnormal movements is diverse and PSM-like clinical picture may be a novel presentation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown P, Thompson PD, Rothwell JC et al (1991) Axial myoclonus of propriospinal origin. Brain 114:197–214
Brown P, Rothwell JC, Thompson PD et al (1994) Propriospinal myoclonus: evidence for spinal “pattern” generation in humans. Mov Disord 9:571–576
Vetrugno R, Provini F, Plazzi G et al (2000) Focal myoclonus and proprospinal propagation. Clin Neurophysiol 111:2175–2179
Montagna P, Provini F, Vetrugno R (2006) Propriospinal myoclonus at sleep onset. Clin Neurophysiol 36:351–355
Toro C, Hallet M (1997) Pathophysiology of myoclonic disorders. In: Watts RL, Koller WC (eds) Movement disorders. McGraw Hill, New York, pp 551–560
Obeso JA, Artieda J, Marsden CD (1988) Different clinical presentation of myoclonus. In: Jankovic J, Tolosa E (eds) Parkinson’s disease and movement disorders. Urban-Schwarzenberg, Baltimore-Munich, pp 263–274
Williams DR, Cowey M, Tuck K et al (2008) Psychogenic propriospinal myoclonus. Mov Disord 23:1312–1313
Monday K, Jankovic J (1993) Psychogenic myoclonus. Neurology 43:349–352
Kang SY, Sohn YH (2006) Electromyography patterns of propriospinal myoclonus can be mimicked voluntarily. Mov Disord 21:1241–1244
Williams DT, Ford B, Fahn S (1995) Phenomenology and psychopathology related to psychogenic movement disorders. Adv Neurol 65:231–257
Fahn S, Wiliams DT (1988) Psychogenic dystonia. Adv Neurol 50:431–455
Shill H, Gerber P (2006) Evaluation of clinical diagnostic criteria for psychogenic movement disorders. Mov Disord 21:1163–1168
Brown J, Lantos P, Stratton M et al (1993) Familial progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 56:473–476
Factor SA, Podskalny GD, Molho ES (1995) Psychogenic movement disorders: frequency, clinical profile, and characteristics. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 59:406–412
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sławek, J., Wichowicz, H.M., Cubała, W.J. et al. Psychogenic axial myoclonus: report on two cases. Neurol Sci 31, 219–222 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-010-0219-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-010-0219-3