Abstract
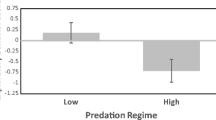
Human-induced perturbations such as crude-oil pollution can pose serious threats to aquatic ecosystems. To understand these threats fully it is important to establish both the immediate and evolutionary effects of pollutants on behaviour and cognition. Addressing such questions requires comparative and experimental study of populations that have evolved under different levels of pollution. Here, we compared the exploratory, activity and social behaviour of four populations of Trinidadian guppies (Poecilia reticulata) raised in common garden conditions for up to three generations. Two of these populations originated from tributaries with a long history of human-induced chronic crude-oil pollution with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons due to oil exploitation in Trinidad, the two others originating from non-polluted control sites. Laboratory-raised guppies from the oil-polluted sites were less exploratory in an experimental maze than guppies from the non-polluted sites and in a similar manner for the two independent rivers. We then compared the plastic behavioural responses of the different populations after an acute short-term experimental exposure to crude oil and found a decrease in exploration (but not in activity or shoaling) in the oil-exposed fish compared to the control subjects over all four populations. Taken together, these results suggest that both an evolutionary history with oil and an acute exposure to oil depressed guppy exploratory behaviour. We discuss whether the behavioural divergence observed represents adaptation to human-induced pollutants, the implications for conservation and the possible knock-on effects for information discovery and population persistence in fish groups.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agard JBR, Gobin J, Warwick RM (1993) Analysis of marine macrobenthic community structure in relation to pollution, natural oil seepage and seasonal disturbance in a tropical environment (Trinidad, West Indies). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 92:233–243
Akaishi FM, de Assis HCS, Jakobi SCG et al (2004) Morphological and neurotoxicological findings in tropical freshwater fish (Astyanax sp.) after waterborne and acute exposure to water soluble fraction (WSF) of crude oil. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 46:244–253
Alkindi AYA, Brown JA, Waring CP, Collins JE (1996) Endocrine, osmoregulatory, respiratory and haematological parameters in flounder exposed to the water soluble fraction of crude oil. J Fish Biol 49:1291–1305. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.1996.tb01796.x
Anderson JW, Neff JM, Cox BA et al (1974) Characteristics of dispersions and water-soluble extracts of crude and refined oils and their toxicity to estuarine crustaceans and fish. Mar Biol 27:75–88. doi:10.1007/BF00394763
Archer J, Birke LIA (eds) (1983) Exploration in animals and humans. Van Nostrand Reinhold, Wokingham
Arnold K, Brown R, Ankley G, Sumpter J (2014) Medicating the environment: assessing risks of pharmaceuticals to wildlife and ecosystems. Phil Trans R Soc B 369:20130569
Baatrup E, Junge M (2001) Antiandrogenic pesticides disrupt sexual characteristics in the adult male guppy Poecilia reticulata. Environ Health Perspect 109:1063–1070
Blumstein DT, Daniel JC, Evans CS (2006) JWatcher
Breckels RD, Neff BD (2010) Pollution-induced behavioural effects in the brown bullhead (Ameiurus nebulosus). Ecotoxicology 19:1337–1346
Brodin T, Piovano S, Fick J, Klaminder J, Heynen M, Jonsson M (2014) Ecological effects of pharmaceuticals in aquatic systems—impacts through behavioural alterations. Phil Trans R Soc B 369:20130580
Brown JA, Johansen PH, Colgan PW, Mathers RA (1985) Changes in the predator-avoidance behaviour of juvenile guppies (Poecilia reticulata) exposed to pentachlorophenol. Can J Zool 63:2001–2005
Budaev SV (1997) ‘‘Personality’’ in the guppy (Poecilia reticulata): a correlational study of exploratory behaviour and social tendency. J Comp Psychol 111:399–411
Chapman BB, Ward AJW, Krause J (2008) Schooling and learning: early social environment predicts social learning ability in the guppy, Poecilia reticulata. Anim Behav 76:923–929. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2008.03.022
Clark BW, Bone AJ, Di Giulio RT (2014) Resistance to teratogenesis by F1 and F2 embryos of PAH-adapted Fundulus heteroclitus is strongly inherited despite reduced recalcitrance of the AHR pathway. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:13898–13908. doi:10.1007/s11356-013-2446-7
Colgan PW, Cross JA, Johansen PH (1982) Guppy behaviour during exposure to a sub-lethal concentration of phenol. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 28:20–27. doi:10.1007/BF01608407
Correia AD, Gonçalves R, Scholze M et al (2007) Biochemical and behavioural responses in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) to phenanthrene. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 347:109–122. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2007.03.015
Dargent F, Scott ME, Hendry AP, Fussmann GF (2013) Experimental elimination of parasites in nature leads to the evolution of increased resistance in hosts. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 280:20132371. doi:10.1098/rspb.2013.2371
Day RL, MacDonald T, Brown C, Laland KN, Reader SM (2001) Interactions between shoal size and conformity in guppy social foraging. Anim Behav 62:917–925
Dunlap AS, Stephens DW (2009) Components of change in the evolution of learning and unlearned preference. Proc R Soc B 276:3201–3208
Endler JA (1995) Multiple-trait coevolution and environmental gradients in guppies. Trends Ecol Evol 10:22–29. doi:10.1016/S0169-5347(00)88956-9
Fodrie FJ, Heck KL Jr (2011) Response of coastal fishes to the Gulf of Mexico oil disaster. PLoS One 6:e21609. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0021609
Gesto M, Tintos A, Soengas JL, Míguez JM (2006) Effects of acute and prolonged naphthalene exposure on brain monoaminergic neurotransmitters in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp Biochem Physiol Part C Toxicol Pharmacol 144:173–183. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2006.08.002
Girvan JR, Braithwaite VA (1998) Population differences in spatial learning in three–spined sticklebacks. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 265:913–918
Gonçalves R, Scholze M, Ferreira AM et al (2008) The joint effect of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on fish behaviour. Environ Res 108:205–213. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2008.07.008
Griffin AS, Guez D (2014) Innovation and problem solving: a review of common mechanisms. Behav Process 109:121–134
Incardona JP, Collier TK, Scholz NL (2004) Defects in cardiac function precede morphological abnormalities in fish embryos exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 196:191–205. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2003.11.026
Incardona JP, Gardner LD, Linbo TL et al (2014) Deepwater horizon crude oil impacts the developing hearts of large predatory pelagic fish. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:E1510–E1518. doi:10.1073/pnas.1320950111
Jacquin L, Reader SM, Boniface A, Matelunna J, Patalas I, Perez-Jvostov F, Hendry AP (2016) Parallel and nonparallel behavioural evolution in response to predation and parasitism in Trinidadian guppies. J Evol Biol 29:1406–1422. doi:10.1111/jeb.12880
Kawecki TJ, Ebert D (2004) Conceptual issues in local adaptation. Ecol Lett 7:1225–1241. doi:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2004.00684.x
Klerks PL, Weis JS (1987) Genetic adaptation to heavy metals in aquatic organisms: a review. Environ Pollut Bark Essex 45:173–205
Laland KN, Reader SM (1999) Foraging innovation in the guppy. Anim Behav 57:331–340
Lürling M, Scheffer M (2007) Info-disruption: pollution and the transfer of chemical information between organisms. Trends Ecol Evol 22:374–379. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2007.04.002
Magurran AE (2005) Evolutionary ecology: the Trinidadian guppy. Oxford University Press, Oxford
McCabe CM, Reader SM, Nunn CL (2015) Infectious disease, behavioural flexibility and the evolution of culture in primates. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 282:20140862
Meyer JN, Di Giulio RT (2003) Heritable adaptation and fitness costs in killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) inhabiting a polluted estuary. Ecol Appl 13:490–503
Mikheev VN, Andreev OA (1993) Two-phase exploration of a novel environment in the guppy, Poecilia reticulata. J Fish Biol 42:375–383. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.1993.tb00340.x
Montiglio P-O, Royauté R (2014) Contaminants as a neglected source of behavioural variation. Anim Behav 88:29–35. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2013.11.018
Mousseau TA, Fox CW (1998) Maternal effects as adaptations. Oxford University Press, USA
Nomakuchi S, Park PJ, Bell MA (2009) Correlation between exploration activity and use of social information in three-spined sticklebacks. Behav Ecol 20:340–345. doi:10.1093/beheco/arp001
Oziolor EM, Bigorgne E, Aguilar L et al (2014) Evolved resistance to PCB- and PAH-induced cardiac teratogenesis, and reduced CYP1A activity in Gulf killifish (Fundulus grandis) populations from the Houston Ship Channel, Texas. Aquat Toxicol 150:210–219. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.03.012
Palumbi SR (2001) Humans as the world’s greatest evolutionary force. Science 293:1786–1790. doi:10.1126/science.293.5536.1786
Pérez-Jvostov F, Hendry AP, Fussmann GF, Scott ME (2015) Testing for local host–parasite adaptation: an experiment with Gyrodactylus ectoparasites and guppy hosts. Int J Parasitol 45:409–417. doi:10.1016/j.ijpara.2015.01.010
Peterson CH, Rice SD, Short JW et al (2003) Long-term ecosystem response to the Exxon Valdez oil spill. Science 302:2082–2086
Pike N (2011) Using false discovery rates for multiple comparisons in ecology and evolution: false discovery rates for multiple comparisons. Methods Ecol Evol 3:278–282
R Development Core Team (2008) R: a language and environment for statistical computing
Reader SM (2015) Causes of individual differences in animal exploration and search. Top Cogn Sci 7:451–468. doi:10.1111/tops.12148
Reader SM, Kendal JR, Laland KN (2003) Social learning of foraging sites and escape routes in wild Trinidadian guppies. Anim Behav 66:729–739. doi:10.1006/anbe.2003.2252
Réale D, Reader SM, Sol D et al (2007) Integrating animal temperament within ecology and evolution. Biol Rev 82:291–318. doi:10.1111/j.1469-185X.2007.00010.x
Renner MJ (1988) Learning during exploration: the role of behavioural topography during exploration in determining subsequent adaptive behaviour. Int J Comp Psychol 2:43–56
Reynaud S, Deschaux P (2006) The effects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on the immune system of fish: a review. Aquat Toxicol 77:229–238. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2005.10.018
Reznick DN, Rodd FH, Cardenas M (1996) Life-history evolution in guppies (Poecilia reticulata: Poeciliidae). IV. Similarism in life-history phenotypes. Am Nat 147:319. doi:10.1086/285854
Rolshausen G, Phillip DAT, Beckles DM et al (2015) Do stressful conditions make adaptation difficult? Guppies in the oil-polluted environments of southern Trinidad. Evol Appl 8:854–870. doi:10.1111/eva.12289
Samanta SK, Singh OV, Jain RK (2002) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: environmental pollution and bioremediation. Trends Biotechnol 20:243–248. doi:10.1016/S0167-7799(02)01943-1
Schantz SL, Moshtaghian J, Ness DK (1995) Spatial learning deficits in adult rats exposed to ortho-substituted PCB congeners during gestation and lactation. Fundam Appl Toxicol Off J Soc Toxicol 26:117–126
Schröder JH, Peters K (1988) Differential courtship activity and alterations of reproductive success of competing guppy males (Poecilia reticulata Peters; Pisces: Poeciliidae) as an indicator for low concentrations of aquatic pollutants. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 41:385–390
Schwarzenbach RP, Escher BI, Fenner K et al (2006) The challenge of micropollutants in aquatic systems. Science 313:1072–1077. doi:10.1126/science.1127291
Scott GR, Sloman KA (2004) The effects of environmental pollutants on complex fish behaviour: integrating behavioural and physiological indicators of toxicity. Aquat Toxicol 68:369–392. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2004.03.016
Seghers BH (1974) Schooling behaviour in the guppy (Poecilia reticulata): an evolutionary response to predation. Evolution 28:486. doi:10.2307/2407174
Seghers BH, Magurran AE (1995) Population differences in the schooling behaviour of the Trinidad guppy, Poecilia reticulata: adaptation or constraint? Can J Zool 73:1100–1105
Shen H, Huang Y, Wang R et al (2013) Global atmospheric emissions of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from 1960 to 2008 and future predictions. Environ Sci Technol 47:6415–6424. doi:10.1021/es400857z
Simonato JD, Guedes CLB, Martinez CBR (2008) Biochemical, physiological, and histological changes in the neotropical fish Prochilodus lineatus exposed to diesel oil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 69:112–120. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2007.01.012
Sih A, Ferrari M, Harris D (2011) Evolution and behavioural responses to human-induced rapid environmental change: behaviour and evolution. Evol Appl 4:367–387
Sojinu OSS, Wang J-Z, Sonibare OO, Zeng EY (2010) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments and soils from oil exploration areas of the Niger Delta, Nigeria. J Hazard Mater 174:641–647. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.099
Tytell ED, Lauder GV (2008) Hydrodynamics of the escape response in bluegill sunfish, Lepomis macrochirus. J Exp Biol 211:359–369
van Oosterhout C, Mohammed RS, Hansen H et al (2007) Selection by parasites in spate conditions in wild Trinidadian guppies (Poecilia reticulata). Int J Parasitol 37:805–812. doi:10.1016/j.ijpara.2006.12.016
Vanzella TP, Martinez CB, Colus IM (2007) Genotoxic and mutagenic effects of diesel oil water soluble fraction on a neotropical fish species. Mutat Res 631:36–43
Vignet C, Menach KL, Lyphout L et al (2014) Chronic dietary exposure to pyrolytic and petrogenic mixtures of PAHs causes physiological disruption in zebrafish—part II: behaviour. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:13818–13832. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-2762-6
Vignet C, Joassard L, Lyphout L et al (2015) Exposures of zebrafish through diet to three environmentally relevant mixtures of PAHs produce behavioural disruptions in unexposed F1 and F2 descendant. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:16371–16383. doi:10.1007/s11356-015-4157-8
Vitousek PM, Mooney HA, Lubchenco J, Melillo JM (1997) Human domination of earth’s ecosystems. Science 277:494–499. doi:10.1126/science.277.5325.494
Weis JS, Candelmo A (2012) Pollutants and fish predator/prey behaviour: a review of laboratory and field approaches. Curr Zool 58:9–20
Weis JS, Weis P, Heber M, Vaidya S (1981) Methylmercury tolerance of killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) embryos from a polluted vs non-polluted environment. Mar Biol 65:283–287
Williams LM, Oleksiak MF (2008) Signatures of selection in natural populations adapted to chronic pollution. BMC Evol Biol 8:282. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-8-282
Wright D, Krause J (2006) Repeated measures of shoaling tendency in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and other small teleost fishes. Nat Protoc 1:1828–1831. doi:10.1038/nprot.2006.287
Zala SM, Penn DJ (2004) Abnormal behaviours induced by chemical pollution: a review of the evidence and new challenges. Anim Behav 68:649–664. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2004.01.005
Acknowledgments
We thank G. Daggupati, C. LeBlond, L. Ljungberg, J Mateluna and PQ Sims for help at different stages of the study. We thank two anonymous referees for their helpful comments. L. Jacquin was supported by a postdoctoral grant from the Fyssen fellowship and an ATER fellowship from the Pau University UPPA, INRA Ecobiop. SM Reader thanks CFI and NSERC, and A Hendry thanks NSERC for funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Special Issue Animal cognition in a human dominated world.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jacquin, L., Dybwad, C., Rolshausen, G. et al. Evolutionary and immediate effects of crude-oil pollution: depression of exploratory behaviour across populations of Trinidadian guppies. Anim Cogn 20, 97–108 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-016-1027-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-016-1027-9