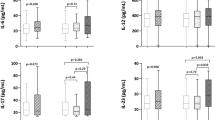
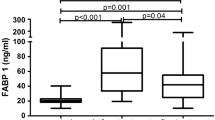
Abstract
Objectives
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), potentially evolving into liver fibrosis (LF), is frequent in psoriasis (PsO), but data in psoriatic arthritis (PsA) are lacking. Our study aimed to investigate the prevalence of NALFD and LF in PsA/PsO and the contribution of arthritis in their onset.
Method
PsA and PsO patients were consecutively enrolled. Exclusion criteria were liver diseases causing fibrosis (except NAFLD), alcohol ≥ 20 g/day, daily use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and current/previous methotrexate use. Clinical history, biochemical and clinimetrical data and insulin-resistance index HOMA (homeostatic model assessment) were assessed. Patients underwent a liver ultrasound to identify steatosis (therefore NAFLD) and transient elastography, to evaluate LF (stiffness≥ 7 kPa = fibrosis). Statistical analysis included basic statistics, logistic and linear regression analyses (to assess the contribution of arthritis to NAFLD and LF grading, respectively) and Spearman’s correlations; p ≤ 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Seventy-six patients were enrolled (PsA/PsO 43/33). MetS and LF prevalence were similar between PsA and PsO (35% vs 33%, p = 0.88; 31% vs 28%, p = 0.77, respectively). NAFLD was more frequent in PsO (65% vs 35%, p = 0.044). In multivariable models with NAFLD and LF grading as outcomes, arthritis was not a significant predictor, while HOMA was independently associated with both (OR 1.34; 95%CI 1.06, 1.69; beta 0.88; 95%CI 0.54, 1.21, respectively). Female sex was independently associated with LF grading (beta 1.81; 95%CI 0.05, 3.57).
Conclusions
NAFLD was more frequent in PsO, but MetS and LF prevalence were similar in PsA and PsO. Insulin resistance is the main determinant of NAFLD and LF, while additional contribution of arthritis seems small.
Key Points • The prevalence of metabolic comorbidities, including liver fibrosis, is overall quite similar between psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis. • NAFLD is more frequently found in psoriasis than psoriatic arthritis. • The contribution of arthritis in the onset of metabolic comorbidities seems small. |


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Helmick CG, Lee-Han H, Hirsch SC, Baird TL, Bartlett CL (2014) Prevalence of psoriasis among adults in the U.S.: 2003-2006 and 2009-2010 National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys. Am J Prev Med 47:37–45
Alamanos Y, Voulgari PV, A a D (2008) Incidence and prevalence of psoriatic arthritis: a systematic review. J Rheumatol 35:1354–1358
Prey S, Paul C, Bronsard V, Puzenat E, Gourraud PA, Aractingi S, Aubin F, Bagot M, Cribier B, Joly P, Jullien D, Maitre ML, Richard-Lallemand MA, Ortonne JP (2010) Assessment of risk of psoriatic arthritis in patients with plaque psoriasis: a systematic review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatology Venereol 24(Suppl 2):31–35
Gisondi P, Tessari G, Conti A, Piaserico S, Schianchi S, Peserico A, Giannetti A, Girolomoni G (2007) Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in patients with psoriasis: a hospital-based case-control study. Br J Dermatol 157:68–73
Raychaudhuri SPSK, Chatterjee S, Nguyen C et al (2010) Increased prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in patients with psoriatic arthritis. Metab Syndr Relat Disord 8:331–334
Shen J, Shang Q, Li EK, Leung YY, Kun EW, Kwok LW, Li M, Li TK, Zhu TY, Yu CM, Tam LS (2015) Cumulative inflammatory burden is independently associated with increased arterial stiffness in patients with psoriatic arthritis: a prospective study. Arthritis Res Ther 17:75
Lin YC, Dalal D, Churton S, Brennan DM, Korman NJ, Kim ESH, Husni ME (2014) Relationship between metabolic syndrome and carotid intima-media thickness: cross-sectional comparison between psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 66:97–103
Farrell GC, Larter CZ (2006) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: from steatosis to cirrhosis. Hepatology 43:S99–S112
Gisondi P, Targher G, Zoppini G, Girolomoni G (2009) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with chronic plaque psoriasis. J Hepatol 51:758–764
van der Voort EAM, Koehler E, Nijsten T, Stricker B, Hofman A, Janssen H, Schouten J, Wakkee M (2016) Increased prevalence of advanced liver fibrosis in patients with psoriasis: a cross-sectional analysis from the Rotterdam study. Acta Derm Venereol 96:213–217
Gisondi P, Barba E, Girolomoni G (2016) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease fibrosis score in patients with psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 30:282–287
Sporea I, Jurchiş A, Şirli R, Bota S, Sendroiu M (2013) Can transient elastography be a reliable method for assessing liver fibrosis in non alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)? Med Ultrason 15:106–110
Hashemi SA, Alavian SM, Gholami-Fesharaki M (2016) Assessment of transient elastography (FibroScan) for diagnosis of fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Casp J Intern Med 7:242–252
Candia R, Ruiz A, Torres-Robles R, Chávez-Tapia N, Méndez-Sánchez N, Arrese M (2015) Risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 29:656–662
Kimball AB, Gladman D, Gelfand JM, Gordon K, Horn EJ, Korman NJ, Korver G, Krueger GG, Strober BE, Lebwohl MG, National Psoriasis Foundation. (2008) National Psoriasis Foundation clinical consensus on psoriasis comorbidities and recommendations for screening. J Am Acad Dermatol 58:1031–1042
Rodríguez-Zúñiga MJM, García-Perdomo HA (2017) Systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between psoriasis and metabolic syndrome. J Am Acad Dermatol 77:657–666.e8
Bostoen J, Van Praet L, Brochez L et al (2014) A cross-sectional study on the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in psoriasis compared to psoriatic arthritis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 28:507–511
Husted JA, Thavaneswaran A, Chandran V, Eder L, Rosen CF, Cook RJ, Gladman DD (2011) Cardiovascular and other comorbidities in patients with psoriatic arthritis: a comparison with patients with psoriasis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 63:1729–1735
Pérez-Plaza A, Carretero G, Ferrandiz C, Vanaclocha F, Gómez-García FJ, Herrera-Ceballos E, de la Cueva-Dobao P, Belinchón I, Sánchez-Carazo JL, Alsina M, López-Estebaranz JL, Ferrán M, Torrado R, Carrascosa JM, Llamas-Velasco M, Rivera R, Jiménez-Puya R, García-Doval I, Descalzo MA, The Biobadaderm Study Group (2017) Comparison of phenotype, comorbidities, therapy and adverse events between psoriatic patients with and without psoriatic arthritis. Biobadaderm registry. J Eur Acad Dermatology Venereol 31:1021–1028
Sakkas LI, Bogdanos DP (2017) Are psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis the same disease? The IL-23/IL-17 axis data. Autoimmun Rev 16:10–15
Haroon M, Gallagher P, Heffernan E, FitzGerald O (2014) High prevalence of metabolic syndrome and of insulin resistance in psoriatic arthritis is associated with the severity of underlying disease. J Rheumatol 41:1357–1365
Taylor W, Gladman D, Helliwell P, Marchesoni A, Mease P, Mielants H, CASPAR Study Group (2006) Classification criteria for psoriatic arthritis: development of new criteria from a large international study. Arthritis Rheum 54:2665–2673
Aithal GP (2011) Hepatotoxicity related to antirheumatic drugs. Nat Rev Rheumatol 7:139–150
Wallace TM, Levy JC, Matthews DR (2004) Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care 27:1487–1495
Gayoso-Diz P, Otero-González A, Rodriguez-Alvarez MX, Gude F, García F, de Francisco A, Quintela AG (2013) Insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) cut-off values and the metabolic syndrome in a general adult population: effect of gender and age: EPIRCE cross-sectional study. BMC Endocr Disord 13:47
Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation and T of HBC in A (2001) Executive summary of the third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (adult treatment panel III). JAMA 285:2486–2497
Torres DM, Williams CD, Harrison SA (2012) Features, diagnosis, and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 10:837–858
Prussick RB, Miele L (2018) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with psoriasis: a consequence of systemic inflammatory burden? Br J Dermatol 179:16–29
Mantovani A, Gisondi P, Lonardo A, Targher G (2016) Relationship between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and psoriasis: a novel Hepato-dermal axis? Int J Mol Sci 17
Ogdie A, Grewal SK, Noe MH, Shin DB, Takeshita J, Chiesa Fuxench ZC, Carr RM, Gelfand JM (2018) Risk of incident liver disease in patients with psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based study. J Invest Dermatol 138:760–767
Eder L, Abji F, Rosen CF, Chandran V, Gladman DD (2017) The association between obesity and clinical features of psoriatic arthritis: a case-control study. J Rheumatol 44:437–443
Boyer WR, Johnson TM, Fitzhugh EC, Richardson MR, Churilla JR (2016) The associations between increasing degrees of HOMA-IR and measurements of adiposity among Euglycemic U.S. adults. In: Metab Syndr Relat Disord, vol 14, pp 108–113
Okorodudu DO, Jumean MF, Montori VM, Romero-Corral A, Somers VK, Erwin PJ, Lopez-Jimenez F (2010) Diagnostic performance of body mass index to identify obesity as defined by body adiposity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Obes 34:791–799
Yilmaz E, Tamer E, Artüz F et al (2017) Evaluation of serum uric acid levels in psoriasis vulgaris. Turkish J Med Sci 47:531–534
Van Der Voort EAM, Koehler EM, Dowlatshahi EA et al (2014) Psoriasis is independently associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients 55 years old or older: results from a population-based study. J Am Acad Dermatol 70:517–524
Abedini R, Salehi M, Lajevardi V, Beygi S (2015) Patients with psoriasis are at a higher risk of developing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Exp Dermatol 40:722–727
Ramonda R, Puato M, Punzi L, Rattazzi M, Zanon M, Balbi G, Ortolan A, Frallonardo P, Faggin E, Plebani M, Zaninotto M, Lorenzin M, Pauletto P, Doria A (2014) Atherosclerosis progression in psoriatic arthritis patients despite the treatment with tumor necrosis factor-alpha blockers: a two-year prospective observational study. Joint Bone Spine 81:421–425
Tveit KS, Duvetorp A, Østergaard M, Skov L, Danielsen K, Iversen L, Seifert O (2019) Treatment use and satisfaction among patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: results from the NORdic PAtient survey of Psoriasis and Psoriatic arthritis (NORPAPP). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 33:340–354
Costa L, Caso F, Ramonda R, del Puente A, Cantarini L, Darda MA, Caso P, Lorenzin M, Fiocco U, Punzi L, Scarpa R (2015) Metabolic syndrome and its relationship with the achievement of minimal disease activity state in psoriatic arthritis patients: an observational study. Immunol Res 61:147–153
Coates LC, Gottlieb AB, Merola JF, Boone C, Szumski A, Chhabra A (2019) Comparison of different remission and low disease definitions in psoriatic arthritis and evaluation of their prognostic value. J Rheumatol 46:160–165
Coates LC, Kavanaugh A, Mease PJ et al (2016) Group for research and assessment of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis 2015 treatment recommendations for psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol (Hoboken, NJ 68:1060–1071
Gossec L, Smolen JS, Ramiro S, de Wit M, Cutolo M, Dougados M, Emery P, Landewé R, Oliver S, Aletaha D, Betteridge N, Braun J, Burmester G, Cañete JD, Damjanov N, FitzGerald O, Haglund E, Helliwell P, Kvien TK, Lories R, Luger T, Maccarone M, Marzo-Ortega H, McGonagle D, McInnes IB, Olivieri I, Pavelka K, Schett G, Sieper J, van den Bosch F, Veale DJ, Wollenhaupt J, Zink A, van der Heijde D (2016) European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) recommendations for the management of psoriatic arthritis with pharmacological therapies: 2015 update. Ann Rheum Dis 75:499–510
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The present study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The local Ethics committee has approved the research protocol and informed consent has been obtained from all subjects.
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 211 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ortolan, A., Lorenzin, M., Tadiotto, G. et al. Metabolic syndrome, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and liver stiffness in psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis patients. Clin Rheumatol 38, 2843–2850 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04646-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04646-7