Abstract
Objective
Our goal was to determine if whole blood viscosity (WBV) can be used to predict the risk of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc).
Methods
Patients with SSc were analyzed. Out of 107 patients, 26 patients, found to have confirmed diagnosis of PAH, were classified as those with (n = 26, PAH group) and without PAH (n = 81, non-PAH group). We calculated estimated WBV at both high (HSR) and low shear rates (LSR) from hematocrit and total serum protein levels.
Results
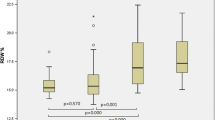
Total protein levels were significantly higher and the anti-centromere antibody (ACA) was more frequent in the PAH group. Furthermore, anti-topoisomerase antibody (anti-scl-70) was significantly less frequent in the PAH group. The WBV values were significantly higher at HSR (16.68 ± 0.38 vs. 16.24 ± 0.58; p < 0.001) and at LSR (51.81 ± 7.21 vs. 42.97 ± 11.76; p < 0.001) in PAH group. The multivariate analysis revealed that the WBV at both shear rates independently designated the presence of PAH in SSc patients. The ROC curve showed that the sensitivity and specificity of LSR and HSR were 92.3% and 61.7% (AUC 0.759, p < 0.001), and 88.5% and 65.4% (AUC 0.770, p < 0.001) with a cutoff value of 43.56 and 16.32 for WBV, respectively.
Conclusion
Higher WBV levels in SSc patients were an independent indicator for PAH development in this cohort. WBV-LSR and WBV-HSR values might help exclude the PAH possibility in patients diagnosed with SSc and remain as an independently associated biomarker for follow-up of these patients for future risk of PAH development. Findings remain to be confirmed by other cohorts.
Key Points • The most important cause of morbidity and mortality in systemic sclerosis patients is considered to be pulmonary arterial hypertension. • When the symptoms of PAH are not recognized earlier in the course of the SSc, the prognosis might be worse. • Higher whole blood viscosity levels in scleroderma patients with PAH was an independent indicator for PAH development. |

Similar content being viewed by others
References
McLaughlin VV, McGoon MD (2006) Pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation 114(13):1417–1431. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.104.503540
Mukerjee D, St George D, Coleiro B, Knight C, Denton CP, Davar J, Black CM, Coghlan JG (2003) Prevalence and outcome in systemic sclerosis associated pulmonary arterial hypertension: application of a registry approach. Ann Rheum Dis 62(11):1088–1093. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.62.11.1088
Hachulla E, Gressin V, Guillevin L, Carpentier P, Diot E, Sibilia J, Kahan A, Cabane J, Frances C, Launay D, Mouthon L, Allanore Y, Tiev KP, Clerson P, de Groote P, Humbert M (2005) Early detection of pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic sclerosis: a French nationwide prospective multicenter study. Arthritis Rheum 52(12):3792–3800. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.21433
Steen VD, Medsger TA (2007) Changes in causes of death in systemic sclerosis, 1972-2002. Ann Rheum Dis 66(7):940–944. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2006.066068
Hao Y, Hudson M, Baron M, Carreira P, Stevens W, Rabusa C, Tatibouet S, Carmona L (2017) Early mortality in a multinational systemic sclerosis inception cohort. Arthritis Rheum 69(5):1067–1077. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.40027
Fisher MR, Mathai SC, Champion HC, Girgis RE, Housten-Harris T, Hummers L, Krishnan JA, Wigley F, Hassoun PM (2006) Clinical differences between idiopathic and scleroderma-related pulmonary hypertension. Arthritis Rheum 54(9):3043–3050. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.22069
Clements PJ, Tan M, McLaughlin VV, Oudiz RJ, Tapson VF, Channick RN, Rubin LJ, Langer A (2012) The pulmonary arterial hypertension quality enhancement research initiative: comparison of patients with idiopathic PAH to patients with systemic sclerosis-associated PAH. Ann Rheum Dis 71(2):249–252. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200265
Ramjug S, Hussain N, Hurdman J, Billings C, Charalampopoulos A, Elliot CA, Kiely DG, Sabroe I, Rajaram S, Swift AJ, Condliffe R (2017) Idiopathic and systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension: a comparison of demographic, hemodynamic, and MRI characteristics and outcomes. Chest 152(1):92–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2017.02.010
Chung L, Liu J, Parsons L, Hassoun PM, McGoon M, Badesch DB, Miller DP, Nicolls MR, Zamanian RT (2010) Characterization of connective tissue disease-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension from REVEAL: identifying systemic sclerosis as a unique phenotype. Chest 138(6):1383–1394. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.10-0260
Yaqub A, Chung L (2013) Epidemiology and risk factors for pulmonary hypertension in systemic sclerosis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 15(1):302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-012-0302-2
Budhiraja R, Tuder RM, Hassoun PM (2004) Endothelial dysfunction in pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 109(2):159–165. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.0000102381.57477.50
Cool CD, Stewart JS, Werahera P, Miller GJ, Williams RL, Voelkel NF, Tuder RM (1999) Three-dimensional reconstruction of pulmonary arteries in plexiform pulmonary hypertension using cell-specific markers. Evidence for a dynamic and heterogeneous process of pulmonary endothelial cell growth. Am J Pathol 155(2):411–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9440(10)65137-1
Proudman SM, Stevens WM, Sahhar J, Celermajer D (2007) Pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic sclerosis: the need for early detection and treatment. Intern Med J 37(7):485–494. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1445-5994.2007.01370.x
Goldberg A (2010) Pulmonary arterial hypertension in connective tissue diseases. Cardiol Rev 18(2):85–88. https://doi.org/10.1097/CRD.0b013e3181cbcde7
Lowe GD, Lee AJ, Rumley A, Price JF, Fowkes FG (1997) Blood viscosity and risk of cardiovascular events: the Edinburgh artery study. Br J Haematol 96(1):168–173. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2141.1997.8532481.x
de Simone G, Devereux RB, Chien S, Alderman MH, Atlas SA, Laragh JH (1990) Relation of blood viscosity to demographic and physiologic variables and to cardiovascular risk factors in apparently normal adults. Circulation 81(1):107–117. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.81.1.107
Kensey KR, Cho YI, Chang M (1997) Effects of whole blood viscosity on Atherogenesis. J Invasive Cardiol 9(1):17–24
Ciuffetti G, Schillaci G, Lombardini R, Pirro M, Vaudo G, Mannarino E (2005) Prognostic impact of low-shear whole blood viscosity in hypertensive men. Eur J Clin Investig 35(2):93–98. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2362.2005.01437.x
Koenig W, Sund M, Filipiak B, Doring A, Lowel H, Ernst E (1998) Plasma viscosity and the risk of coronary heart disease: results from the MONICA-Augsburg cohort study, 1984 to 1992. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 18(5):768–772. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.ATV.18.5.768
Velcheva I, Antonova N, Titianova E, Damianov P, Dimitrov N, Ivanov I (2006) Hemorheological parameters in correlation with the risk factors for carotid atherosclerosis. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 35(1–2):195–198
Silber HA, Bluemke DA, Ouyang P, Du YP, Post WS, Lima JA (2001) The relationship between vascular wall shear stress and flow-mediated dilation: endothelial function assessed by phase-contrast magnetic resonance angiography. J Am Coll Cardiol 38(7):1859–1865. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0735-1097(01)01649-7
Tietjen GW, Chien S, Leroy EC, Gavras I, Gavras H, Gump FE (1975) Blood viscosity, plasma proteins, and Raynaud syndrome. Arch Surg 110(11):1343–1346. https://doi.org/10.1001/archsurg.1975.01360170083011
McGrath MA, Peek R, Penny R (1977) Blood hyperviscosity with reduced skin blood flow in scleroderma. Ann Rheum Dis 36(6):569–574. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.36.6.569
Jacobs MJ, Jorning PJ, van der Kloot EJ VR, Kitslaar PJ, Lemmens HA, Slaaf DW, Reneman RS (1991) Plasmapheresis in Raynaud's phenomenon in systemic sclerosis: a microcirculatory study. Int J Microcirc Clin Exp 10(1):1–11
Jacobs MJ, Breslau PJ, Slaaf DW, Reneman RS, Lemmens JA (1987) Nomenclature of Raynaud's phenomenon: a capillary microscopic and hemorheologic study. Surgery 101(2):136–145
Vaya A, Todoli J, Calvo J, Romagnoli M, Ricart JM (2008) Haemorheological profile in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 40(3):243–248
Johnson SR (2015) New ACR EULAR guidelines for systemic sclerosis classification. Curr Rheumatol Rep 17(5):32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-015-0506-3
Galie N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, Simonneau G, Peacock A, Vonk Noordegraaf A, Beghetti M, Ghofrani A, Gomez Sanchez MA, Hansmann G, Klepetko W, Lancellotti P, Matucci M, McDonagh T, Pierard LA, Trindade PT, Zompatori M, Hoeper M (2016) 2015 ESC/ERS guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the joint task force for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Heart J 37(1):67–119. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehv317
Price LC, Wort SJ, Perros F, Dorfmuller P, Huertas A, Montani D, Cohen-Kaminsky S, Humbert M (2012) Inflammation in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Chest 141(1):210–221. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.11-0793
Patan S (2000) Vasculogenesis and angiogenesis as mechanisms of vascular network formation, growth and remodeling. J Neuro-Oncol 50(1–2):1–15
Risau W (1997) Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature 386(6626):671–674. https://doi.org/10.1038/386671a0
Ranchoux B, Harvey LD, Ayon RJ, Babicheva A, Bonnet S, Chan SY, Yuan JX, Perez VJ (2018) Endothelial dysfunction in pulmonary arterial hypertension: an evolving landscape (2017 Grover conference series). Pulm Circ 8(1):2045893217752912. https://doi.org/10.1177/2045893217752912
Kim J, Chung H, Cho M, Lee BK, Karimi A, Shin S (2013) The role of critical shear stress on acute coronary syndrome. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 55(1):101–109. https://doi.org/10.3233/ch-131694
Antonova N, Velcheva I (1999) Hemorheological disturbances and characteristic parameters in patients with cerebrovascular disease. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 21(3–4):405–408
Cecchi E, Giglioli C, Valente S, Lazzeri C, Gensini GF, Abbate R, Mannini L (2011) Role of hemodynamic shear stress in cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis 214(2):249–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.09.008
Korsten P, Niewold TB, Zeisberg M, Utset TO, Cho D, Zachary LS, Sweiss NJ, Volkov S (2017) Increased whole blood viscosity is associated with the presence of digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis: results from a cross-sectional pilot study. Autoimmune diseases 2017(3529214):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3529214
Wei A, Gu Z, Li J, Liu X, Wu X, Han Y, Pu J (2016) Clinical adverse effects of endothelin receptor antagonists: insights from the meta-analysis of 4894 patients from 24 randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trials. J Am Heart Assoc 5(11). https://doi.org/10.1161/jaha.116.003896
Hughes M, Herrick AL (2017) Digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford, England) 56(1):14–25. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kew047
Kolstad KD, Li S, Steen V, Chung L (2018) Long-term outcomes in systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension from the pulmonary hypertension assessment and recognition of outcomes in scleroderma registry (PHAROS). Chest 154(4):862–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2018.05.002
Launay D, Sitbon O, Hachulla E, Mouthon L, Gressin V, Rottat L, Clerson P, Cordier JF, Simonneau G, Humbert M (2013) Survival in systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension in the modern management era. Ann Rheum Dis 72(12):1940–1946. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202489
McLaughlin VV, Archer SL, Badesch DB, Barst RJ, Farber HW, Lindner JR, Mathier MA, McGoon MD, Park MH, Rosenson RS, Rubin LJ, Tapson VF, Varga J, Harrington RA, Anderson JL, Bates ER, Bridges CR, Eisenberg MJ, Ferrari VA, Grines CL, Hlatky MA, Jacobs AK, Kaul S, Lichtenberg RC, Lindner JR, Moliterno DJ, Mukherjee D, Pohost GM, Rosenson RS, Schofield RS, Shubrooks SJ, Stein JH, Tracy CM, Weitz HH, Wesley DJ (2009) ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary hypertension: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation task force on expert consensus documents and the American Heart Association: developed in collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians, American Thoracic Society, Inc., and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association. Circulation 119(16):2250–2294. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.109.192230
Williams MH, Handler CE, Akram R, Smith CJ, Das C, Smee J, Nair D, Denton CP, Black CM, Coghlan JG (2006) Role of N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide (N-TproBNP) in scleroderma-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J 27(12):1485–1494. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehi891
Harris ES, Meiselman HJ, Moriarty PM, Metzger A, Malkovsky M (2018) Therapeutic plasma exchange for the treatment of systemic sclerosis: a comprehensive review and analysis. J Scleroderma Relat Disord 3(2):132–152. https://doi.org/10.1177/2397198318758606
Hunzelmann N, Genth E, Krieg T, Lehmacher W, Melchers I, Meurer M, Moinzadeh P, Muller-Ladner U, Pfeiffer C, Riemekasten G, Schulze-Lohoff E, Sunderkoetter C, Weber M, Worm M, Klaus P, Rubbert A, Steinbrink K, Grundt B, Hein R, Scharffetter-Kochanek K, Hinrichs R, Walker K, Szeimies RM, Karrer S, Muller A, Seitz C, Schmidt E, Lehmann P, Foeldvari I, Reichenberger F, Gross WL, Kuhn A, Haust M, Reich K, Bohm M, Saar P, Fierlbeck G, Kotter I, Lorenz HM, Blank N, Grafenstein K, Juche A, Aberer E, Bali G, Fiehn C, Stadler R, Bartels V (2008) The registry of the German network for systemic scleroderma: frequency of disease subsets and patterns of organ involvement. Rheumatology (Oxford, England) 47(8):1185–1192. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/ken179
Denton CP, Hachulla E (2011) Risk factors associated with pulmonary arterial hypertension in patients with systemic sclerosis and implications for screening. Eur Respir Rev 20(122):270–276. https://doi.org/10.1183/09059180.00006111
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Senturk, B., Akdeniz, B., Yilmaz, M.B. et al. Whole blood viscosity in systemic sclerosis: a potential biomarker of pulmonary hypertension?. Clin Rheumatol 39, 49–56 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04603-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04603-4