Abstract
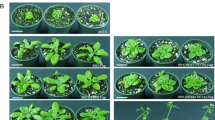
The plasma membrane-localized BRASSINOSTEROID-INSENSITIVE1 (BRI1) and BRI1-ASSOCIATED KINASE1 (BAK1) are a well-known receptor pair involved in brassinosteroids (BR) signaling in Arabidposis. The formation of a receptor complex in response to BRs and the subsequent activation of cytoplasmic domain kinase activity share mechanistic characteristics with animal receptor kinases. Here, we demonstrate that BRI1 and BAK1 are BR-dependently phosphorylated, and that phosphorylated forms of the two proteins persist for different lengths of time. Mutations of either protein abolished phosphorylation of the counterpart protein, implying transphosphorylation of the receptor kinases. To investigate the specific amino acids critical for formation of the receptor complex and activation of BAK1 kinase activity, we expressed several versions of BAK1 in yeast and plants. L32E and L46E substitutions resulted in a loss of binding of BAK1 to BRI1, and threonine T455 was essential for the kinase activity of BAK1 in yeast. Transgenic bri1 mutant plants overexpressing BAK1(L46E) displayed reduced apical dominance and seed development. In addition, transgenic wild type plants overexpressing BAK1(T455A) lost the phosphorylation activity normally exhibited in response to BL, leading to semi-dwarfism. These results suggest that BAK1 is a critical component regulating the duration of BR efficacy, even though it cannot directly bind BRs in plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asami, T., Min, Y.K., Nagata, N., Yamaguchi, K., Takatsuto, S., Fujioka, S., Murofushi, N., Yamaguchi, I., and Yoshida, S. (2000). Characterization of brassinazole, a triazole-type brassinosteroid biosynthesis inhibitor. Plant Physiol. 123, 93–100.
Bradford, M.M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254.
Burgess, A.W., Cho, H.S., Eigenbrot, C., Furguson, K.M., Gareet T.P., Leahy, D.J., Lemmon, M.A., Sliwkowski, M.X., Ward, C.W., Yokoyama, S. (2003). An open-and-shut case? Recent insights into the activation of EGF/ErbB receptors. Mol. Cell 12, 541–552.
Chinchilla, D., Zipfel, C., Robatzek, S., Kemmerling, B., Nürnberger, T., Jones, J.D.G., Felix, G., and Boiler, T. (2007). A flagellin-induced complex of the receptor FLS2 and BAK1 initiates plant defense. Nature 448, 497–500.
Chono M., Honda I., Zeniya H., Yoneyama K., Saisho D., Takeda K., Takatsuto S., Hoshino T., and Watanabe Y. (2003). A semidwarf phenotype of barley uzu results from a nucleotide substitution in the gene encoding a putative brassinosteroid receptor, Plant Physiol. 133, 1209–1219
Clause, S.D., and Sasse, J.M. (1998). Brassinosteroids: Essential regulators of plant growth and development. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 49, 427–451.
Ehsan, H., Ray, W.K., Phinney, B., Wang, X., Huber, S.C., Clause, S.D. (2005). Interaction of Arabidopsis BRASSINOSTEROID-INSENSITIVE 1 receptor kinase with a homolog of mammalian TGF-beta receptor interacting protein. Plant J. 43, 251–261.
Friedrichsen, D.M., Joazeiro, C.A., Li, J., Hunter, T., and Chory, J. (2003). Brassinosteroid-insensitive-1 is a ubiquitously expressed leucine-rich repeat receptor serine/threonine kinase. Plant Physiol. 123, 1247–1256.
Goda, H., Shimada, Y., Asmami, T., Fujioka, S., and Yishida, S. (2002). Microarray analysis of brassinostroid-regulated genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 130, 1319–1334.
Goda, H., Sawa, S., Asami, T., Fujioka, S., Shimada, Y., Yoshida, S. (2004). Comprehensive comparison of auxin-regulated and brassinosteroid-regulated genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 134, 1555–1573.
He, Z., Gendron, J. M., Yang, Y., Li, J., and Wang, Z.Y. (2002). The GSK3-like kinase BIN2 phosphorylates abd destabilized BZR1, a positive regulator of the brassinosteroid signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 10185–10190.
Hecht, V., Vielle-Calzada, J., Hartog, M.V., Schmidt, E.D.L, Boutilier, K., Grossniklasu, U., and de Vries, S.C. (2001) The Arabidopsis SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPROE KINASE 1 gene is expressed in developing ovule and embryos and enhances embryogenic competence in culture. Plant Physiol. 127, 803–816.
Heese, A., Hann, D.R., Glimenez-Ibanez, S., Jones, A.M.E., He, K., Li, J., Schroeder, J.I., Peck, S.C., and Rathjen, J.P. (2007). The receptor-like kinase SERK3/BAK1 is a central regulator of innate immunity in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 12217–12222.
Karlova, R., Boeren, S., Russinova, E., Aker, J., Vervoort, J., and de Vries, S.C. (2006). The Arabidopsis SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE1 protein complex includes BRASSINOSTEROID-INSENSITIVE 1. Plant Cell 18, 626–638.
Kinoshita, T., Caňo-Delgado, A., Seto, H., Hiranuma, S., Fujuika, S., and Chory, J. (2005). Binding of brassinosteroids to the extracellular domain of plant receptor kinase BRI1. Nature 433, 167–171.
Li, J., and Chory, M. (1997). A putative leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase involve in brassinosteroid signal transduction. Cell 90, 927–938.
Li, J., and Nam, K.H. (2002). Regulation of brassinosteroid signaling by a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase. Science 295, 1299–1301.
Li, J., Wen, J., Lease, K.A., Dorke, J.T., Tax, F.E., and Walker, J.C. (2002). BAK1, an Arabidopsis LRR receptor-like kinase, interacts with BRI1 and modulates brassinosteroid signaling. Cell 110, 213–222.
Liu, Z.B., Ulmasov, T., Shi, X.Y., Hagen, G., and Guilfoyle, T.L (1994). Soybean GH3 promoter contains multiple auxin-inducible elements. Plant Cell 6, 645–657.
Massagué, J. (1998). TGF-beta signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67, 753–791
Mitchell, J.W., Mandava, N.B., Worley, J.F., Plimmer, J.R., and Smith, M.V. (1970). Brassins: a new family of plant hormones from rape pollen. Nature 225, 1065–1066.
Mora-Garcia, S., Vert, G., Yin, Y., Cano-Delgado, A., Cheong, H., and Chory, J. (2004). Nuclear protein phosphatase with Kelchrepeat domains modulates the response to brassinosteroids in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev. 18, 448–460.
Nam, K.H., and Li, J. (2002). BRI1/BAK1, a receptor kinase pair mediating brassinosteroid signaling. Cell 110, 203–212.
Nam, K.H., and Li, J. (2004). The Arabidopsis transthyretin-like protein is a potential substrate of BRASSINOSTEROID-INSENSITIVE 1. Plant Cell 16, 2406–2417.
Noguchi, T., Fusioka, S., Choe, S., Takatsuto, S., Yoshida, S., Yuan, H., Feldmann, K.A., and Tax, F.E. (1999). Brassinosteroid-insensitive dwarf mutants of Arabidopsis accumulates brassinosteroids. Plant Physiol. 121, 743–752.
Nomura, T., Kitasaka, Y., Takatsuto, S., Reid, J.B., Fukami, M., and Yokoda, T. (1999). Brassinosteroid/sterol synthesis and plant growth as affected by Ika and Ikb mutations of peas. Plant Physiol. 119, 1517–1526.
Oh, M.H., Ray, W.K., Huber, S.C., Asara, J.M., Gage, D.A., and Clause, S.D. (2000). Recombinant brassinosteroid insensitive 1 receptor-like kinase autophosphorylates on serine and threonine residues and phosphorylates a conserved peptode motif in vitro. Plant Physiol. 124, 751–766.
Pwason, T., and Nash, P. (2000). protein-protein interactions define specificity in signal transduction. Genes Dev. 14, 1027–1047.
Shah, K., Vervoort, J., and de Vries, S.C. (2001). Role of threonines in the Arabidopsis thaliana somatic embryogenesis receptor kinasel activation loop in phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 41263–41269
Shiu, S.H., and Bleeker, AB. (2001). Receptor-like kinases from Arabidopsis form a monophyletic gene family related to animal receptor kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 10763–10768.
TenDijke, P., and Hill, C.S. (2004). New insight into TGF-beta-Smad signaling. Trends Biochem. Sci. 29, 265–273.
Ulrich, A., and Schlessinger, J. (1990). Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell 61, 203–212.
Vert, G., Nemhauser, J.L., Geldner, N., Hong, F., and Chory, J. (2005). Molecular mechanisms of steroid hormone signaling in plants. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 21, 177–201.
Wang, Z.Y., Seto, H., Fujioka, S., Yoshida, S., and Chory, J. (2001). BRI1 is a critical component of a plasma-membrane receptor for plant steroids. Nature 410, 380–383.
Wang, Z.Y., Nakano, T., Gendron, J., He, J.X., Chen, M., Vafedos, D., Yang, Y., Fujioka, S., Yoshida, S., Asami, T, et al. (2002). Nuclear-localized BZR1 mediates brassinosteroid-induced growth and feedback suppression of brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Dev. Cell 2, 505–515.
Wang, X., Goshe, M.B., Soderblom, E.J., Phinney, B.S., Kuchar, J.A., Li, J., Asami, T., Yoshida, S., Huber, S.C., and Clouse, S.D. (2005a). Identification and functional analysis of in vitro phosphorylation sites of the Arabidopsis BRASSINOSTEROID-INSENSITIVE1 receptor kinase. Plant Cell 17, 1685–1703
Wang, X., Li, X., Meisenhelder, J., Hunter, T., Yoshida, S., Asami, T., and Chory, J. (2005b). Autoregulation and homodimerization are involved in the activation of the plant steroid receptor BRI1. Dev. Cell 8, 855–865.
Wang, X., and Chory, J. (2006). Brassinosteroids regualate dissociation of BKI1, a negative regulator of BRI1 signaling from a plasma membrane. Science 131, 1118–1122.
Yamamuro, C., Ihara, Y., Wu, X., Noguchi, T., Fujoka, S., Takatsuto, S., Ashikari, M., Kitano, H., and Matsuoka, M. (2002). Loss of Function of a rice brassinosteroid insensitive1 homolog prevents internode elongation and bending of the lamina joint. Plant Cell 12, 1591–1606.
Yin, Y., Mora-Garcia, S., Li, J., Yoshida, S., Asami, T., and Chory, J. (2002). BES1 accumulates in the nucleus in response to brassinosteriods to regulate gene expression and promote stem elongation. Cell 109, 181–191.
Zurek, D.M., Rayle, D.L., McMorris, T.C., and Clause, S.D. (1994). Investigation of gene-expression, growth-kinetics, and wall extensibility during brassinosteroid-regulated stem elongation. Plant Physiol. 104, 505–513.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Yun, H.S., Bae, Y.H., Lee, Y.J. et al. Analysis of phosphorylation of the BRI1/BAK1 complex in arabidopsis reveals amino acid residues critical for receptor formation and activation of BR signaling. Mol Cells 27, 183–190 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0023-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0023-1