Abstract
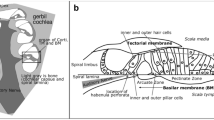
The annular ligament across the stapediovestibular joint connects the stapes footplate and the vestibular window and plays an important role in the sound conductive system of the ear. In this study, we investigated the distribution of extracellular matrix components in the ligament by histochemical methods at light and electron microscopic levels. As results, light microscopic immunohistochemistry of fibrillin and 36-kDa microfibril-associated glycoprotein (MAGP-36) showed intense immunoreactivities in the annular ligament between the stapes footplate and vestibular window. In addition, the histochemical localization of hyaluronic acid by using biotinylated hyaluronic acid-binding protein (HABP) clarifi ed the presence of hyaluronic acid in the annular ligament. At the electron microscopic level, the immunogold labeling of fibrillin showed intense labeling on the periphery of the electron-dense mantle. Furthermore, the labeling of fibrillin was preferentially seen on the fibrous components among the electronlucent amorphous substance. The immunogold labeling of MAGP-36 was seen on the electron-dense mantle and scattered on the electron-lucent amorphous substance. The gold labeling with biotinylated HABP clearly showed a distribution of hyaluronic acid throughout the amorphous space in the ligament. The present results provide a histochemical profile of the annular ligament of the rat stapediovestibular joint that may provide clues to elucidation of pathological changes in the ligaments and conductive hearing loss in humans.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Graham MD (1985) The annular ligament attachment to the normal human stapes footplate. A scanning electron microscopic study. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 94:171–175
Ohashi M, Ide S, Kimitsuki T, Komune S, Suganuma T (2006) Three-dimensional regular arrangement of the annular ligament of the rat stapediovestibular joint. Hear Res 213:11–16
Ohashi M, Sawaguchi A, Ide S, Kimitsuki T, Komune S, Suganuma T (2005) Histochemical characterization of the rat ossicular joint cartilage with a special reference to stapediovestibular joint. Acta Histochem Cytochem38:387–392
Davies J (1948) A note on the articulations of the auditory ossicles and related structures. J Laryngol Otol 62:533–536
Wolff D, Bellucci R (1956) The human ossicular ligaments. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 65:895–909
Gussen R (1968) Articular and internal remodeling in the human otic capsule. Am J Anat 122:397–418
Bolz EA, Lim DJ (1972) Morphology of the stapediovestibular joint. Acta Otolaryngol 73:10–17
De Souza A, Montes GS, Villela BT, Cruz AC, Cotta-Pereira G (1991) Elastic-related fibers in the annular ligament of the stapes-oval window articulation. An electron microscopic and histochemical study in the rat and the rabbit. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol 112:7–10
Schuknecht H (1974) Pathology of the ear. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, pp 21–96
Lim DJ (1970) A scanning electron microscopic investigation on otosclerotic stapes. Ann Otol 79:780–799
Gussen R (1969) The stapediovestibular joint: normal structures and pathogenesis of otosclerosis. Acta Otolaryngol 248(suppl): 5–38
Gros A, Vatovec J, Sereg-Bahar M (2003) Histologic changes on stapedial footplate in otosclerosis. Correlations between histologic activity and clinical findings. Otol Neurotol 24:43–47
Ramirez F, Pereira L (1999) The fibrillins. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 31:255–259
Sakai LY, Keene DR, Engvall E (1986) Fibrillin, a new 350-kD glycoprotein, is a component of extracellular microfibrils. J Cell Biol 103:2499–2509
Toyoshima T, Yamashita K, Furuichi H, Shishibori T, Itano T, Kobayashi R (1999) Ultrastructural distribution of 36-kD microfibril-associated glycoprotein (MAGP-36) in human and bovine tissues. J Histochem Cytochem 47:1049–1056
Kobayashi R, Tashima Y, Masuda H, Shozawa T, Numata Y, Miyauchi K, Hayakawa T (1989) Isolation and characterization of a new 36-kDa microfi bril-associated glycoprotein from porcine aorta. J Biol Chem 264:17437–17444
Yasui T, Tsukise A, Meyer W (2004) Localization of epidermal hyaluronan in the foot pads of the North American raccoon (Procyon lotor). Arch Histol Cytol 67:219–226
Zea-Aragon Z, Terada N, Ohno N, Fujii Y, Baba T, Yoshida M, Ohtsuki K, Ohnishi M, Ohno S (2004) Replica immnoelectron microscopic study of the upper surface layer in rat mandibular condylar cartilage by a quick-freezing method. Histochem Cell Biol 121:255–259
Slot JW, Geuze HJ (1985) A new method of preparing gold probes for multiple-labeling cytochemistry. Eur J Cell Biol 38:87–93
De Mey J, Moeremans M, Geuens R, Nuydens R, Brabander MD (1981) High resolution light and electron microscopic localization of tubulin with the IGS (immunogold staining) method. Cell Biol Int Rep 5:889–899
Ramirez F, Dietz HC (2007) Fibrillin-rich microfibrils: structural determinants of morphogenetic and homeostatic events. J Cell Physiol 213:326–330
Fraser JRE, Laurent TC, Laurent UBG (1997) Hyaluronan: its nature, distribution, functions and turnover. J Intern Med 242: 27–33
Ribari O, Pereplica M, Sziklai I (1991) Oversulfated mucopolysaccharides in the otosclerotic bone. Acta Otolaryngol 111:362–365
Locci P, Becchetti E, Venti G, Lilli C, Marinucci L, Donti E, Paludetti G, Maurizi M (1996) Glycosaminoglycan metabolism in otosclerotic bone cells. Biol Cell 86:73–78
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohashi, M., Ide, S., Sawaguchi, A. et al. Histochemical localization of the extracellular matrix components in the annular ligament of rat stapediovestibular joint with special reference to fibrillin, 36-kDa microfibril-associated glycoprotein (MAGP-36), and hyaluronic acid. Med Mol Morphol 41, 28–33 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-007-0394-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-007-0394-3