Abstract
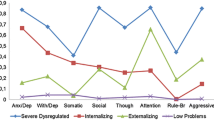
Psychiatric disorders have been increasingly recognized in preschool children; at present, however, we know comparatively less about how well current diagnostic manuals capture the symptoms described in this age group and how comorbidity is patterned. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate whether the symptoms defined by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fourth edition (DSM-IV) load on their respective disorders, examine whether individual symptoms exist that load particularly high or low on the disorder they allegedly define, and analyze how comorbidity clusters in individual children. Parents of a community sample of Norwegian 4-year-olds (N = 995) were interviewed using the Preschool Age Psychiatric Assessment. A confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) and a latent profile analysis (LPA) were performed on the symptoms of seven DSM disorders: attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), oppositional defiant disorder, conduct disorder, major depressive disorder (MDD), generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), social phobia, and separation anxiety disorder. The results showed that the CFA solution that closely resembled the disorders delineated in the DSM-IV fitted the data best. However, vegetative symptoms did not define preschool depression. The LPA identified nine symptom profiles among preschoolers, of which four showed evidence of psychopathology: comorbid MDD/GAD + ADHD combined type, comorbid MDD/GAD + ADHD hyperactive/impulsive type, separation anxiety only, and social phobia only. In conclusion, the symptoms observed in preschoolers fit the DSM-IV well, and comorbidity followed specific patterns.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
Keenan K, Wakschlag LS (2002) Can a valid diagnosis of disruptive behavior disorder be made in preschool children? Am J Psychiatry 159(3):351–358
Egger HL, Angold A (2006) Common emotional and behavioral disorders in preschool children: presentation, nosology, and epidemiology. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 47(3–4):313–337
Egger HL, Emde RN (2011) Developmentally sensitive diagnostic criteria for mental health disorders in early childhood the diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders-IV, the research diagnostic criteria-preschool age, and the diagnostic classification of mental health and developmental disorders of infancy and early childhood-revised. Am Psychol 66(2):95–106. doi:10.1037/a0021026
Egger HL (2009) Psychiatric assessment of young children. Child Adolesc Psychiatry N Am 18(3):559. doi:10.1016/j.chc.2009.02.004
Egger HL, Erkanli A, Keeler G, Potts E, Walter BK, Angold A (2006) Test–retest reliability of the preschool age psychiatric assessment (PAPA). J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 45(5):538–549
Lavigne JV, LeBailly SA, Hopkins J, Gouze KR, Binns HJ (2009) The prevalence of ADHD, ODD, depression, and anxiety in a community sample of 4-year-olds. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol 38(3):315–328. doi:10.1080/15374410902851382
Wichstrøm L, Berg-Nielsen TS, Angold A, Egger HL, Solheim E, Sveen TH (2012) Prevalence of psychiatric disorders in preschoolers. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 53(6):695–705. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2011.02514.x
Luby JL, Si X, Belden AC, Tandon M, Spitznagel E (2009) Preschool depression homotypic continuity and course over 24 months. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66(8):897–905
Harvey EA, Youngwirth SD, Thakar DA, Errazuriz PA (2009) Predicting attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and oppositional defiant disorder from preschool diagnostic assessments. J Consult Clin Psychol 77(2):349–354. doi:10.1037/a0014638
Keenan K, Boeldt D, Chen D, Coyne C, Donald R, Duax J, Hart K, Perrott J, Strickland J, Danis B, Hill C, Davis S, Kampani S, Humphries M (2011) Predictive validity of DSM-IV oppositional defiant and conduct disorders in clinically referred preschoolers. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 52(1):47–55. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2010.02290.x
Scheeringa M, Anders T, Boris N, Carter A, Chatoor-Koch I, Egger H, Harmon R, Keenan K, Luby J, Thomas J, Warren SL, Wright H, Boyce C, del Carmen-Wiggins R, Hann D, Wieder S, Task Force Res Diagnostic C (2003) Research diagnostic criteria for infants and preschool children: the process and empirical support. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 42(12):1504–1512. doi:10.1097/01.chi.0000091504.46853.0a
Sterba S, Egger HL, Angold A (2007) Diagnostic specificity and nonspecificity in the dimensions of preschool psychopathology. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 48(10):1005–1013. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2007.01770.x
Strickland J, Keller J, Lavigne J, Gouze K, Hopkins J, LeBailly S (2011) The structure of psychopathology in a community sample of preschoolers. J Abnorm Child Psychol. doi:10.1007/s10802-011-9487-5
Hardy KK, Kollins SH, Murray DW, Riddle MA, Greenhill L, Cunningham C, Abikoff HB, McCracken JT, Vitiello B, Davies M, McGough JJ, Posner K, Skrobala AM, Swanson JM, Wigal T, Wigal SB, Ghuman JK, Chuang SZ (2007) Factor structure of parent- and teacher-rated attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms in the Preschoolers with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Treatment Study (PATS). J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 17(5):621–633. doi:10.1089/cap.2007.0073
Angold A, Costello EJ, Farmer EMZ, Burns BJ, Erkanli A (1999) Impaired but undiagnosed. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 38(2):129–137
Bergman LR, Magnusson D (1997) A person-oriented approach in research on developmental psychopathology. Dev Psychopathol 9(2):291–319
Acosta MT, Castellanos FX, Bolton KL, Balog JZ, Eagen P, Nee L, Jones J, Palacio L, Sarampote C, Russell HF, Berg K, Arcos-Burgos M, Muenke M (2008) Latent class subtyping of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and comorbid conditions. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 47(7):797–807. doi:10.1097/CHI.0b013e318173f70b
Herman KC, Ostrander R, Walkup JT, Silva SG, March JS (2007) Empirically derived subtypes of adolescent depression: latent profile analysis of co-occurring symptoms in the treatment for adolescents with depression study (TADS). J Consult Clin Psychol 75(5):716–728. doi:10.1037/0022-006x.75.5.716
Eddy KT, Le Grange D, Crosby RD, Hoste RR, Doyle AC, Smyth A, Herzog DB (2010) Diagnostic classification of eating disorders in children and adolescents: how does DSM-IV-TR compare to empirically-derived categories? J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 49(3):277–287. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2009.10.012
Degnan KA, Calkins SD, Keane SP, Hill-Soderlund AL (2008) Profiles of disruptive behavior across early childhood: contributions of frustration reactivity, physiological regulation, and maternal behavior. Child Dev 79(5):1357–1376
Ostrander R, Herman K, Sikorski J, Mascendaro P, Lambert S (2008) Patterns of psychopathology in children with ADHD: a latent profile analysis. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol 37(4):833–847. doi:10.1080/15374410802359668
Goodman R (1997) The strengths and difficulties questionnaire: a research note. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 38(5):581–586
World Health Organization (2001) ICF: international classification of functioning, disability and health. World Health Organization, Geneva
Walrath CM, Petras H, Mandell DS, Stephens RL, Holden EW, Leaf PJ (2004) Gender differences in patterns of risk factors among children receiving mental health services: latent class analyses. J Behav Health Serv Res 31(3):297–311
Nylund KL, Asparoutiov T, Muthen BO (2007) Deciding on the number of classes in latent class analysis and growth mixture modeling: a Monte Carlo simulation study. Struct Equ Model 14(4):535–569
Muthén LK, Muthén BO (1998–2010) Mplus user’s guide, 6th edn. Muthén & Muthén, Los Angeles
Lubke GH, Muthen B (2005) Investigating population heterogeneity with factor mixture models. Psychol Methods 10(1):21–39. doi:10.1037/1082-989x.10.1.21
Martel MM, von Eye A, Nigg JT (2010) Revisiting the latent structure of ADHD: is there a ‘g’ factor? J Child Psychol Psychiatry 51(8):905–914. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2010.02232.x
Kerr DCR, Lunkenheimer ES, Olson SL (2007) Assessment of child problem behaviors by multiple informants: a longitudinal study from preschool to school entry. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 48(10):967–975. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2007.01776.x
Kuschel A, Heinrichs N, Bertram H, Naumann S, Hahlweg K (2007) How well do parents and teachers’ reports agree on behaviour problems in pre-school aged children? Z Kinder-und Jugendpsy Psychother 35(1):51–58. doi:10.1024/1422-4917.35.1.51
Ivanova MY, Achenbach TM, Rescorla LA, Harder VS, Ang RP, Bilenberg N, Bjarnadottir G, Capron C, De Pauw SSW, Dias P, Dobrean A, Doepfner M, Duyme M, Eapen V, Erol N, Esmaeili EM, Ezpeleta L, Frigerio A, Goncalves MM, Gudmundsson HS, Jeng SF, Jetishi P, Jusiene R, Kim YA, Kristensen S, Lecannelier F, Leung PWL, Liu JH, Montirosso R, Oh KJ, Plueck J, Pomalima R, Shahini M, Silva JR, Simsek Z, Sourander A, Valverde J, Van Leeuwen KG, Woo BSC, Wu YT, Zubrick SR, Verhulst FC (2010) Preschool psychopathology reported by parents in 23 societies: testing the seven-syndrome model of the child behavior checklist for ages 1.5–5. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 49(12):1215–1224. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2010.08.019
Obel C, Heiervang E, Rodriguez A, Heyerdahl S, Smedje H, Sourander A, Gudmundsson OO, Clench-Aas J, Christensen E, Heian F, Mathiesen KS, Magnusson P, Njaovik U, Koskelainen M, Ronning JA, Stormark KM, Olsen J (2004) The strengths and difficulties questionnaire in the Nordic countries. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 13:32–39. doi:10.1007/s00787-004-2006-2
Rescorla L, Achenbach T, Ivanova MY, Dumenci L, Almqvist F, Bilenberg N, Bird H, Chen W, Dobrean A, Dopfner M, Erol N, Fombonne E, Fonseca A, Frigerio A, Grietens H, Hannesdottir H, Kanbayashi Y, Lambert M, Larsson B, Leung P, Liu XC, Minaei A, Mulatu MS, Novik TS, Oh KJ, Roussos A, Sawyer M, Simsek Z, Steinhausen HC, Weintraub S, Weisz J, Metzke CW, Wolanczyk T, Yang HJ, Zilber N, Zukauskiene R, Verhulst F (2007) Behavioral and emotional problems reported by parents of children ages 6 to 16 in 31 societies. J Emot Behav Disord 15(3):130–142
Kristensen S, Henriksen TB, Bilenberg N (2010) The child behavior checklist for ages 1.5–5 (CBCL/11/2-5): assessment and analysis of parent- and caregiver-reported problems in a population-based sample of Danish preschool children. Nord J Psychiatry 64(3):203–209. doi:10.3109/08039480903456595
Angold A, Costello EJ, Erkanli A (1999) Comorbidity. J Child Psychol Psychiatry Allied Discip 40(1):57–87
Caron C, Rutter M (1991) Comorbidity in child psychopathology. Concepts, issues and research strategies. J Child Psychol Psychiatry Allied Discip 32(7):1063–1080. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.1991.tb00350.x
Moffitt TE, Harrington H, Caspi A, Kim-Cohen J, Goldberg D, Gregory AM, Poulton R (2007) Depression and generalized anxiety disorder—cumulative and sequential comorbidity in a birth cohort followed prospectively to age 32 years. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64(6):651–660. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.64.6.651
Strickland J, Keller J, Lavigne JV, Gouze K, Hopkins J, LeBailly S (2011) The structure of psychopathology in a community sample of preschoolers. J Abnorm Child Psychol 39(4):601–610. doi:10.1007/s10802-011-9487-5
Sterba SK, Copeland W, Egger HL, Costello EJ, Erkanli A, Angold A (2010) Longitudinal dimensionality of adolescent psychopathology: testing the differentiation hypothesis. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 51(8):871–884. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2010.02234.x
Lahey BB, Rathouz PJ, Van Hulle C, Urbano RC, Krueger RF, Applegate B, Garriock HA, Chapman DA, Waldman ID (2008) Testing structural models of DSM-IV symptoms of common forms of child and adolescent psychopathology. J Abnorm Child Psychol 36(2):187–206. doi:10.1007/s10802-007-9169-5
Trosper SE, Whitton SW, Brown TA, Pincus DB (2012) Understanding the latent structure of the emotional disorders in children and adolescents. J Abnorm Child Psychol 40(4):621–632. doi:10.1007/s10802-011-9582-7
Keenan K, Wakschlag LS, Danis B, Hill C, Humphries M, Duax J, Donald R (2007) Further evidence of the reliability and validity of DSM-IV ODD and CD in preschool children. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 46(4):457–468. doi:10.1097/CHI.0b013e31803062d3
Kim-Cohen J, Arseneault L, Caspi A, Tomas MP, Taylor A, Moffitt TE (2005) Validity of DSM-IV conduct disorder in 4 1/2 5-year-old children: a longitudinal epidemiological study. Am J Psychiatry 162(6):1108–1117
Burke JD, Loeber R, Birmaher B (2002) Oppositional defiant disorder and conduct disorder: a review of the past 10 years, part II. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 41(11):1275–1293. doi:10.1097/01.chi.0000024839.60748.e8
Lewinsohn PM, Holm-Denoma JM, Gau JM, Joiner TE, Striegel-Moore R, Bear P, Lamoureux B (2005) Problematic eating and feeding behaviors of 36-month-old children. Int J Eat Disord 38(3):208–219
Carnell S, Haworth CMA, Plomin R, Wardle J (2008) Genetic influence on appetite in children. Int J Obes 32(10):1468–1473. doi:10.1038/ijo.2008.127
Frayling TM, Timpson NJ, Weedon MN, Zeggini E, Freathy RM, Lindgren CM, Perry JRB, Elliott KS, Lango H, Rayner NW, Shields B, Harries LW, Barrett JC, Ellard S, Groves CJ, Knight B, Patch AM, Ness AR, Ebrahim S, Lawlor DA, Ring SM, Ben-Shlomo Y, Jarvelin MR, Sovio U, Bennett AJ, Melzer D, Ferrucci L, Loos RJF, Barroso I, Wareham NJ, Karpe F, Owen KR, Cardon LR, Walker M, Hitman GA, Palmer CNA, Doney ASF, Morris AD, Smith GD, Hattersley AT, McCarthy MI, Wellcome Trust Case C (2007) A common variant in the FTO gene is associated with body mass index and predisposes to childhood and adult obesity. Science 316(5826):889–894. doi:10.1126/science.1141634
Larsson JO, Bergman LR, Earls F, Rydelius PA (2004) Behavioral profiles in 4-5 year-old children: normal and pathological variants. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 35(2):143–162
Wilens TE, Biederman J, Brown S, Tanguay S, Monuteaux MC, Blake C, Spencer TJ (2002) Psychiatric comorbidity and functioning in clinically referred preschool children and school-age youths with ADHD. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 41(3):262–268
Neuman RJ, Heath A, Reich W, Bucholz KK, Madden PAF, Sun LW, Todd RD, Hudziak JJ (2001) Latent class analysis of ADHD and comorbid symptoms in a population sample of adolescent female twins. J Child Psychol Psychiatry Allied Discip 42(7):933–942
Moffitt TE (1993) Adolescent-limited and life-course persistent antisocial behavior. A developmental taxonomy. Psychol Rev 100(4):674–701
Neuman RJ, Todd RD, Heath AC, Reich W, Hudziak JJ, Bucholz KK, Madden PAF, Begleiter H, Porjesz B, Kuperman S, Hesselbrock V, Reich T (1999) Evaluation of ADHD typology in three contrasting samples: a latent class approach. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 38(1):25–33. doi:10.1097/00004583-199901000-00016
Foley DL, Rowe R, Maes H, Silberg J, Eaves L, Pickles A (2008) The relationship between separation anxiety and impairment. J Anxiety Disord 22(4):635–641. doi:10.1016/j.janxdis.2007.06.002
Kessler RC (2003) The impairments caused by social phobia in the general population: implications for intervention. Acta Psychiatry Scand 108:19–27
Ranta K, Kaltiala-Heino R, Rantanen P, Marttunen M (2009) Social phobia in Finnish general adolescent population: prevalence, comorbidity, individual and family correlates, and service use. Depress Anxiety 26(6):528–536. doi:10.1002/da.20422
Ruscio AM, Brown TA, Chiu WT, Sareen J, Stein MB, Kessler RC (2008) Social fears and social phobia in the USA: results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Psychol Med 38(1):15–28. doi:10.1017/s0033291707001699
Acknowledgments
Grants 170449/V50, 190622/V50, 185760/V50, and 175309/V50 from the Research Council of Norway and Grant 4396 from the Liaison Committee between the Central Norway RHA and NTNU funded this research.
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wichstrøm, L., Berg-Nielsen, T.S. Psychiatric disorders in preschoolers: the structure of DSM-IV symptoms and profiles of comorbidity. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 23, 551–562 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-013-0486-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-013-0486-7