Abstract
Goal models represent interests, intentions, and strategies of different stakeholders. Reasoning about the goals of a system unavoidably involves the transformation of unclear stakeholder requirements into goal-oriented models. The ability to validate goal models would support the early detection of unclear requirements, ambiguities, and conflicts. In this paper, we propose a novel validation approach based on the Goal-oriented Requirement Language (GRL) to check the correctness of GRL goal models through statistical analyses of data collected from generated questionnaires. System stakeholders (e.g., customers, shareholders, and managers) may have different objectives, interests, and priorities. Stakeholder conflicts arise when the needs of some group of stakeholder compromise the expectations of some other group(s) of stakeholders. Our proposed approach allows for early detection of potential conflicts amongst intervening stakeholders of the system. In order to illustrate and demonstrate the feasibility of the approach, we apply it to a case study of a GRL model describing the fostering of the relationship between the university and its alumni. The approach brings unique benefits over the state of the art and is complementary to existing validation approaches.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhigbe O, Alhaj M, Amyot D, Badreddin O, Braun E, Cartwright N, Richards G, Mussbacher G (2014) Creating quantitative goal models: governmental experience. In: 33rd international conference on conceptual modeling (ER’14), lecture notes in computer science, vol 8824. Springer, Berlin, pp 466–473
Almeida C, Goulão M, Araújo J A systematic comparison of i* modelling tools based on syntactic and well-formedness rules. In: Castro et al. (eds) Proceedings of the 6th international i* workshop 2013, Valencia, Spain, June 17–18, 2013, CEUR workshop proceedings, vol 978. CEUR-WS.org, pp 43–48
Amyot D, Ghanavati S, Horkoff J, Mussbacher G, Peyton L, Yu E (2010) Evaluating goal models within the goal-oriented requirement language. Int J Intell Syst 25:841–877. doi:10.1002/int.v25:8
Amyot D, Horkoff J, Gross D, Mussbacher G (2009) A lightweight GRL profile for i* modeling. In: Proceedings of the ER 2009 workshops (CoMoL, ETheCoM, FP-UML, MOST-ONISW, QoIS, RIGiM, SeCoGIS) on advances in conceptual modeling—challenging perspectives, ER ’09, pp 254–264. Springer, Berlin. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-04947-7_31
Amyot D, Rashidi-Tabrizi R, Mussbacher G, Kealey J, Tremblay E, Horkoff J (2013) Improved GRL modeling and analysis with jUCMNav 5. In: Castro et al. (eds) Proceedings of the 6th international i* workshop 2013, Valencia, Spain, June 17–18, 2013, CEUR workshop proceedings, vol 978. CEUR-WS.org, pp 137–139
Ayala CP, Cares C, Carvallo JP, Grau G, Haya M, Salazar G, Franch X, Mayol E, Quer C (2005) A comparative analysis of i*-based agent-oriented modeling languages. In: Proceedings of the 17th international conference on software engineering and knowledge engineering (SEKE’2005), Taipei, Taiwan, Republic of China, July 14–16, pp 43–50
Brown MB, Forsythe AB (1974) Robust tests for the equality of variances. J Am Stat Assoc 69(346):364–367. doi:10.1080/01621459.1974.10482955
Castro J, Horkoff J, Maiden NAM, Yu ESK (eds) (2013) Proceedings of the 6th international i* workshop 2013, Valencia, Spain, June 17–18, 2013, CEUR workshop proceedings, vol 978. CEUR-WS.org
Chung L, Nixon BA, Yu E, Mylopoulos J (1999) Non-functional requirements in software engineering. The Kluwer international series in software engineering. Kluwer Academic Publishers Group, Dordrecht
de Castro JB, Franch X, Mylopoulos J, Yu ESK (eds) (2011) Proceedings of the 5th international i* workshop 2011, Trento, Italy, August 28–29, 2011, CEUR workshop proceedings, vol 766. CEUR-WS.org
Espada P, Goulão M, Araújo J (2013) A framework to evaluate complexity and completeness of KAOS goal models. In: Salinesi C, Norrie MC, Pastor O (eds) CAiSE. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 7908. Springer, Berlin, pp 562–577
Fernandes PCB, Guizzardi RSS, Guizzardi G (2011) Using goal modeling to capture competency questions in ontology-based systems. JIDM 2(3):527–540
Fisher R (1925) Statistical methods for research workers. Cosmo study guides. Cosmo Publications, New Delhi
Franch X (2009) A method for the definition of metrics over i* models. In: van Eck P, Gordijn J, Wieringa R (eds) CAiSE. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 5565. Springer, Berlin, pp 201–215
Games PA, Howell JF (1976) Pairwise multiple comparison procedures with unequal n’s and/or variances: a monte carlo study. J Educ Behav Stat 1(2):113–125
Giorgini P, Mylopoulos J, Sebastiani R (2005) Goal-oriented requirements analysis and reasoning in the tropos methodology. Eng Appl Artif Intell 18:159–171. doi:10.1016/j.engappai.2004.11.017
Gosset WS (1908) The probable error of a mean. Biometrika 6(1):1–25 (Originally published under the pseudonym “Student”)
Hassine J, Amyot D (2013) GRL model validation: a statistical approach. In: Haugen Ø, Reed R, Gotzhein R (eds) System analysis and modeling: theory and practice. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 7744. Springer, Berlin, pp 212–228. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-36757-1_13
Hesse-Biber SN, Leavy P (2006) The practice of qualitative research. SAGE, Beverley Hills
Horkoff J, Barone D, Jiang L, Yu E, Amyot D, Borgida A, Mylopoulos J (2013) Strategic business modeling—representation and reasoning. Softw Syst Model 13(3):1015–1041
Horkoff J, Yu ESK (2013) Comparison and evaluation of goal-oriented satisfaction analysis techniques. Requir Eng 18(3):199–222
Horkoff J, Yu ESK (2008) Qualitative, interactive, backward analysis of i* models. In: de Castro JB, Franch X, Perini A, Yu ESK (eds) Proceedings of the 3rd international i* workshop (iStar), Recife, Brazil, CEUR workshop proceedings, vol 322. CEUR-WS.org, pp 43–46
Horkoff J, Yu E, Liu L (2006) Analyzing trust in technology strategies. In: Proceedings of the 2006 international conference on privacy, security and trust: bridge the gap between PST technologies and business services, PST ’06. ACM, New York, pp 9:1–9:12. doi:10.1145/1501434.1501446
Iarossi G (2006) The power of survey design: a user’s guide for managing surveys, interpreting results, and influencing respondents. Stand Alone Series. World Bank http://books.google.tn/books?id=x964AAAAIAAJ
IBM (2012) SPSS software http://www-01.ibm.com/software/analytics/spss/
ITU-T (2012) Recommendation Z.151 (10/12) user requirements notation (URN) language definition, Geneva, Switzerland. http://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-Z.151/en
Jamieson S (2004) Likert scales: how to (ab)use them. Med Educ 38(12):1217–1218. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2929.2004.02012.x
jUCMNav (2014) jUCMNav Project, v6.0.0 (tool, documentation, and meta-model). http://softwareengineering.ca/jucmnav
Jureta IJ, Faulkner S, Schobbens PY (2008) Clear justification of modeling decisions for goal-oriented requirements engineering. Requir Eng 13:87–115. doi:10.1007/s00766-007-0056-y
Jureta I, Mylopoulos J, Faulkner S (2009) Analysis of multi-party agreement in requirements validation. In: RE. IEEE Computer Society, pp 57–66
Kassab M (2013) An integrated approach of AHP and NFRs framework. In: Wieringa R, Nurcan S, Rolland C, Cavarero JL (eds) RCIS, pp 1–8. IEEE
Knapp TR (1990) Treating ordinal scales as interval scales: an attempt to resolve the controversy. Nurs Res 39(2):121–123
Labovitz S (1967) Some observations on measurement and statistics. Social Forces 46(2):151–160. doi:10.2307/2574595
Levene H (1960) Robust tests for equality of variances. In: Olkin I (ed) Contributions to probability and statistics: essays in honor of Harold Hotelling. Stanford University Press, Palo Alto, pp 278–292
Liaskos S, Jalman R, Aranda J (2012) On eliciting contribution measures in goal models. In: Heimdahl MPE, Sawyer P (eds) RE. IEEE, pp 221–230
Likert R (1932) A technique for the measurement of attitudes. Arch Psychol 140(140):1–55
Mirbel I, Villata S (2012) Enhancing goal-based requirements consistency: an argumentation-based approach. In: Fisher M, van der Torre L, Dastani M, Governatori G (eds) CLIMA. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 7486. Springer, Berlin, pp 110–127
Moody DL, Heymans P, Raimundas Matulevičius R (2010) Visual syntax does matter: improving the cognitive effectiveness of the i* visual notation. Requir Eng 15(2):141–175. doi:10.1007/s00766-010-0100-1
Munro S, Liaskos S, Aranda J (2011) The mysteries of goal decomposition. In: de Castro et al. (eds) Proceedings of the 5th international i* workshop 2011, Trento, Italy, August 28–29, 2011, CEUR workshop proceedings, vol 766. CEUR-WS.org, pp. 49–54
Mussbacher G, Amyot D, Heymans P (2011) Eight deadly sins of GRL. In: de Castro et al. (eds) Proceedings of the 5th international i* workshop 2011, Trento, Italy, August 28–29, 2011, CEUR workshop proceedings, vol 766. CEUR-WS.org, pp 2–7
Norman G (2010) Likert scales, levels of measurement and the “laws” of statistics. Adv Health Sci Educ 15(5):625–632. doi:10.1007/s10459-010-9222-y
Robinson WN (1989) Integrating multiple specifications using domain goals. In: Proceedings of the 5th international workshop on software specification and design, IWSSD ’89. ACM, New York, pp 219–226. doi:10.1145/75199.75232
Robinson WN (1990) Negotiation behavior during requirements specification. In: Proceedings of the 12th international conference on software engineering, ICSE ’90. IEEE Computer Society Press, Los Alamitos, pp. 268–276.http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=100296.100335
Saaty TL (1990) How to make a decision: the analytic hierarchy process. Eur J Oper Res 48(1):9–26. doi:10.1016/0377-2217(90)90057-I
Schuman H, Presser S (1981) Questions and answers in attitude surveys: experiments on question form, wording, and context. Academic Press, London
Shamsaei A, Amyot D, Pourshahid A, Yu E, Mussbacher G, Tawhid R, Braun E, Cartwright N (2013) An approach to specify and analyze goal model families. In: Haugen Ø, Reed R, Gotzhein R (eds) System analysis and modeling: theory and practice. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 7744. Springer, Berlin, pp 34–52. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-36757-1_13
StatSoft (2012) Electronic statistics textbook. Tulsa, OK: Statsoft http://www.statsoft.com/textbook/
Tabachnick BG, Fidell LS (2006) Using multivariate statistics, 5th edn. Allyn & Bacon Inc, Needham Heights
Tukey J (1977) Exploratory data analysis. Addison-Wesley series in behavioral science. Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Reading
van Lamsweerde A (2008) Requirements engineering: from craft to discipline. In: Harrold MJ, Murphy GC (eds) Proceedings of the 16th ACM SIGSOFT international symposium on foundations of software engineering (FSE 2008), Atlanta, GA. ACM, New York, pp 238–249
Vinay S, Aithal S, Sudhakara G (2012) A quantitative approach using goal-oriented requirements engineering methodology and analytic hierarchy process in selecting the best alternative. In: Kumar AM, Kumar TVS (eds) Proceedings of international conference on advances in computing, advances in intelligent systems and computing, vol 174. Springer, India, pp. 441–454. doi:10.1007/978-81-322-0740-5_54
Welch BL (1947) The generalization of ‘student’s’ problem when several different population variances are involved. Biometrika 34(1–2):28–35. doi:10.1093/biomet/34.1-2.28
Wright HK, Kim M, Perry DE (2010) Validity concerns in software engineering research. In: Roman GC, Sullivan KJ (eds) FoSER. ACM, New York, pp 411–414
Yu ESK (1997) Towards modeling and reasoning support for early-phase requirements engineering. In: Proceedings of the 3rd IEEE international symposium on requirements engineering., RE ’97IEEE computer society, Washington, DC, pp 226–235
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the support provided by the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals for funding this work through project No. IN111017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
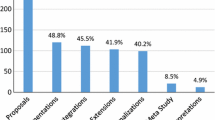
Appendix: SPSS generated histograms
Appendix: SPSS generated histograms
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassine, J., Amyot, D. A questionnaire-based survey methodology for systematically validating goal-oriented models. Requirements Eng 21, 285–308 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00766-015-0221-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00766-015-0221-7