Abstract
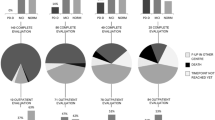
Normal cognition is an established selection criteria for subthalamic (STN) deep brain stimulation (DBS) in Parkinson’s disease (PD), while concern has been raised as to aggravated cognitive decline in PD patients following STN-DBS. The present longterm study investigates cognitive status in all patients (n = 104) suffering from PD, who were treated via continuous bilateral STN-DBS between 1997 and 2006 in a single institution. Preoperative neuropsychological results were available in 79/104 of the patients. Thirty-seven of these patients were additionally assessed after 6.3 ± 2.2 years (range 3.6–10.5 years) postsurgery via neuropsychological and motor test batteries, classifying cognitive conditions according to established criteria. At DBS-surgery patients, available for longterm follow-up (n = 37; mean age 67.6 ± 6.9 years, mean disease duration 11.3 ± 4.1 years), showed no (24.3%; 9/37) or mild preoperative cognitive impairment (MCI, 75.7%; 28/37). Postoperatively (mean disease duration: 17.1 ± 5.1 years), 19% of the patients (7/37) had no cognitive impairment, while 41% of the patients presented with either MCI or dementia (15/37, respectively). Preoperative MCI correlated with conversion to dementia by trend. Overall, STN-DBS-treated patients deteriorated by 1.6/140 points/year in the Mattis dementia rating scale. Disease duration, but not age, at DBS-surgery negatively correlated with postoperative cognitive decline and positively correlated with conversion to dementia. This observational, “real-life” study provides longterm results of cognitive decline in STN-DBS-treated patients with presurgical MCI possibly predicting the conversion to dementia. Although, the present data is lacking a control group of medically treated PD patients, comparison with other studies on cognition and PD do not support a disease-modifying effect of STN-DBS on cognitive domains.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BAI:
-
Beck Anxiety Inventory
- BDI:
-
Beck Depression Inventory
- BPRS:
-
Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale
- BRMS:
-
Bech-Rafaelsen-Mania Scale
- DBS:
-
Deep brain stimulation
- LED:
-
Levodopa equivalent dosage
- MADRS:
-
Montgomery and Asberg Depression Rating Scale
- mMDRS:
-
Modified Mattis Dementia Rating Scale
- MDMQ:
-
Multidimensional Mood State Questionnaire
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- PD-D:
-
Parkinson’s disease with dementia
- PD-MCI:
-
Parkinson’s disease with mild cognitive impairment
- PD-NC:
-
Parkinson’s disease with normal cognition
- PDQ 39:
-
Parkinson’s Disease Questionnaire
- QoL:
-
Quality of life
- RBD:
-
REM sleep behaviour disorder
- RAVLT:
-
Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test
- SF 36:
-
36-item Short-Form Health Survey
- SHAPS-D:
-
Snaith–Hamilton-Pleasure-Scale
- STN:
-
Nucleus subthlamicus
- TMT:
-
Trail Making Test
- UPDRSm:
-
Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale, motor subscore
References
Aarsland D, Kurz MW (2010) The epidemiology of dementia associated with Parkinson disease. J Neurol Sci 289(1–2):18–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2009.08.034
Aarsland D, Andersen K, Larsen JP, Lolk A, Nielsen H, Kragh-Sorensen P (2001) Risk of dementia in Parkinson’s disease: a community-based, prospective study. Neurology 56(6):730–736
Aarsland D, Andersen K, Larsen JP, Lolk A, Kragh-Sorensen P (2003) Prevalence and characteristics of dementia in Parkinson disease: an 8-year prospective study. Arch Neurol 60(3):387–392
Aarsland D, Zaccai J, Brayne C (2005) A systematic review of prevalence studies of dementia in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 20(10):1255–1263. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.20527
Aarsland D, Bronnick K, Williams-Gray C, Weintraub D, Marder K, Kulisevsky J, Burn D, Barone P, Pagonabarraga J, Allcock L, Santangelo G, Foltynie T, Janvin C, Larsen JP, Barker RA, Emre M (2010) Mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson disease: a multicenter pooled analysis. Neurology 75(12):1062–1069. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181f39d0e
Anang JB, Gagnon JF, Bertrand JA, Romenets SR, Latreille V, Panisset M, Montplaisir J, Postuma RB (2014) Predictors of dementia in Parkinson disease: a prospective cohort study. Neurology 83(14):1253–1260. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000000842
Anang JB, Nomura T, Romenets SR, Nakashima K, Gagnon JF, Postuma RB (2017) Dementia predictors in parkinson disease: a validation study. J Parkinsons Dis 7(1):159–162. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-160925
Aybek S, Gronchi-Perrin A, Berney A, Chiuve SC, Villemure JG, Burkhard PR, Vingerhoets FJ (2007) Long-term cognitive profile and incidence of dementia after STN-DBS in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 22(7):974–981. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21478
Balzer-Geldsetzer M, Costa AS, Kronenburger M, Schulz JB, Roske S, Spottke A, Wullner U, Klockgether T, Storch A, Schneider C, Riedel O, Wittchen HU, Seifried C, Hilker R, Schmidt N, Witt K, Deuschl G, Mollenhauer B, Trenkwalder C, Liepelt-Scarfone I, Graber-Sultan S, Berg D, Gasser T, Kalbe E, Bodden M, Oertel WH, Dodel R (2011) Parkinson’s disease and dementia: a longitudinal study (DEMPARK). Neuroepidemiology 37(3–4):168–176. https://doi.org/10.1159/000331490
Bech P, Bolwig TG, Kramp P, Rafaelsen OJ (1979) The Bech–Rafaelsen Mania Scale and the Hamilton Depression Scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand 59(4):420–430
Beck AT (1987) Beck Depression Inventory: manual. Psychological Corporation, San Antonia
Beck AT, Epstein N, Brown G, Steer RA (1988) An inventory for measuring clinical anxiety: psychometric properties. J Consult Clin Psychol 56(6):893–897
Bullinger M (1996) Assessment of health related quality of life with the SF-36 health survey. Rehabilitation (Stuttg) 35(3):XVII–XXVII (quiz XXVII–XXIX)
Castrioto A, Lozano AM, Poon YY, Lang AE, Fallis M, Moro E (2011) Ten-year outcome of subthalamic stimulation in Parkinson disease: a blinded evaluation. Arch Neurol 68(12):1550–1556. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneurol.2011.182
Cereda E, Cilia R, Klersy C, Siri C, Pozzi B, Reali E, Colombo A, Zecchinelli AL, Mariani CB, Tesei S, Canesi M, Sacilotto G, Meucci N, Zini M, Isaias IU, Barichella M, Cassani E, Goldwurm S, Pezzoli G (2016) Dementia in Parkinson’s disease: is male gender a risk factor? Parkinsonism Relat Disord 26:67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2016.02.024
Coelho M, Ferreira JJ (2012) Late-stage Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurol 8(8):435–442. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2012.126
Combs HL, Folley BS, Berry DT, Segerstrom SC, Han DY, Anderson-Mooney AJ, Walls BD, van Horne C (2015) Cognition and depression following deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus and globus pallidus pars internus in Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis. Neuropsychol Rev 25(4):439–454. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-015-9302-0
Daniels C, Krack P, Volkmann J, Pinsker MO, Krause M, Tronnier V, Kloss M, Schnitzler A, Wojtecki L, Botzel K, Danek A, Hilker R, Sturm V, Kupsch A, Karner E, Deuschl G, Witt K (2010) Risk factors for executive dysfunction after subthalamic nucleus stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 25(11):1583–1589. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.23078
Deuschl G, Schade-Brittinger C, Krack P, Volkmann J, Schafer H, Botzel K, Daniels C, Deutschlander A, Dillmann U, Eisner W, Gruber D, Hamel W, Herzog J, Hilker R, Klebe S, Kloss M, Koy J, Krause M, Kupsch A, Lorenz D, Lorenzl S, Mehdorn HM, Moringlane JR, Oertel W, Pinsker MO, Reichmann H, Reuss A, Schneider GH, Schnitzler A, Steude U, Sturm V, Timmermann L, Tronnier V, Trottenberg T, Wojtecki L, Wolf E, Poewe W, Voges J (2006) A randomized trial of deep-brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 355(9):896–908
Domellof ME, Ekman U, Forsgren L, Elgh E (2015) Cognitive function in the early phase of Parkinson’s disease, a five-year follow-up. Acta Neurol Scand 132(2):79–88. https://doi.org/10.1111/ane.12375
Eggert K, Oertel W, Reichmann H (2012) Parkinsonsyndrome-Diagnostik und Therapie. Leitlinien für Diagnostik und Therapie in der Neurologie. Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart
Emre M, Aarsland D, Brown R, Burn DJ, Duyckaerts C, Mizuno Y, Broe GA, Cummings J, Dickson DW, Gauthier S, Goldman J, Goetz C, Korczyn A, Lees A, Levy R, Litvan I, McKeith I, Olanow W, Poewe W, Quinn N, Sampaio C, Tolosa E, Dubois B (2007) Clinical diagnostic criteria for dementia associated with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 22(12):1689–1707. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21507 (quiz 1837)
Fahn S, Elton R, Members of the UPDRS Development Committee (1987) The unified parkinson’s disease rating scale. In: Fahn S, Marsden CD, Calne DB, Goldstein M (eds) Recent developments in parkinson’s disease, vol 2. McMellam Health Care Information, Florham Park, pp 153–163
Flemenbaum A, Zimmermann RL (1973) Inter- and intra-rater reliability of the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale. Psychol Rep 32(3):783–792
Hely MA, Reid WG, Adena MA, Halliday GM, Morris JG (2008) The Sydney multicenter study of Parkinson’s disease: the inevitability of dementia at 20 years. Mov Disord 23(6):837–844. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21956
Hoehn MM, Yahr MD (1967) Parkinsonism: onset, progression and mortality. Neurology 17(5):427–442
Kim HY (2014) Statistical notes for clinical researchers: nonparametric statistical methods: 2. Nonparametric methods for comparing three or more groups and repeated measures. Restor Dent Endod 39(4):329–332. https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.329
Kim HJ, Jeon BS, Paek SH, Lee KM, Kim JY, Lee JY, Kim HJ, Yun JY, Kim YE, Yang HJ, Ehm G (2014) Long-term cognitive outcome of bilateral subthalamic deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-014-7321-z
Lezak M (1995) Neuropsychological assessment. Oxford University Press, New York
Litvan I, Goldman JG, Troster AI, Schmand BA, Weintraub D, Petersen RC, Mollenhauer B, Adler CH, Marder K, Williams-Gray CH, Aarsland D, Kulisevsky J, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Burn DJ, Barker RA, Emre M (2012) Diagnostic criteria for mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease: movement disorder society task force guidelines. Mov Disord 27(3):349–356. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.24893
Marder K, Tang MX, Cote L, Stern Y, Mayeux R (1995) The frequency and associated risk factors for dementia in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Arch Neurol 52(7):695–701
Martinez-Martin P, Rodriguez-Blazquez C, Kurtis MM, Chaudhuri KR, Group NV (2011) The impact of non-motor symptoms on health-related quality of life of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 26(3):399–406. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.23462
Mattis S (1988) Dementia Rating Scale: professional manual. Psychological Assessment Resources, Odessa
Merola A, Zibetti M, Angrisano S, Rizzi L, Ricchi V, Artusi CA, Lanotte M, Rizzone MG, Lopiano L (2011) Parkinson’s disease progression at 30 years: a study of subthalamic deep brain-stimulated patients. Brain 134(Pt 7):2074–2084. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awr121
Merola A, Rizzi L, Artusi CA, Zibetti M, Rizzone MG, Romagnolo A, Bernardini A, Lanotte M, Lopiano L (2014) Subthalamic deep brain stimulation: clinical and neuropsychological outcomes in mild cognitive impaired parkinsonian patients. J Neurol 261(9):1745–1751. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-014-7414-8
Montgomery SA, Asberg M (1979) A new depression scale designed to be sensitive to change. Br J Psychiatry 134:382–389
Odekerken VJ, Boel JA, Schmand BA, de Haan RJ, Figee M, van den Munckhof P, Schuurman PR, de Bie RM, Group Ns (2016) GPi vs STN deep brain stimulation for Parkinson disease: three-year follow-up. Neurology 86(8):755–761. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000002401
Pedersen KF, Larsen JP, Tysnes OB, Alves G (2017) Natural course of mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson disease: a 5-year population-based study. Neurology 88(8):767–774. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000003634
Perez-Lloret S, Negre-Pages L, Damier P, Delval A, Derkinderen P, Destee A, Meissner WG, Tison F, Rascol O, of the CSG (2017) L-DOPA-induced dyskinesias, motor fluctuations and health-related quality of life: the COPARK survey. Eur J Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13466
Peto V, Jenkinson C, Fitzpatrick R, Greenhall R (1995) The development and validation of a short measure of functioning and well being for individuals with Parkinson’s disease. Qual Life Res 4(3):241–248
Pigott K, Rick J, Xie SX, Hurtig H, Chen-Plotkin A, Duda JE, Morley JF, Chahine LM, Dahodwala N, Akhtar RS, Siderowf A, Trojanowski JQ, Weintraub D (2015) Longitudinal study of normal cognition in Parkinson disease. Neurology 85(15):1276–1282. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000002001
Rahman S, Griffin HJ, Quinn NP, Jahanshahi M (2008) Quality of life in Parkinson’s disease: the relative importance of the symptoms. Mov Disord 23(10):1428–1434. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21667
Rizzone MG, Fasano A, Daniele A, Zibetti M, Merola A, Rizzi L, Piano C, Piccininni C, Romito LM, Lopiano L, Albanese A (2014) Long-term outcome of subthalamic nucleus DBS in Parkinson’s disease: from the advanced phase towards the late stage of the disease?. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.01.012
Schrag A, Jahanshahi M, Quinn N (2000) What contributes to quality of life in patients with Parkinson’s disease? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 69(3):308–312
Schuepbach WM, Rau J, Knudsen K, Volkmann J, Krack P, Timmermann L, Halbig TD, Hesekamp H, Navarro SM, Meier N, Falk D, Mehdorn M, Paschen S, Maarouf M, Barbe MT, Fink GR, Kupsch A, Gruber D, Schneider GH, Seigneuret E, Kistner A, Chaynes P, Ory-Magne F, Brefel Courbon C, Vesper J, Schnitzler A, Wojtecki L, Houeto JL, Bataille B, Maltete D, Damier P, Raoul S, Sixel-Doering F, Hellwig D, Gharabaghi A, Kruger R, Pinsker MO, Amtage F, Regis JM, Witjas T, Thobois S, Mertens P, Kloss M, Hartmann A, Oertel WH, Post B, Speelman H, Agid Y, Schade-Brittinger C, Deuschl G (2013) Neurostimulation for Parkinson’s disease with early motor complications. N Engl J Med 368(7):610–622. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1205158
Smeding HM, Speelman JD, Koning-Haanstra M, Schuurman PR, Nijssen P, van Laar T, Schmand B (2006) Neuropsychological effects of bilateral STN stimulation in Parkinson disease: a controlled study. Neurology 66(12):1830–1836. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000234881.77830.66
Smeding HM, Speelman JD, Huizenga HM, Schuurman PR, Schmand B (2011) Predictors of cognitive and psychosocial outcome after STN DBS in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 82(7):754–760. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2007.140012
Snaith RP, Hamilton M, Morley S, Humayan A, Hargreaves D, Trigwell P (1995) A scale for the assessment of hedonic tone the Snaith–Hamilton Pleasure Scale. Br J Psychiatry 167(1):99–103
Steyer R, Schwenkmezger P, Notz P, Eid M (1997) Der Mehrdimensionale Befindlichkeitsfragebogen (MDBF). Hogrefe, Göttingen
Volkmann J, Daniels C, Witt K (2010) Neuropsychiatric effects of subthalamic neurostimulation in Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurol 6(9):487–498. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2010.111
Weaver FM, Follett K, Stern M, Hur K, Harris C, Marks WJ Jr, Rothlind J, Sagher O, Reda D, Moy CS, Pahwa R, Burchiel K, Hogarth P, Lai EC, Duda JE, Holloway K, Samii A, Horn S, Bronstein J, Stoner G, Heemskerk J, Huang GD, Group CSPS (2009) Bilateral deep brain stimulation vs best medical therapy for patients with advanced Parkinson disease: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 301(1):63–73. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2008.929
Williams A, Gill S, Varma T, Jenkinson C, Quinn N, Mitchell R, Scott R, Ives N, Rick C, Daniels J, Patel S, Wheatley K, Group PSC (2010) Deep brain stimulation plus best medical therapy versus best medical therapy alone for advanced Parkinson’s disease (PD SURG trial): a randomised, open-label trial. Lancet Neurol 9(6):581–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70093-4
Witt K, Daniels C, Reiff J, Krack P, Volkmann J, Pinsker MO, Krause M, Tronnier V, Kloss M, Schnitzler A, Wojtecki L, Botzel K, Danek A, Hilker R, Sturm V, Kupsch A, Karner E, Deuschl G (2008) Neuropsychological and psychiatric changes after deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease: a randomised, multicentre study. Lancet Neurol 7(7):605–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70114-5
York MK, Dulay M, Macias A, Levin HS, Grossman R, Simpson R, Jankovic J (2008) Cognitive declines following bilateral subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79(7):789–795. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2007.118786
Zangaglia R, Pacchetti C, Pasotti C, Mancini F, Servello D, Sinforiani E, Cristina S, Sassi M, Nappi G (2009) Deep brain stimulation and cognitive functions in Parkinson’s disease: a three-year controlled study. Mov Disord 24(11):1621–1628. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.22603
Zangaglia R, Pasotti C, Mancini F, Servello D, Sinforiani E, Pacchetti C (2012) Deep brain stimulation and cognition in Parkinson’s disease: an eight-year follow-up study. Mov Disord 27(9):1192–1194. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.25047
Acknowledgements
We thank our patients for their continued support of our work.
Funding
University Medicine Berlin, Charité.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
DG has received honoraria for speaking from Medtronic, outside the submitted work. AAK is a consultant to Boston Scientific and has received honoraria for speaking from Medtronic, Boston Scientific and Abbott, also grants from Medtronic, all outside the submitted work. GHS has received honoraria for speaking from Medtronic, and Boston Scientific, outside the submitted work. AK has received honoraria for speaking from Medtronic and Abbott, outside the submitted work. LC and UK declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gruber, D., Calmbach, L., Kühn, A.A. et al. Longterm outcome of cognition, affective state, and quality of life following subthalamic deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 126, 309–318 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-019-01972-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-019-01972-7