Summary.
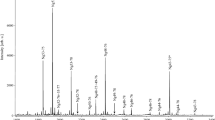
We examined the quantity and quality of G proteins in membrane preparations of post-mortem human brain, i.e. in parietal, temporal and occipital cortical regions, from normal subjects over age (17–89 years old) and with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in comparison with aged-matched controls. In normal aging, the immunoreactivities determined of Giα, Gqα and Gβ were inversely correlated with age. The function of G proteins was examined by photoaffinity GTP analogue [azidoanilido GTP (AAGTP)] labelling. AAGTP labelling to Gsα and Gi/oα, and the ratio of Gsα to Gi/oα AAGTP labelling showed no age-dependent changes. In AD compared to age-matched controls, there were no significant differences in the levels of GsHα, GsLα, Giα, Goα, Gqα and Gβ subunits. Functional effects of G proteins, however, as measured by AAGTP labelling to Gsα, but not to Gi/oα, was significantly decreased in AD compared to controls in the parietal and temporal cortex, but not in the occipital cortex. These results suggest that the disturbances of post-receptor trans-membrane signalling in AD can be attributed to functional changes of Gsα, and these are independent of alterations in the level for those proteins in normal aging.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hashimoto, E., Ozawa, H., Saito, T. et al. Impairment of Gsα function in human brain cortex of Alzheimer’s disease: comparison with normal aging. J Neural Transm 111, 311–322 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-003-0089-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-003-0089-4