Abstract
Purpose
Spinal instrumented arthrodesis improves health-related quality of life (HRQOL), although mobility is impaired. This study evaluates activities of daily livings after thoracolumbosacroiliac arthrodesis for adult spinal deformity and patient satisfaction.
Methods
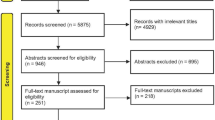
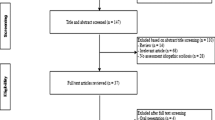
Fifty patients who underwent surgery filled self-administered questionnaires (1-year preoperative and postoperative conditions), and 36 patients (3 men and 33 women; mean age 71.4 years) participated in the study. Twenty-five activities, including weeding, snow shoveling, toilet activities, and sleeping postures, were examined. Spinal alignment with Scoliosis Research Society (SRS)—Schwab classification, HRQOL with SRS-22, complications, and patient satisfaction were evaluated. Pre- and postoperative conditions were statistically compared.
Results
Spinal alignment improved postoperatively. Comparison data revealed that strenuous activities, such as weeding and farm work, significantly deteriorated postoperatively in 42.1–87.5% patients. Other basic activities, excluding Western toilet usage, sleeping supine, laundry and kitchen chores, and changing jacket/pants, also significantly deteriorated in 21–88% patients. Only activities such as sleeping supine, standing upright, vacuuming, doing laundry, and reaching for objects placed at heights became possible with significant difference postoperatively among activities that could not be performed preoperatively. Light activities were continued, but strenuous activities were restricted. Nevertheless, the patient satisfaction rate was 70%. Six patients exhibited complications; however, none were dissatisfied with surgery outcomes. Instrumentation or proximal junctional failures were associated with at least one strenuous work activity.
Conclusions
Thoracolumbosacroiliac arthrodesis does not always improve activities postoperatively. Therefore, surgical indication for patients who continue activities preoperatively should be carefully decided.
Level of Evidence
Level 3.
Graphical abstract
These slides can be retrieved under Electronic Supplementary Material.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Glassman SD, Berven S, Bridwell K, Horton W, Dimar JR (2005) Correlation of radio-graphic parameters and clinical symptoms in adult scoliosis. Spine 30:682–688
Glassman SD, Bridwell K, Dimar JR, Horton W, Berven S, Schwab F (2005) The impact of positive sagittal balance in adult spinal deformity. Spine 30:2024–2029
Lafage V, Schwab F, Patel A, Hawkinson N, Farcy JP (2009) Pelvic tilt and truncal inclination: two key radiographic parameters in the setting of adults with spinal deformity. Spine 34:E599–E606. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181aad219
Schwab FJ, Smith VA, Biserni M, Gamez L, Farcy JP, Pagala M (2002) Adult scoliosis: a quantitative radiographic and clinical analysis. Spine 27:387–392
Schwab F, Patel A, Ungar B, Farcy JP, Lafage V (2010) Adult spinal deformity-postoperative standing imbalance: how much can you tolerate? An overview of key parameters in assessing alignment and planning corrective surgery. Spine 35:2224–2231. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181ee6bd4
Ishikawa Y, Miyakoshi N, Kasukawa Y, Hongo M, Shimada Y (2009) Spinal curvature and postural balance in patients with osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 20:2049–2053. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-009-0919-9
Ishikawa Y, Miyakoshi N, Hongo M, Kasukawa Y, Kudo D, Shimada Y (2017) Relationships among spinal mobility and sagittal alignment of spine and lower extremity to quality of life and risk of falls. Gait Posture 53:98–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2017.01.011
Kimura H, Fujibayashi S, Otsuki B, Takahashi Y, Nakayama T, Matsuda S (2016) Effects of lumbar stiffness after lumbar fusion surgery on activities of daily living. Spine 41:719–727. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.000000000000130
Hart RA, Marshall LM, Hiratzka SL, Kane MS, Volpi J, Hiratzka JR (2014) Functional limitations due to stiffness as a collateral impact of instrumented arthrodesis of the lumbar spine. Spine 39:E1468–E1474. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0000000000000595
Asher M, Min Lai S, Burton D, Manna B (2003) The reliability and concurrent validity of the scoliosis research society-22 patient questionnaire for idiopathic scoliosis. Spine 28:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.BRS.0000047634.95839.67
Kanda Y (2012) Investigation of the freely-available easy-to-use software “EZR” (Easy R) for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant 48:452–458. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2012.244
United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2017) World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision, Key Findings and Advance Tables. Working paper no. ESA/P/WP/248
Djurasovic M, Glassman SD (2007) Correlation of radiographic and clinical findings in spinal deformities. Neurosurg Clin N Am 18:223–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nec.2007.01.006
Schwab FJ, Blondel B, Bess S, Hostin R, Shaffrey CI, Smith JS, Boachie-Adjei O, Burton DC, Akbarnia BA, Mundis GM, Ames CP, Kebaish K, Hart RA, Farcy JP, Lafage V, International Spine Study Group (ISSG) (2013) Radiographical spinopelvic parameters and disability in the setting adult spinal deformity. Spine 38:803–812. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e318292b7b9
Schwab F, Ungar B, Blondel B, Buchowski J, Coe J, Deinlein D, DeWald C, Mehdian H, Shaffrey C, Tribus C, Lafage V (2012) Scoliosis Research Society—Schwab adult spinal deformity classification. Spine 37:1077–1082. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e31823e15e2
Terran J, Schwab F, Shaffrey CI, Smith JS, Devos P, Ames CP, Fu KM, Burton D, Hostin R, Klineberg E, Gupta M, Deviren V, Mundis G, Hart R, Bess S, Lafage V, International Spine Study Group (2013) The SRS-Schwab adult spinal deformity classification: assessment and clinical correlations based on a prospective operative and nonoperative cohort. Neurosurgery 73:559–568. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000000012
Smith JS, Klineberg E, Schwab F, Shaffrey CI, Moal B, Ames CP, Hostin R, Fu KM, Burton D, Akbarnia B, Gupta M, Hart R, Bess S, Lafage V, International Spine Study Group (2013) Change in classification grade by the SRS-Schwab adult spinal deformity classification predicts impact on health-related quality of life measures. Spine 38:1663–1671. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e31829ec563
Faraj SSA, van Hooff ML, Holewijn RM, Polly DW Jr, Haanstra TM, de Kleuver M (2017) Measuring outcomes in adult spinal deformity surgery: a systematic review to identify current strengths, weaknesses and gaps in patient-reported outcome measures. Eur Spine J 26:2084–2093. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-017-5125-4
Miyakoshi N, Hongo M, Kobayashi T, Abe T, Abe E, Shimada Y (2015) Improvement of spinal alignment and quality of life after corrective surgery for spinal kyphosis in patients with osteoporosis: a comparative study with non-operated patients. Osteoporos Int 26:2657–2664. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-015-3163-5
Miyakoshi N, Itoi E, Kobayashi M, Kodama H (2003) Impact of postural deformities and spinal mobility on quality of life in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 14:1007–1012. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-003-1510-4
Martín-Buitrago MP, Pizones J, Sánchez Pérez-Grueso FJ, Díaz Almirón M, Vila-Casademunt A, Obeid I, Alanay A, Kleinstück F, Acaroglu ER, Pellisé F, ESSG European Spine Study Group (2018) Impact of iliac instrumentation on the quality of life of patients with adult spine deformity. Spine 43:913–918. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0000000000002476
Sciubba DM, Scheer JK, Smith JS, Lafage V, Klineberg E, Gupta M, Mundis GM, Protopsaltis TS, Kim HJ, Hiratzka JR, Koski T, Shaffrey CI, Bess S, Hart RA, Ames CP, International Spine Study Group (ISSG) (2015) Which daily functions are most affected by stiffness following total lumbar fusion: comparison of upper thoracic and thoracolumbar proximal endpoints. Spine 40:1338–1344. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0000000000000968
Yoshida G, Boissiere L, Larrieu D, Bourghli A, Vital JM, Gille O, Pointillart V, Challier V, Mariey R, Pellisé F, Vila-Casademunt A, Perez-Grueso FJ, Alanay A, Acaroglu E, Kleinstück F, Obeid I, ESSG, European Spine Study Group (2017) Advantages and disadvantages of adult spinal deformity surgery and its impact on health-related quality of life. Spine 42:411–419. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0000000000001770
De la Garza Ramos R, Goodwin CR, Elder BD, Boah AO, Miller EK, Jain A, Klineberg EO, Ames CP, Neuman BJ, Kebaish KM, Lafage V, Schwab F, Bess S, Sciubba DM (2017) Preoperative functional status as a predictor of short-term outcome in adult spinal deformity surgery. J Clin Neurosci 39:118–123
Hongo M, Miyakoshi N, Shimada Y, Sinaki M (2012) Association of spinal curve deformity and back extensor strength in elderly women with osteoporosis in Japan and the United States. Osteoporos Int 23:1029–1034. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-011-1624-z
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishikawa, Y., Miyakoshi, N., Kobayashi, T. et al. Activities of daily living and patient satisfaction after long fusion for adult spinal deformity: a retrospective study. Eur Spine J 28, 1670–1677 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-019-05893-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-019-05893-7