Abstract
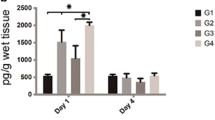
To assess the effect of magnetic field in experimental tendon injuries, ten clinically healthy adult indigenous dogs were divided into two equal groups (control and experimental). The left superficial digital flexor tendon was exposed and three windows of 6 mm thickness, 3 mm length, and 2 mm intervals were made under general anesthesia. In the experimental group, the dogs were subjected to a magnetic field of 6 × 800 G for 30 days. The tendon biopsy was collected from the site of operation on the postoperative day 30. Histomorphological changes indicated low rate of inflammatory cells, high rate of mature fibroblast, and increased normal collagen fibers, and these were better in the experimental group. The biomechanical test revealed that the tendons of the dogs in the experimental group were more resistant than tendons of the dogs in the control group. The result of this study indicated that magnetic field therapy reduced edema and local swelling, enhanced proliferation of fibroblasts, and regulated arrangement of collagen fibers, providing a good noninvasive physical therapy for tendinous injuries.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaron RK, Ciombor DM (1993) Therapeutic effects of electromagnetic fields in stimulation of connective tissue repair. J Cell Biochem 52(1):42–46
Agren MS, Engle MA, Mertz PM (1994) Collagenase during burn wound healing: influence of a hydrogel dressing and pulsed electrical stimulation. Plast Reconstr Surg 94:518–524
Anderson DE, Jean G (1996) Diagnosis and management of tendon disorders in cattle. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract 12:85–116
Bassett CA (1993) Beneficial effects of electromagnetic fields. J Cell Biochem 51(4):387–393
Bassett CA, Becker RO (1962) Generation of electric potentials by bone in response to mechanical stress. Science 137:1063–1064
Bassett CA, Chokshi HR, Hernandez E et al (1979) The effect of pulsing electromagnetic fields on cellular calcium and calcification of nonunions. In: Brighton CT, Black J, Pollack SR (eds) Electrical properties of bone and cartilage: experimental effects and clinical applications. Grune & Stratton, New York, pp 427–441
Farndale RW, Murray JC (1985) Pulsed electromagnetic fields promote collagen production in bone marrow fibroblasts via athermal mechanisms. Calcif Tissue Int 37:178–182
Fredericks DC, Nepola JV, Baker JT, Abbott J, Simon B (2000) Effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields on bone healing in a rabbit tibial osteotomy model. J Orthop Trauma 14:93–100
Gmitrov J, Ohkubo C, Okano H (2002) Effect of 0.25 T static magnetic field on microcirculation in rabbits. Bioelectromagnetics 23:224–229
Greenough CG (1996) The effect of pulsed electromagnetic fields on flexor tendon healing in the rabbit. J Hand Surg 21A:808–812
Inoue N, Ohnishi I, Chen D, Deitz LW, Schwardt JD, Chao EY (2002) Effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF) on late-phase osteotomy gap healing in a canine tibial model. J Orthop Res 20:1106–1114
James R, Kesturu G, Gary Balian A, Chhabra B (2008) Tendon: biology, biomechanics, repair, growth factors, and evolving treatment options. JHS 33:103–112
Kumar NA, Sharma A, Sharma K, Kumar S (2002) Carbon fibres and plasma-preserved tendon allografts for gap repair of flexor tendon in bovines: gross, microscopic and scanning electron microscopic observations. J Vet Med A 49:269–276
Linovitz RJ, Pathria M, Bernhardt M et al (2002) Combined magnetic fields accelerate and increase spine fusion: a double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled study. Spine 27:1383–1389
Macias MY, Battocletti JH, Sutton CH, Pintar FA, Maiman DJ (2000) Directed and enhanced neurite growth with pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation. Bioelectromagnetics 21(4):272–286
Mayrovitz HN, Groseclose EE (2005) Effects of static magnetic field of either polarity on skin microcirculation. Microvasc Res 69:24–27
Norton LA (1985) Pulsed electromagnetic field effects on chondroblast culture. Reconstr Surg Traumatol 19:70–86
Norton LA, Rovetti LA (1988) Calcium incorporation in cultured chondroblasts perturbed by electromagnetic field. J Orthop Res 6:559–566
Ramey DW, Kirschvink JL (1998) Effect of therapeutic magnetic warps on circulation in the third metacarpal region. AAEP Proc 44:272–274
Robotti E, Zimbler AG, Kenna D, Grossman JA (1999) The effect of pulsed electromagnetic fields on flexor tendon healing in chickens. J Hand Surg [Br] 24(1):56–58
Ryaby JT (1998) Clinical effects of electromanetic and electric fields on fracture healing. Clin Orthop Relat Res 355(Suppl):S205–S215
Saini NS, Roy NS, Bansal NS, Singh B, Simran PS (2002) A preliminary study on the effect of ultrasound therapy on the healing of surgically severed Achilles tendons in five dogs. J Vet Med A 49:321–328
Seiler JG III (2001) Flexor tendon repair. J Am Soc Surg Hand 1(3):177–190
Sharrard WJ (1990) A double-blind trial of pulsed electromagnetic fields for delayed union of tibial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg 72B:347–355
Steyn PE, Ramey DW, Kirschrink J, Uhring J (2000) Effect of a static magnetic field on blood flow to the metacarpus in horses. J Am-Vet-Med Assoc 217:874–877
Strauch B, Patel MK, Navarro JA, Berdichevsky M, Yu HL, Pilla AA (2007) Pulsed magnetic fields accelerate cutaneous wound healing in rats. Plast Reconstr Surg 120:425–430
Tepper OM, Callaghan MJ, Chang EI et al (2004) Electromagnetic fields increase in vitro and in vivo angiogenesis through endothelial release of FGF-2. FASEB J 18:1231–1233
Verma PRP, Khan AA, Dass LL, Eshan Md, Jha GJ (1983) Autogenous facial tendon grafting in buffalo calves: an experimental study. Indian Vet Med J 7:23–27
Yen-Patton GP, Patton WF, Beer DM, Jacobson BS (1988) Endothelial cell response to pulsed electromagnetic fields: stimulation of growth rate and angiogenesis in vitro. J Cell Physiol 134:37–46
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aliabadi, A., Dehghani, S.N., Farahmand, M. et al. Evaluation of the effect of static magnetic field in treatment of tendon injuries in dog. Comp Clin Pathol 22, 1057–1060 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-012-1525-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-012-1525-3