Abstract
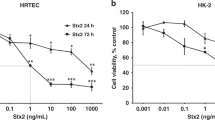
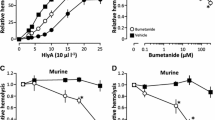
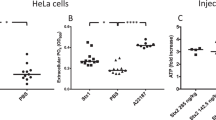
Postdiarrhea hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) is the most common cause of acute renal failure in children in Argentina. It is well established that Shiga toxin type 2 (Stx2) causes direct damage to glomerular endothelial cells and tubular epithelial cells, leading to a reduction in the water handling capacity of the kidney. In this study, we demonstrate that Stx2 and its B subunit (Stx2B) were able to inhibit water absorption across human renal tubular epithelial cell (HRTEC) monolayers without altering the short circuit current and the 3H-mannitol permeability. Quantitative evaluation of 14C-inulin transport across HRTEC monolayers showed a similar transport rate both before and after HRTEC treatment with Stx2 that confirmed the integrity of the paracellular pathway. Furthermore, Stx2 produced significant protein synthesis inhibition of HRTEC at concentrations as low as 0.001 ng/ml and 1 h of incubation, whereas Stx2B did not modify it at concentrations as high as 10,000 ng/ml and 6 h of incubation. Our findings suggest that whereas the action of Stx2 appears to be caused mainly by the inhibition of protein synthesis mediated by the A subunit, the binding of Stx2B subunit to the Gb3 receptor may affect the membrane mechanisms related to water absorption. We speculate that inhibition of water absorption may occur in proximal tubular cells in vivo in response to Stx2 and may contribute to the early event of HUS pathogenesis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gianantonio C, Vitacco M, Mendiaharzu F, Rutty A (1964) The hemolytic-uremic syndrome. J Pediatr 64:478–491
Repetto HA (1997) Epidemic hemolytic-uremic syndrome in children. Kidney Int 52:1708–1719
Rivas M, Miliwebsky E, Chinen I, Deza N, Leotta G (2006) The epidemiology of hemolytic uremic syndrome in Argentina. Diagnosis of the etiologic agent, reservoirs and routes of transmission. Medicina (Buenos Aires) 66:27–32
Lindgwood CA (1996) Role of verotoxin receptors in pathogenesis. Trends Microbiol 4:147–153
Taga S, Carlier K, Mishal Z, Capoulade C, Mangeney M, Lecluse Y, Coulaud D, Tetaud C, Prichard LL, Tursz T, Wiels J (1997) Intracellular signaling events in CD77-mediated apoptosis of Burkitt’s lymphoma cells. Blood 90:2757–2767
Pistone Creydt V, Silberstein C, Zotta E, Ibarra C (2006) Cytotoxic effect of Shiga toxin-2 holotoxin and its B subunit on human renal tubular epithelial cells. Microbes Infect 8:410–419
Kojio S, Zhang H, Ohmura M, Gondaira F, Kobayashi N, Yamamoto T (2000) Caspase-3 activation and apoptosis induction coupled with the retrograde transport of shiga toxin: inhibition by brefeldin A. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 29:275–281
Williams JM, Lea N, Lord JM, Roberts LM, Milford DV, Taylor CM (1997) Comparison of ribosome-inactivating proteins in the induction of apoptosis. Toxicol Lett 91:121–127
Lingwood CA (1994) Verotoxin-binding in human renal sections. Nephron 66:21–28
Ray PE, Liu XH (2001) Pathogenesis of shiga toxin-induced hemolytic uremic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 16:823–839
Richardson SE, Karmali MA, Becker LE, Smith CR (1988) The histopathology of the hemolytic uremic syndrome associated with verocytotoxin-producing E. coli. Hum Pathol 19:1102–1108
Kaplan BS (1998) Shiga toxin-induced tubular injury in hemolytic uremic syndrome. Kidney Int 54:648–649
Hughes AK, Stricklett PK, Kohan DE (1998) Cytotoxic effect of Shiga toxin-1 on human proximal tubules cells. Kidney Int 54:426–437
Karpman D, Hakansson A, Perez MT, Isaksson C, Carlemalm E, Caprioli A, Svanborg C (1998) Apoptosis of renal cortical cells in the hemolytic-uremic syndrome: in vivo and in vitro studies. Infect Immun 66:636–644
Exeni R, Grimold I, Amore A, Antonuccio M (1977) Función tubular en niños con SUH. Arch Argent Pediatr 75:149–153
Takeda T, Dohi S, Igarashi T, Yamanaka T, Yoshiya K, Kobayashi N (1993) Impairment by verotoxin of tubular function contributes to the renal damage seen in haemolytic uraemic syndrome. J Infect 27:339–341
Taylor FB Jr, Tesh VL, DeBault L, Li A, Chang AC, Kosanke SD, Pysher TJ, Siegler RL (1999) Characterization of the baboon responses to Shiga-like toxin: descriptive study of a new primate model of toxic responses to Stx-1. Am J Pathol 154:1285–1299
Brenner & Rector (2004) The kidney, 7th edn, Philadelphia, pp 429
Diamond JM, Bossert WH (1967) Standing gradient osmotic flow. A mechanism for coupling of water and solute transport in epithelia. J Gen Physiol 50:2062–2083
Larsen EH, Mobjerg N, Sorensen JN (2006) Fluid transport and ion fluxes in mammalian kidney proximal tubule: a model analysis of isotonic transport. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 187:177–189
Schnermann J, Chou CL, Ma T, Traynor T, Knepper MA, Verkman AS (1998) Defective proximal tubule reabsorptive capacity in transgenic aquaporin-1 null mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:9660–9664
Carpi-Medina P, Whittembury G (1988) Comparison of transcellular and transepithelial water osmotic permeabilities (Pos) in the isolated proximal straight tubule (PST) of the rabbit kidney. Pflugers Arch 412:66–74
Nielsen S, Agre P (1995) The aquaporin family of water channels in kidney. Kidney Int 48:1057–1068
Pistone Creydt V, Martín F, Fernández Miyakawa M, Zotta E, Silberstein C, Ibarra C (2004) Shiga toxin 2 B subunit inhibits net fluid absorption in human colon and elicits fluid accumulation in rat colon loops. Brazilian J Med Biol Res 37:799–808
Toriano R, Ford P, Rivarola V, Tamarappoo BK, Verkman AS, Parisi M (1998) Reconstitution of a regulated transepithelial water pathway in cells transfected with AQP2 and an AQP1/AQP2 hybrid containing the AQP2-C terminus. J Membr Biol 161:141–149
Dorr RA, Kierbel A, Vera J, Parisi M (1997) A new data-acquisition system for the measurement of the net water flux across epithelia. Comput Meth Prog Biomed 53:9–14
Fernandez-Miyakawa ME, Dorr R, Fernandez LE, Uzal FA, Ibarra C (2007) Simple multichannel system for the measurement of the net water flux across biological tissues. Comput Meth Prog Biomed 85:95–100
Parisi M, Merot J, Bourguet J (1985) Glutaraldehyde fixation preserves the permeability properties of the ADH-induced water channels. J Membr Biol 86:239–245
Hidalgo IJ, Raub TJ, Borchardt RT (1989) Characterization of the human colon carcinoma cell line (Caco-2) as a model system for intestinal epithelial permeability. Gastroenterology 96:736–749
Ozu M, Toriano R, Capurro C, Parisi M (2005) Electrical parameters and water permeability properties of monolayers formed by T84 cells cultured on permeable supports. Braz J Med Biol Res 38:133–140
Berry CA (1983) Water permeability and pathways in the proximal tubule. Am J Physiol 245:F279–F294
Parisi M, Ibarra C (1996) Aquaporins and water transfer across epithelial barriers. Braz J Med Biol Res 29:933–939
Smith WE, Kane AV, Campbell ST, Acheson DW, Cochran BH, Thorpe CM (2003) Shiga toxin 1 triggers a ribotoxic stress response leading to p38 and JNK activation and induction of apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells. Infect Immun 71:1497–1504
Romer W, Berland L, Chambon V, Gaus K, Windschiegl B, Tenza D, Aly MR, Fraisier V, Florent JC, Perrais D, Lamaze C, Raposo G, Steinem C, Sens P, Bassereau JL (2007) Shiga toxin induces tubular membrane invaginations for its uptake into cells. Nature 450:670–675
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Osvaldo N. Mazza, Unidad de Urologia, Hospital de Clínicas “José de San Martín”, for provision of human kidney fragments; and Eugene Chang, University of Chicago, for providing the purified Ig G antibody against NHE3. This work was supported by grants to Cristina Ibarra from Universidad de Buenos Aires, CONICET and ANPCYT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silberstein, C., Pistone Creydt, V., Gerhardt, E. et al. Inhibition of water absorption in human proximal tubular epithelial cells in response to Shiga toxin-2. Pediatr Nephrol 23, 1981–1990 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-008-0896-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-008-0896-9