Abstract
Background
50 % of esophageal cancers are inoperable at the time of diagnosis, and around 15 % involve the cervical esophagus. The hypopharynx is often involved by these malignancies as well. Palliation of cervical esophageal malignancies through stent insertion is considered limited due to technical challenges, poor patient tolerance and high complication rate. The aim of this study is to review our experience with stent insertion in the cervical segment of the esophagus and to evaluate outcome differences between stent insertions involving or sparing the hypopharynx.
Methods
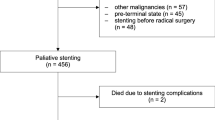
We retrospectively reviewed data on 69 consecutive patients that underwent stent insertion for malignant strictures in the cervical esophagus at our Department. Patients were divided according to involvement or sparing of the lower hypopharynx. Dysphagia severity was measured with the Mellow–Pinkas scale before the procedure and on monthly follow-ups. Any complication and its management were recorded. The main outcome parameters were as follows: dysphagia improvement, rate of successful dysphagia palliation (i.e., a reduction of the score to 0 or 1 after stent insertion) and complication rate. Multivariable analysis was carried out to assess the influence of patient- and procedure-related factors on the outcome of the procedure.
Results
Stent insertion was achieved in 100 % patients. At 4 weeks, dysphagia score improved from a median of 3–0 (p < 0.001), and a successful palliation was achieved in 76.8 % patients. The 30-day mortality rate was 14.5 %. Successful palliation throughout the follow-up was achieved in 72.9 % of the surviving patients. Complications occurred in 31.9 % patients. Dilation before stent insertion was associated with a less efficient short-term dysphagia palliation (OR 6.77, 95 % CI 1.46–31.29, p = 0.02).
Conclusions
Stent insertion is a safe and effective palliative treatment for malignant cervical esophageal strictures. Results are consistent even in patients with hypopharyngeal lesions. Dilation should be avoided before stent insertion.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hill JL, Norberg HP, Smith MD, Young JA, Reyes HM (1976) Clinical technique and success of the esophageal stent to prevent corrosive strictures. J Pediatr Surg 11:443–450
Costamagna G, Marchese M, Iacopini F (2006) Self-expanding stents in oesophageal cancer. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 18(11):1177–1180
Diamantis G, Scarpa M, Bocus P, Realdon S, Castoro C, Ancona E, Battaglia G (2011) Quality of life in patients with esophageal stenting for the palliation of malignant dysphagia. World J Gastroenterol 17:144–150
Sharma P, Kozarek R, Practice Parameters Committee of American College of Gastroenterology (2010) Role of esophageal stents in benign and malignant diseases. Am J Gastroenterol 105:258–273
Raymondi R, Pereira-Lima JC, Valves A, Morales GF, Marques D, Lopes CV, Marroni CA (2008) Endoscopic dilation of benign esophageal strictures without fluoroscopy: experience of 2750 procedures. Hepatogastroenterology 55(85):1342–1348
Swinnen J, Eisendrath P, Rigaux J, Kahegeshe L, Lemmers A, Le Moine O, Deviére J (2011) Self-expandable metal stents for the treatment of benign upper GI leaks and perforations. Gastrointest Endosc 73(5):890–899
Baron TH (2001) Expandable metal stents for the treatment of cancerous obstruction of the gastrointestinal tract. N Engl J Med 344:1681–1687
Conigliaro R, Battaglia G, Repici A, De Pretis G, Ghezzo L, Bittinger M, Messmann H, Demarquay JF, Togni M, Blanchi S, Filiberti R, Conio M (2007) Polyflex stents for malignant oesophageal and oesophagogastric strictures: a prospective, multicentric study. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 19:195–203
Johnson E, Enden T, Noreng HJ (2006) Survival and adverse events after insertion of self-expandable metal stents for malignant oesophageal stenosis. Scand J Gastroenterol 41:252–256
Martinez JC, Puc MM, Quiros RM (2011) Esophageal stenting in the setting of malignancy. ISRN Gastroenterol 2011:719575
Wang MQ, Sze DY, Wang ZP, Wang ZQ, Gao YA, Dake MD (2001) Delayed adverse events after esophageal stent placement for treatment of malignant esophageal obstructions and esophagorespiratory fistulas. J Vasc Interv Radiol 12:465–474
Homann N, Noftz MR, Klingenberg-Noftz RD, Ludwig D (2008) Delayed adverse events after placement of self-expanding stents in malignant esophageal obstruction: treatment strategies and survival rate. Dig Dis Sci 53:334–340
Ramirez FC, Dennert B, Zierer ST, Sanowski RA (1997) Esophageal self-expandable metallic stents—indications, practice, techniques, and adverse events: results of a national survey. Gastrointest Endosc 45:360–364
Triboulet JB, Mariette C, Chevalier D, Amrouni H (2001) Surgical management of carcinoma of the hypopharynx and cervical esophagus: analysis of 209 cases. Arch Surg 136(10):1164–1170
Laterza E, Mosciaro O, Urso US, Inaspettato C, Cordiano G (1994) Primary carcinoma of the hypopharynx and cervical esophagus: evolution of surgical therapy. Hepatogastroenterology 41(3):278–282
Loizou LA, Rampton D, Bown SG (1992) Treatment of malignant strictures of the cervical segment of the esophagus by endoscopic intubation using modified endoprosthesis. Gastrointest Endosc 38:158–164
Goldshmid S, Boyce HW Jr, Nord HJ, Brady PG (1988) Treatment of pharyngoesophageal stenosis by polyvinyl prosthesis. Am J Gastroenterol 83:513–518
Gislason GT, Pasricha PJ (1997) Crossing the upper limit: esophageal stenting in the proximal esophagus. Dysphagia 12:84–85
Elefteriadis E, Kotzampassi K (2006) Endoprosthesis implantation at the pharyngo-esophageal level: problems, limitations and challenges. World J Gastroenterol 12(13):2103–2108
Bayratkar O, Bayratkar B, Atasoy D, Erenler I, Ozdemir IA, Boluk S, Bayraktar OU, Bayraktar A, Tortum OB, Yigitbasi R (2013) Covered self expandable metallic stents could be successful in the palliation of malignant esophageal strictures: preliminary report. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 23(2):e41–e44. doi:10.1097/SLE.0b013e318275b35f
Choi EK, Song HY, Kim JW, Shin JH, Kim KR, Kim JH, Kim SB, Jung HY, Park SI (2007) Covered metallic stent placement in the management of cervical esophageal strictures. J Vasc Interv Radiol 18(7):888–895
Gallo A, Pagliuca G, de Vincentiis M, Martellucci S, Iallonardi E, Fanello G, Cereatti F, Fiocca F (2012) Endoscopic treatment of benign and malignant strictures of the cervical esophagus and hypopharynx. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 121(2):104–109
Conio M, Caroli-Bosc F, Demarquay JF, Sorbi D, Maes B, Delmont J, Dumas R (1999) Self-expanding metal stents in the palliation of neoplasms of the cervical esophagus. Hepatogastroenterology 46:272–277
Knyrim K, Wagner HJ, Bethge N (1993) A controlled trial of expansible metal stent for palliation of esophageal cancer due to inoperable cancer. N Engl J Med 329:1307
Spinelli P, Cerrai FG, Meroni E (1991) Pharyngo-esophageal prostheses in malignancies of the cervical esophagus. Endoscopy 23:213–214
Profili S, Meloni GB, Feo CF, Pischedda A, Bozzo C, Ginesu GC, Canalis GC (2002) Self-expandable metal stents in the management of cervical oesophageal and/or hypopharyngeal strictures. Clin Radiol 57:1028–1103
Sarper A, Oz N, Cihangir C, Demircan A, Isin E (2003) The efficacy of self-expanding metal stents for palliation of malignant esophageal strictures and fistulas. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 23:794–798
Morgan RA, Ellul JP, Denton ER, Glynos M, Mason RC, Adam A (1997) Malignant esophageal fistulas and perforations: management with plastic covered metallic endoprosthesis. Radiology 204:527–532
Shin JH, Song HY, Ko GY, Lim JO, Yoon HK, Sung KB (2004) Esophagorespiratory fistula: long-term results of palliative treatment with covered expandable metallic stents in 61 patients. Radiology 232:252–259
Paganin F, Schouler L, Cuissard L, Noel JB, Becquart J, Besnard M, Bourdin A (2008) Airway and esophageal stenting in patients with advanced esophageal cancer and pulmonary involvement. PLoS One 3(8):e3101
Bethge N, Sommer A, Vakil N (1997) A prospective trial of self-expanding metal stents in the palliation of malignant esophageal strictures near the upper esophageal sphincter. Gastrointest Endosc 45:300–303
Verschuur EM, Kuipers EJ, Siersema PD (2007) Esophageal stents for malignant strictures close to the upper esophageal sphincter. Gastrointest Endosc 66(6):1082–1090
Madhusudhan C, Saluja SS, Pal S, Ahuja V, Saran P, Dash NR, Sahni P, Chattopadhyay TK (2009) Palliative stenting for relief of dysphagia in patients with inoperable esophageal cancer: impact on quality of life. Dis Esophagus 22(4):331–336
Bergquist H, Johnsson E, Nyman J, Rylander H, Hammerlid E, Friesland S, Ejnell H, Lundell L, Ruth M (2012) Combined stent insertion and single high-dose brachytherapy in patients with advanced esophageal cancer—results of a prospective safety study. Dis Esophagus 25:410–415
Yu Y, Tang G, Liu Y, Zhen BZ (2004) Clinical evaluation of radiotherapy for advanced esophageal cancer after metallic stent placement. World J Gastroenterol 10:2145–2146
Maier A, Pinter H, Friehs GB, Renner H, Smolle-Jüttner FM (1999) Self-expandable coated stent after intraluminal treatment for esophageal cancer: a risky procedure? Ann Thorac Surg 67:781–784
Hirdes MM, van Hooft JE, Wijrdeman HK, Hulshof MC, Fockens P, Reerink O, van Oijen MG, van der Tweel I, Vleggaar FP, Siersema PD (2012) Combination of biodegradable stent placement and single-dose brachytherapy is associated with an unacceptably high complication rate in the treatment of dysphagia from esophageal cancer. Gastrointest Endosc 76(2):267–274
Disclosures
Giorgio Battaglia, Alessandro Antonello, Francesco Cavallin, Francesca Giacomini, Stefano Realdon and Sauid Ishaq declare that they have no conflict of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Battaglia, G., Antonello, A., Realdon, S. et al. Feasibility, efficacy and safety of stent insertion as a palliative treatment for malignant strictures in the cervical segment of the esophagus and the hypopharynx. Surg Endosc 30, 159–167 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4176-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4176-z